
Wat Phra Kaew, commonly known in English as the Temple of the Emerald Buddha and officially as Wat Phra Si Rattana Satsadaram, is regarded as the most sacred Buddhist temple in Thailand. The complex consists of a number of buildings within the precincts of the Grand Palace in the historical centre of Bangkok. It houses the statue of the Emerald Buddha, which is venerated as the country's palladium.

The Emerald Buddha is an image of the meditating Gautama Buddha seated in a meditative posture, made of a semi-precious green stone, clothed in gold. and about 66 centimetres (26 in) tall. The image is considered the sacred palladium of Thailand. It is housed in the Temple of the Emerald Buddha on the grounds of the Grand Palace in Bangkok.

The Phra Bang is a statue of Buddha in the city of Luang Prabang, Laos; it is the namesake of that city. The statue stands at 83-centimetre (33 in)s, with palms facing forward, cast using thong, an alloy of bronze, gold, and silver. According to local lore, it was cast in Ceylon sometime between the 1st and 9th century. However, the features of the image suggest a much later Khmer origin.

Sukhothai Historical Park covers the ruins of Sukhothai, literally 'dawn of happiness', capital of the Sukhothai Kingdom in the 13th and 14th centuries, in north central Thailand. It is near the city of Sukhothai, capital of Sukhothai Province.

Thai art refers to a diverse range of art forms created in Thailand from prehistoric times to the present day, including architecture, sculpture, painting, textiles, decorative arts, crafts, ceramics, and more. While Buddhism has played a significant role in Thai art, with many sculptures and paintings depicting Buddha images and religious themes, nature, including flora and fauna, as well as mythical creatures, has been a major inspiration for Thai art, with colorful motifs appearing in various types of art forms. In contemporary Thai art, traditional works remain significant and continue to influence artists' concepts.

Wat Pho, also spelled Wat Po, is a Buddhist temple complex in the Phra Nakhon District, Bangkok, Thailand. It is on Rattanakosin Island, directly south of the Grand Palace. Known also as the Temple of the Reclining Buddha, its official name is Wat Phra Chetuphon Wimon Mangkhalaram Rajwaramahawihan. The more commonly known name, Wat Pho, is a contraction of its older name, Wat Photaram.

A reclining Buddha is an image that represents Buddha lying down and is a major iconographic theme in Buddhist art. It represents the historical Buddha during his last illness, about to enter the parinirvana. He is lying on his right side, his head resting on a cushion or relying on his right elbow, supporting his head with his hand.

Wat Benchamabophit Dusitvanaram is a Buddhist temple (wat) in the Dusit District of Bangkok, Thailand. Also known as the Marble Temple, it is one of Bangkok's best-known temples and a major tourist attraction. It typifies Bangkok's ornate style of high gables, stepped-out roofs and elaborate finials.

Wat Phra That Doi Suthep is a Theravada Buddhist temple (wat) in Chiang Mai Province, Thailand. The temple is often referred to as "Doi Suthep" although this is actually the name of the mountain where it is located. It is a sacred site to many Thai people. The temple is 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) from the city of Chiang Mai and situated at an elevation of 1,073 meters. From the temple, impressive views of downtown Chiang Mai can be seen.

Thai temple art and architecture is the art and architecture of Buddhist temples in Thailand. Temples are known as wats, from the Pāḷi vāṭa, meaning "enclosure". A temple has an enclosing wall that divides it from the secular world. Temples served as a stabilizing center in these communities because their sacred teachings became a basis of authority and boundaries, their precincts became places of instruction, their regimes of common ownership of property formed them into economic centers, and their functions allowed them to serve at the heart of these communities in a variety of ways.

Wat Phra Sri Rattana Mahathat (Thai: วัดพระศรีรัตนมหาธาตุ; "Temple of the Great Jewelled Reliquary"), colloquially referred to as Wat-Phra-Sri or Wat Yai (Thai: วัดใหญ่; "Big Temple"), is a Buddhist temple (wat) in Phitsanulok Province, Thailand, where it is located on east bank of Nan River, near Naresuan Bridge and opposite Phitsanulok Provincial Hall. It is about 337 km from Bangkok.

A Buddha image in Thailand typically refers to three-dimensional stone, wood, clay, or metal cast images of the Buddha. While there are such figures in all regions where Buddhism is commonly practiced, the appearance, composition and position of the images vary greatly from country to country in Buddhist art.

The Si Satchanalai Historical Park is a historical park in Si Satchanalai district, Sukhothai Province, northern Thailand. The park covers the ruins of Si Satchanalai and Chaliang. Si Satchanalai, which literally means "City of good people", was founded in 1250 as the second center of the Sukhothai Kingdom and as a residence of the crown prince in the 13th and 14th centuries.

Wat Intharawihan or Wat Intharavihan is a Third Class Royal wat (temple) located in the Phra Nakhon District of Bangkok, Thailand. It is noted for its 32 metres (105 ft) high standing Buddha statue known as Luang Pho To or "Phra Si Ariyamettrai" that was erected on the inspiration of the still highly revered abbott Somdej Toh.
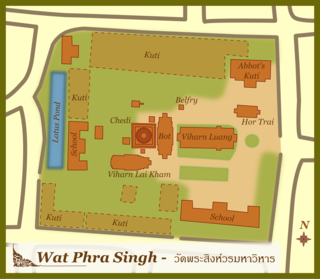
Wat Phra Singh is a Buddhist temple in Chiang Mai, northern Thailand. King Ananda Mahidol, bestowed upon it the status of Royal temple of the first grade in 1935.

Wat Traimit Witthayaram Worawihan is a Theravada Buddhist temple (wat) in Samphanthawong district, the Chinatown area of the Thai capital Bangkok. Probably dating to the early Rattanakosin period, it was previously known as Wat Sam Chin (วัดสามจีน) and received its current name in 1940. Today, the temple is best known for the golden Buddha statue enshrined there. It also houses the Yaowarat Chinatown Heritage Center.

Wat Phra Mahathat Woramahawihan is the main Buddhist temple (wat) of Nakhon Si Thammarat Province in southern Thailand. The main stupa of the temple, Phra Borommathat Chedi, was built by King Sri Dhammasokaraja in the early-13th century CE to establish a symbol for the Theravada Buddhism sect in the province. The temple is believed to house a tooth of Gautama Buddha.

Wat Hong Rattanaram Ratchaworawihan, or just called Wat Hong Rattanaram is an ancient Thai Buddhist temple located in Bangkok rim the Khlong Bangkok Yai canal. It is classified as the second rank of royal temple and can be considered a temple of Prince Pinklao.

Wat Ratchapradit Sathit Mahasimaram Ratcha Wora Maha Viharn is a Buddhist temple in the Phra Nakhon District of Bangkok. Wat Ratchaparadit was designated a first-class royal monastery in 1915, making it one of the most significant temples in Thailand.

The Phra Phuttha Sihing is a highly revered image of the Gautama Buddha in Bangkok, Thailand, second in importance only after the Emerald Buddha. The image is currently housed at the Phutthaisawan Hall, now the Bangkok National Museum. The image was brought to Bangkok from Wat Phra Singh, Chiang Mai in 1795 by Viceroy Maha Sura Singhanat, the brother of King Rama I.

























