
Apteromantis aptera is a species of praying mantis endemic to the Iberian Peninsula. It was first described by José María Hugo de la Fuente Morales in 1894. It was previously considered to be endangered by the IUCN, but has been downgraded to least concern, as the populations are rising and they are spreading to new habitats in south-central Spain and southern Portugal.

Ameles spallanzania, common name European dwarf mantis, is a species of praying mantis.
Gonatista jaiba is a species of praying mantis living in Hispaniola that was first described in 2004.
Gonatista major is a species of praying mantis native to the Caribbean and is found in Puerto Rico, Hispaniola, and perhaps elsewhere. In comparing G. grisea and G. reticulata in 2008, an entomologist with the United States Department of Agriculture wrote:
In general color this species is lighter than either of the preceding ones and is decidedly larger than either of them. The infuscation of the elytra is no more profuse than in grisea but is gathered in decidedly larger blotches, in this respect more like reticulata. The female is unknown to me. The measurements of the males are as follows: Length, pronotum, 13.5-14.5 mm.; elytra, 45-48 mm.
Epaphrodita lobivertex is a species of praying mantis, native to Hispaniola, that was first described in 2004.

Sphodromantis is a large genus of praying mantises concentrated in Africa, sometimes considered a synonym of the genus Hierodula: from the same tribe, Paramantini. Outside their range especially, many share the common name African Mantis.

Rhombodera is a genus of praying mantises native to Asia and possessing common names such as shield mantis, hood mantis, and leaf mantis because of their extended, leaf-like thoraxes.
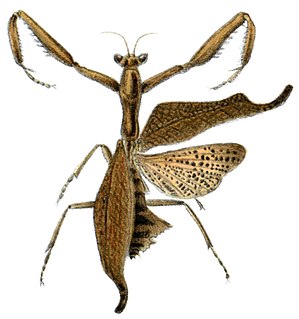
Acanthops is a genus of mantises in the family Acanthopidae, containing 20 species that can be found in Central and South America.

Antistia is a genus of mantids in the family Tarachodidae. There are at least four described species in Antistia.

Mantises are an order (Mantodea) of insects that contains over 2,400 species in about 460 genera in 33 families. The largest family is the Mantidae ("mantids"). Mantises are distributed worldwide in temperate and tropical habitats. They have triangular heads with bulging eyes supported on flexible necks. Their elongated bodies may or may not have wings, but all Mantodea have forelegs that are greatly enlarged and adapted for catching and gripping prey; their upright posture, while remaining stationary with forearms folded, has led to the common name praying mantis.

Stenophylla is a genus of praying mantis in the subfamily Stenophyllinae, which is now placed in the family Acanthopidae. It the sole genus of the tribe Stenophyllini.
Charieis is a genus of mantids in the family Tarachodidae. It is a monotypic genus with a single recognised species, Charieis peeli.

Acontistini is a tribe of neotropical mantids in the superfamily Acanthopoidea, and family Acanthopidae. There are 7 genera and more than 30 described species in Acontistini. In 2016, several genera were moved from Acanthopidae to a newly created family Acontistidae, but this has not been accepted in most recent classifications.

Coptopterygidae is a family of mantids in the order Mantodea. There are at least 2 genera and more than 20 described species in Coptopterygidae.

Photinaidae is a family of mantids in the order Neotropical Mantodea, in the superfamily Acanthopoidea. There are about 11 genera and more than 40 described species in Photinaidae.
Thespinae is a subfamily of mantids in the family Thespidae. There are 16 genera and at least 40 described species: found in Australasia, Central and South America.

Euchomenellini is a recently (2017) restored, southeast Asian tribe of praying mantids. It is now placed in the new (2019) family Deroplatyidae, genera having previously been placed in the Angelidae: which now consists only of neotropical mantids.
Rhombomantis is a genus of mantids in the family Mantidae. There are at least four described species in Rhombomantis.

Pseudovates is a genus of praying mantis in the family Mantidae. There are more than 20 described species in Pseudovates, found in North, Central, and South America.













