
Andersonia is a subgenus of Stylidium that is characterized by a linear hypanthium, recurved mature capsule walls, an erect and persistent septum, and many seeds. This subgenus occurs in areas of tropical northern Australia and into Southeast Asia and was named in honour of William Anderson, the surgeon and naturalist who sailed with James Cook.
Solanum exiguum is a species of plant in the family Solanaceae. It is endemic to Bolivia.

Geoglossaceae is a family of fungi in the order Geoglossales, class Geoglossomycetes. These fungi are broadly known as earth tongues. The ascocarps of most species in the family Geoglossaceae are terrestrial and are generally small, dark in color, and club-shaped with a height of 2–8 cm. The ascospores are typically light-brown to dark-brown and are often multiseptate. Other species of fungi have been known to parasitize ascocarps. The use of a compound microscope is needed for accurate identification.

Bulbophyllum exiguum, commonly known as the tiny strand orchid, is a species of epiphytic or lithophytic orchid that is endemic to eastern Australia. It has small, roughly spherical pseudobulbs each with a single leaf and up to three small creamy white to yellow flowers emerging from the base of the pseudobulb. This orchid grows in rainforest and dry forest where it often covers the branches of trees or rocks on which it grows.
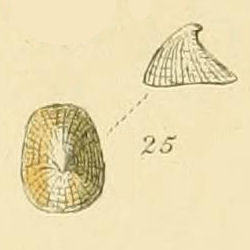
Propilidium exiguum is a species of sea snail, a true limpet, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Lepetidae, one of the families of true limpets.

Propilidium is a genus of sea snails, the true limpets, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Lepetidae.

Cyclostrema exiguum is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Liotiidae.

Eulimastoma is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Pyramidellidae, the pyrams and their allies.
Microibidion is a genus of beetles in the family Cerambycidae, containing the following species:

Glutinoglossum glutinosum, commonly known as the viscid black earth tongue or the glutinous earthtongue, is a species of fungus in the family Geoglossaceae. Widely distributed in the Northern Hemisphere, it has been found in northern Africa, Asia, Europe, and North America. Although previously thought to exist in Australasia, collections made from these locations have since been referred to new species. G. glutinosum is a saprophytic species that grows on soil in moss or in grassy areas. The smooth, nearly black, club-shaped fruitbodies grow to heights ranging from 1.5 to 5 cm. The head is up to 0.7 cm (0.3 in) long, and the stipes are sticky. Several other black earth tongue species are quite similar in external appearance, and many can be reliably distinguished only by examining differences in microscopic characteristics, such as spores, asci, and paraphyses. First described in 1796 as a species of Geoglossum, the fungus has gone through several changes of genera in its taxonomic history. It was placed in its current genus, Glutinoglossum, in 2013.

Glutinoglossum is a genus of six species of earth-tongue fungi in the family Geoglossaceae. The widespread type species, G. glutinosum, is commonly known as the "glutinous earth tongue". G. heptaseptatum is known only from the Czech Republic. Four additional species were described in 2015.

Glutinoglossum heptaseptatum is a species of earth tongue fungus in the family Geoglossaceae. Described in 2013, it is indistinguishable from its close relative G. glutinosum without the use of a microscope, and is known for certain only from the Czech Republic.
Glutinoglossum methvenii is a species of earth tongue fungus that was described as new to science in 2015. It is found in Australia and New Zealand, where it grows on moss and decaying logs in mixed deciduous forests. The specific epithet honours mycologist Andrew Methven.
Glutinoglossum australasicum is a species of earth tongue fungus that was described as new to science in 2015. It is found in Australia and New Zealand, where it grows singly or in groups on the ground and in rich humus.
Glutinoglossum americanum is a species of earth tongue fungus that was described as new to science in 2015. It is found in the United States, where it grows on the ground, often among moss, in mixed deciduous forests.

Serenichthys kowiensis is a fossil species of coelacanth described in 2015 from near Grahamstown in South Africa.
Abrosoma exiguum is a species of phasmid or stick insect of the genus Abrosoma. It is found in Sri Lanka.
Maccaffertium exiguum is a species of flatheaded mayfly in the family Heptageniidae. It is found in North America.
Hoffmaneumatidae is a family of millipedes belonging to the order Chordeumatida. This family includes two genera, one (Hoffmaneuma) found in the Russian Far East and the other (Japanoparvus) found in Japan. Millipedes in this family range from 4 mm to 6 mm in length. Adult millipedes in this family have only 28 segments, not the 30 segments usually found in this order. Adult males in this family feature a reduced leg pair 10 in addition to the two pairs normally modified into gonopods in this order. In the adult male of the species Hoffmaneuma exiguum, for example, the gonopod complex derives from all three leg pairs rather than from just the usual two.







