
Isopoda is an order of crustaceans. Members of this group are called isopods and include both aquatic species, and terrestrial species such as woodlice. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons, two pairs of antennae, seven pairs of jointed limbs on the thorax, and five pairs of branching appendages on the abdomen that are used in respiration. Females brood their young in a pouch under their thorax.
Mexistenasellus is a genus of isopod crustaceans in the family Stenasellidae.
Onchotelson is a genus of isopod crustaceans in the family Phreatoicidae, which is endemic to Tasmania. It contains two species, both of which are listed as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List:
Sphaerolana is a genus of isopod crustaceans in the family Cirolanidae, all of which are endemic to Mexico.

The Cymothoidae are a family of isopods in the suborder Cymothoida found in both marine and freshwater environments. Cymoithoids are ectoparasites, usually of fish, and they include the bizarre "tongue-biter", which attaches to a fish's tongue, causing it to atrophy, and replaces the tongue with its own body. Ceratothoa oestroides is one of the most devastating ectoparasites in Mediterranean aquaculture. Around 40 genera and more than 380 species of cymothoid are recognised. Species of the Cymothoidae are generally found in warmer waters and rarely in the cool and cold climates.
Ceratoserolis is a genus of isopods in the family Serolidae from the Southern Ocean around Antarctica and some Sub-Antarctic Islands. They prefer to live on soft bottoms and range of least between 24 and 950 m (80–3,120 ft) in depth. They are superficially similar to the unrelated, extinct trilobites and reach up to about 8 cm (3.1 in) in length. They were once considered to be part of the genus Serolis and for a long time only Ceratoserolis trilobitoides was recognized. The validity of the other species has been disputed, but there are some morphological and genetic differences between them and C. trilobitoides, and there are indications that additional, currently unrecognized species of Ceratoserolis exist.
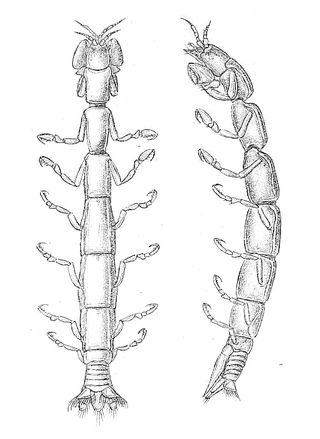
Anthuroidea is a superfamily of isopod crustaceans, formerly treated as a suborder, Anthuridea. The group is characterised by "an elongate cylindrical body form, without dorsal coxal plates, and with a uropodal exopod attached to the peduncle proximally and dorsally". There are more than 500 described species in 57 genera, arranged across six families:
Iais is a genus of isopod crustaceans. Iais species are found in association with larger isopods of the family Sphaeromatidae, usually on the ventral surface of the larger animal, between the pereiopods and on the pleopods. They are native to Australasia and South America, although Iais californica and its host Sphaeroma quoyanum have invaded California, and I. californica was first described from Sausalito, California.

Cirolanidae is a family of aquatic isopods.
The Microcerberidea are a suborder of isopod crustaceans. They are less than 2 mm (0.079 in) long, and live interstitially. They may be found in the eastern Pacific Ocean, and around the coasts of South America, Africa, the Mediterranean Sea, and India.
The Microcerberidae are a family of isopod crustaceans. They are less than 2 mm (0.079 in) long, and live interstitially in shallow marine or freshwater sand habitats.

Cymothoida is the name of a suborder of isopod crustaceans with a mostly carnivorous or parasitic lifestyle. It contains more than 2,700 described species in four superfamilies. Members of the suborder are characterised by their specialised mouthparts which include a mandible with a tooth-like process which is adapted for cutting or slicing.

Sphaeromatidea is a suborder of isopod crustaceans.
Hemioniscus balani, a species of isopod crustacean, is a widespread parasitic castrator of barnacles in the northern Atlantic Ocean. Its range extends from Norway to the Atlantic coast of France, and as far west as Massachusetts. It is also commonly found on the Pacific coast of North America; it is not known if the Pacific and Atlantic populations are the same species, or if the Pacific population exists following human-assisted introduction.

The Chaetiliidae are a family of isopod crustaceans in the suborder Valvifera, comprising these genera:

Saduria is a genus of benthic isopod crustaceans in the family Chaetiliidae, containing the following species:

Styloniscidae is a family of woodlice, including the following genera:
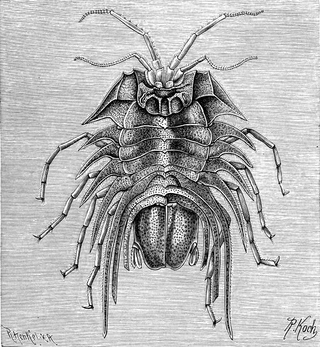
Serolidae is a family of isopod crustaceans. The family encompasses 22 genera with 109 species. These species are exclusively marine and are distributed across the marine realms as follows: one species can be found in the Temperate Northern Atlantic, one species in the Temperate Northern Pacific, seven species in the Tropical Atlantic, six species in the Central Indo-Pacific, 16 species in Temperate South America, one species in Temperate Southern Africa, 20 species in Temperate Australasia, and 31 species in the Southern Ocean.

Glyptonotus antarcticus is a benthic marine isopod crustacean in the suborder Valvifera. This relatively large isopod is found in the Southern Ocean around Antarctica. It was first described by James Eights in 1852 and the type locality is the South Shetland Islands.

Dynoides elegans is a species of isopod crustacean in the genus Dynoides. It was originally described in 1923 by Pearl Lee Boone as "Cianella elegans" based on specimens from La Jolla and San Pedro, Los Angeles. It was transferred to the genus Dynoides in 2000, when Boone's genus was sunk into synonymy with Dynoides.










