Related Research Articles

Quail is a collective name for several genera of mid-sized birds generally placed in the order Galliformes.

A raven is one of several larger-bodied species of the genus Corvus. These species do not form a single taxonomic group within the genus.

Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 60 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, just 14 species can be found—2 in North America, 9 in Central and South America, and 3 in Australia. It is nicknamed the king of all birds.

Owls are birds from the order Strigiformes, which includes over 200 species of mostly solitary and nocturnal birds of prey typified by an upright stance, a large, broad head, binocular vision, binaural hearing, sharp talons, and feathers adapted for silent flight. Exceptions include the diurnal northern hawk-owl and the gregarious burrowing owl.

In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature, also called binominal nomenclature or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name, a binomen, binominal name or a scientific name; more informally it is also called a Latin name.

Otters are carnivorous mammals in the subfamily Lutrinae. The 13 extant otter species are all semiaquatic, aquatic or marine, with diets based on fish and invertebrates. Lutrinae is a branch of the Mustelidae family, which also includes weasels, badgers, mink, and wolverines, among other animals.

The Lagomorphs are the members of the taxonomic order Lagomorpha, of which there are two living families: the Leporidae and the Ochotonidae (pikas). The name of the order is derived from the Ancient Greek lagos + morphē. There are 102 extant species of lagomorph, including 37 species of pika, 33 species of rabbit and cottontail, and 32 species of hare.

Anseriformes is an order of birds that comprise about 180 living species in three families: Anhimidae, Anseranatidae, and Anatidae, the largest family, which includes over 170 species of waterfowl, among them the ducks, geese, and swans. Most modern species in the order are highly adapted for an aquatic existence at the water surface. With the exception of screamers, males have penises, a trait that has been lost in the Neoaves. Due to their aquatic nature, most species are web-footed.
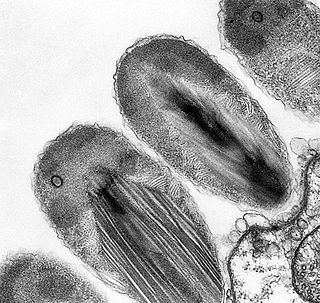
Verrucomicrobia is a phylum of bacteria that contains only a few described species. The species identified have been isolated from fresh water, marine and soil environments and human faeces. A number of as-yet uncultivated species have been identified in association with eukaryotic hosts including extrusive explosive ectosymbionts of protists and endosymbionts of nematodes residing in their gametes.

The Xylariaceae are a family of mostly small ascomycetous fungi. It is one of the most commonly encountered groups of ascomycetes and is found throughout the temperate and tropical regions of the world. They are typically found on wood, seeds, fruits, or plant leaves, some even associated with insect nests. Most decay wood and many are plant pathogens.

Cyclanorbis is a genus of softshell turtles in the family Trionychidae. The genus is endemic to Africa.
Acrogenospora is a genus of fungi in the family Hysteriaceae.
Wettsteinina is a genus of 23 fungi in the class Dothideomycetes. The type species Wettsteinina gigantospora was first described by Franz Xaver Rudolf von Höhnel in 1907. The relationship of this taxon to other taxa within the class is unknown.

Smerinthini is a tribe of moths of the family Sphingidae. The genus was erected by Augustus Radcliffe Grote and Herbert C. Robinson in 1865.

Campanella is a genus of fungi in the family Marasmiaceae. The genus has a widespread distribution, especially in tropical regions, and contains about 40 species.
Paradoxa is a genus of truffles in the family Tuberaceae. Originally described by the Italian botanist Oreste Mattirolo in 1935, the genus remained monotypic until a second species P. gigantospora was transferred from Tuber in 2009. A third species, P. sinensis, was also described, representing the second species from China. P. sinensis differs from P. gigantospora by having a somewhat smaller fruit body, and differs from P. monospora by having yellowish to yellow-brown ascomata.

Badhamia is a genus of slime molds in the family Physaraceae. It was circumscribed by English naturalist Miles Joseph Berkeley in 1853. The widespread genus contains about 30 species.

Bertia is a genus of fungi within the Bertiaceae family.

The Solanaceae, or nightshades, are a family of flowering plants that ranges from annual and perennial herbs to vines, lianas, epiphytes, shrubs, and trees, and includes a number of agricultural crops, medicinal plants, spices, weeds, and ornamentals. Many members of the family contain potent alkaloids, and some are highly toxic, but many—including tomatoes, potatoes, eggplant, bell and chili peppers—are used as food. The family belongs to the order Solanales, in the asterid group and class Magnoliopsida (dicotyledons). The Solanaceae consists of about 98 genera and some 2,700 species, with a great diversity of habitats, morphology and ecology.
References
- ↑ Lumbsch TH, Huhndorf SM. (December 2007). "Outline of Ascomycota – 2007". Myconet. Chicago, USA: The Field Museum, Department of Botany. 13: 1–58. Archived from the original on 2009-03-18.