
Olea is a genus of about 40 species in the family Oleaceae, native to warm temperate and tropical regions of the Middle East, southern Europe, Africa, southern Asia, and Australasia. They are evergreen trees and shrubs, with small, opposite, entire leaves. The fruit is a drupe. Leaves of Olea contain trichosclereids.

Odontochilus is a small genus from the orchid family (Orchidaceae). These terrestrial, mycoparasitic orchids occur from China, Japan, the Himalayas, Southeast Asia, New Guinea and Melanesia. The genus is related to Gonatostylis, endemic to New Caledonia.
Dischidia is a genus of plants in the Milkweed family, Apocynaceae. They are epiphytes native to tropical areas of China, India and most areas of Indo-China. Dischidia are closely aligned with the sister genus Hoya. Unlike Hoya, the genus Dischidia is poorly known and has not been studied as closely.

Anodendron is a genus of plant in family Apocynaceae first described as a genus in 1844. It is native to China, the Indian Subcontinent, Southeast Asia, New Guinea, and some islands of the western Pacific.
- Anodendron affine(Hook. & Arn.) Druce - China, Japan, Ryukyu Islands, Philippines, Vietnam, Laos, Thailand, Myanmar, Bangladesh
- Anodendron axillareMerr. - Philippines, Borneo, W Malaysia, Java, Sumatra
- Anodendron benthamianumHemsl. - Taiwan
- Anodendron borneense(King & Gamble) D.J.Middleton - Borneo, Palawan
- Anodendron candolleanumWight - Thailand, W Malaysia, Borneo, Java, Sumatra, Philippines
- Anodendron coriaceum(Blume) Miq. - Thailand, W Malaysia, Borneo, Java, Bali, Lombok, Timor, Flores
- Anodendron gracile(King & Gamble) D.J.Middleton - Borneo, Palawan, W Malaysia
- Anodendron howiiTsiang - Guangxi, Hainan
- Anodendron nervosumKerr - Yunnan, Assam, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, Java, Sumatra
- Anodendron oblongifoliumHemsl. - Borneo, Philippines, Maluku, New Guinea, Bismarck Archipelago, Solomon Islands, Vanuatu
- Anodendron paniculatum(Roxb.) A.DC. - India, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Andaman & Nicobar Is, Malaysia, Indonesia, Philippines
- Anodendron pauciflorumHook.f - Borneo, W Malaysia, Sumatra
- Anodendron punctatumTsiang - Cambodia, Thailand, Guangxi, Hainan, Sichuan
- Anodendron seramenseD.J.Middleton - Maluku
- Anodendron tubulosum(Ridl. ex Burkill & M.R.Hend.) D.J.Middleton - W Malaysia, Sumatra
- Anodendron whitmoreiD.J.Middleton - Maluku, New Guinea, Solomon Islands
- Anodendron wrayiKing & Gamble - W Malaysia

Kopsia is a genus of plant in family Apocynaceae first described as a genus in 1823. Kopsia is native to China, Southeast Asia, Australia, and various islands of the western Pacific.
- Kopsia angustipetalaKerr - Thailand, Laos
- Kopsia arboreaBlume - S China, SE Asia, N Australia, Andaman & Nicobar Is
- Kopsia dasyrachisRidl. - Sabah
- Kopsia deverreiL.Allorge - Johor
- Kopsia flavidaBlume - Philippines, Maluku, New Guinea, Solomon Is, Vanuatu, Micronesia
- Kopsia fruticosa(Roxb.) A.DC. - Myanmar, Andaman Is
- Kopsia grandifoliaD.J.Middleton - Johor, Anambas Is
- Kopsia griffithiiKing & Gamble - W Malaysia
- Kopsia hainanensisTsiang - Hainan
- Kopsia harmandianaPierre ex Pit. - Vietnam
- Kopsia lapidilectaSleesen - Natuna Is
- Kopsia larutensisKing & Gamble - W Malaysia
- Kopsia macrophyllaHook.f. - W Malaysia
- Kopsia paucifloraHook.f. - Indochina, W Malaysia, Sumatra
- Kopsia profundaKing & Gamble - W Malaysia
- Kopsia rajangensisD.J.Middleton - Sarawak
- Kopsia roseaD.J.Middleton - S Thailand, Kelantan
- Kopsia singapurensisRidl. - Singapore, W Malaysia
- Kopsia sleesianaMarkgraf - Sarawak
- Kopsia sumatranaD.J.Middleton - Sumatra
- Kopsia tenuisLeenh. & Steenis - Sarawak
- Kopsia teoiL.Allorge - W Malaysia
- Kopsia tonkinensisPit. - Vietnam
- Kopsia vidaliiD.J.Middleton - Vietnam

Marsdenia is a genus of plant in family Apocynaceae first described as a genus in 1810. It is named in honor of the plant collector and Secretary of the Admiralty, William Marsden. The plants are native to tropical regions in Asia, Africa, Australia, and the Americas.

Sarcostemma is a genus of flowering plants in the dogbane family, Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1810. The name is derived from the Greek words σαρκὸς (sarkos), meaning "flesh," and στέμμα (stemma), meaning "garland". Members of the genus are known generally as climbing milkweeds or caustic bushes. They are found across Africa and tropical Asia, in Australia, and in parts of North America. These plants are perennial flowering shrubs with trailing vines or lianas. They are often adapted to heat and/or desert conditions. Some have few or no leaves and photosynthesize in the tissues of the green stems. The soft stems are filled with a milky white latex that is poisonous and caustic in some species. The flowers have a ring of thick tissue at the base which extends into hollow spherical appendages within the flower corolla.

Willughbeia is a genus of plant in the family Apocynaceae,first described as a genus in 1820. It is native to Southeast Asia with a few species in the Indian Subcontinent. Several species have edible fruits enjoyed in many countries. Many species are vines with sticky latex.

Gymnema is a genus in the family Apocynaceae first described as a genus in 1810.
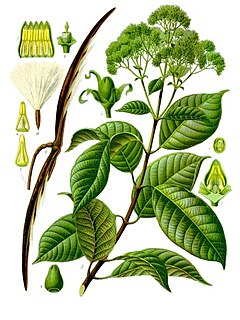
Urceola is a plant genus in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1798. It is native to China, the Himalayas, Southeast Asia, and New Guinea.
- Urceola brachysepalaHook.f. - Borneo, Java, W Malaysia, Sumatra, Philippines
- Urceola elasticaRoxb. - Borneo, Java, W Malaysia, Sumatra
- Urceola huaitingii(Chun & Tsiang) Mabb. - Guizhou, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan
- Urceola javanica(Blume) Boerl. - Borneo, Java, Maluku, Sumatra, Sulawesi, New Guinea
- Urceola laevis(Elmer) Merr. - Palawan, Sabah, Sulawesi
- Urceola lakhimpurensis(S.K.Srivast. & Mehrotra) Karthik. & Moorthy - Assam
- Urceola latifolia(Pierre ex Spire) Mabb. - Laos, Thailand, Vietnam
- Urceola lucida(A.DC.) Benth. ex Kurz - Myanmar, Thailand, W Malaysia, Sumatra
- Urceola malayanaMabb. - Cameron Highlands of W Malaysia
- Urceola micrantha(Wall. ex G.Don) Mabb. - Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Sichuan, Taiwan, Tibet, Yunnan, Ryukyu Islands, Assam, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Arunachal Pradesh, Nepal, Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, Myanmar, W Malaysia
- Urceola minutiflora(Pierre) Mabb. - Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam
- Urceola napeensis(Quint.) Mabb. - Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, Guangdong, Guangxi
- Urceola quintaretii(Pierre) Mabb. - Laos, Vietnam, Guangdong, Guangxi
- Urceola rosea(Hook. & Arn.) D.J.Middleton - Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, Laos, W Malaysia, Java, Sumatra, Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, Guizhou, Hainan, Hunan, Sichuan, Taiwan, Yunnan
- Urceola torulosaHook.f. - W Malaysia, Sumatra, Borneo
- Urceola tournieri(Pierre) Mabb. - Yunnan, Nepal, Bhutan, Assam, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam
- Urceola xylinabariopsoides(Tsiang) Mabb. - Hainan, Vietnam

Periploca is a genus of plants in the Apocynaceae family, first described for modern science by Linnaeus in 1753. It is native to Europe, Asia, and Africa.
- Periploca aphyllaDecne. - Middle East from Sinai to Pakistan
- Periploca calophylla(Wight) Falc. - S China, Nepal, Bhutan, Assam, E Himalayas, Vietnam
- Periploca chevalieriBrowicz - Cape Verde Islands
- Periploca chrysanthaD.S. Yao, X.D. Chen & J.W. Ren - Gansu Province in China
- Periploca floribundaTsiang - Yunnan, Vietnam
- Periploca forrestiiSchltr. - Guangxi, Guizhou, Qinghai, Sichuan, Tibet, Yunnan, India, Kashmir, Myanmar, Nepal
- Periploca graecaL. - Mediterranean
- Periploca hydaspidisFalc. - Kashmir
- Periploca laevigataAiton - Canary Islands, Savage Islands
- Periploca linearifoliaQuart.-Dill. & A. Rich - Ethiopia
- Periploca nigrescensAfzel. - W Africa
- Periploca refractifoliaGilli - Tanzania
- Periploca sepiumBunge - widespread across much of China
- Periploca tsiangiiD. Fang & H.Z. Ling - Guangxi Province in China
- Periploca visciformis(Vatke) K. Schum. - Somalia

Cleghornia is a genus of plants in the dogbane family; its various species are distributed in Borneo, China, Laos, Malaysia, Sri Lanka, Thailand, and Vietnam.
Diplospora is a genus of flowering plants in the Rubiaceae family. The genus is found in tropical and subtropical Asia.
Micrechites is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1857. It is native to China, the eastern Himalayas, Southeast Asia, Papuasia, and Queensland.
Aganosma is a genus of plants in family Apocynaceae first described as a genus in 1837. It is native to China, the Indian Subcontinent, and Southeast Asia.
- Aganosma brevilobaKerr - Guizhou, Myanmar, Thailand
- Aganosma cymosa(Roxb.) G.Don - Guangxi, Yunnan, Bangladesh, Assam, Sri Lanka, Indochina
- Aganosma gracilisHook.f. - Assam, Bhutan, Arunachal Pradesh
- Aganosma heynei(Spreng.) ined. - India
- Aganosma laceiRaizada - Myanmar
- Aganosma petelotiiLý - N Vietnam
- Aganosma schlechterianaH.Lév. - S China, Assam, N Indochina
- Aganosma siamensisCraib - Thailand, Vietnam, Guangxi, Guizhou, Yunnan
- Aganosma wallichiiG.Don - Myanmar, Thailand, W Malaysia, Java, Sumatra

Dregea is a genus of vines in the Apocynaceae, first described as a genus with this name in 1838. It is native to Africa and southern Asia.
- Dregea abyssinica(Hochst.) K.Schum. - Ethiopia
- Dregea crinita(Oliv.) Bullock - Nigeria
- Dregea cuneifoliaTsiang & P.T.Li - Guangxi Province in China
- Dregea faulkneraeBullock - Tanzania
- Dregea floribundaE.Mey. - South Africa
- Dregea lanceolata(Cooke) Santapau & Wagh - Maharashtra
- Dregea rubicundaK.Schum. - Kenya, Uganda
- Dregea sinensisHemsl. - China
- Dregea schimperi(Decne.) Bullock - Ethiopia
- Dregea stelostigma(K.Schum.) Bullock - tropical Africa
- Dregea volubilis(L.f.) Benth. ex Hook.f. - China Bangladesh, Cambodia, India, Indonesia, Kashmir, Laos, Malaysia, Nepal, Philippines, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Vietnam
- Dregea yunnanensis(Tsiang) Tsiang & P.T.Li - China
- Dregea volubilisStapf - Sri Lanka

Genianthus is a genus of plants in the Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1883. It is native to southern China, the Indian Subcontinent, and Southeast Asia.
Toxocarpus is a genus of plants in the Milkweed family, Apocynaceae. It is native to China, the Himalayas, and Southeast Asia.

Leptadenia is a genus of plant in family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1810. It is native to Africa, including Madagascar, as well as southwest Asia and the Indian Subcontinent.
- Leptadenia arborea(Forssk.) Schweinf. - Sudan, Ethiopia
- Leptadenia lancifolia(Schumach. & Thonn.) Decne. - tropical Africa
- Leptadenia madagascariensisDecne. - Madagascar
- Leptadenia pyrotechnica(Forssk.) Decne. - widespread from Algeria to India
- Leptadenia reticulata(Retz.) Wight & Arn. - Madagascar
Pentatropis is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1834. It is native to Africa and southern Asia.















