
The Great Western Railway 4000 or Star were a class of 4-cylinder 4-6-0 passenger steam locomotives designed by George Jackson Churchward for the Great Western Railway (GWR) in 1906 and introduced from early 1907. The prototype was built as a 4-4-2 Atlantic. They proved to be a successful design which handled the heaviest long-distance express trains, reaching top speeds of 90 mph (145 km/h), and established the design principles for GWR 4-cylinder classes over the next twenty-five years.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of locomotives, 4-6-4 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels and four trailing wheels. In France where the type was first used, it is known as the Baltic while it became known as the Hudson in most of North America.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-6-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and no trailing wheels. This arrangement is commonly called a Mogul.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-8-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and two trailing wheels on one axle, usually in a trailing truck. This configuration of steam locomotive is most often referred to as a Mikado, frequently shortened to Mike.
Locomotive classification on the Pennsylvania Railroad took several forms. Early on, steam locomotives were given single-letter classes. As the 26 letters were quickly assigned, that scheme was abandoned for a more complex system. This was used for all of the PRR's steam locomotives, and — with the exception of the final type bought — all electric locomotives also used this scheme.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-2-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, two powered driving wheels on one axle, and two trailing wheels on one axle.

The GWR 4100 Class was a class of steam locomotives in the Great Western Railway (GWR) of the United Kingdom.

The Great Western Railway 2900 Class or Saint Class, which was built by the Great Western Railway's Swindon Works, incorporated several series of 2-cylinder passenger steam locomotives designed by George Jackson Churchward and built between 1902 and 1913 with differences in the dimensions. The majority of these were built as 4-6-0 locomotives; but thirteen examples were built as 4-4-2. They proved to be a highly successful class which established the design principles for GWR 2-cylinder classes over the next fifty years, and influenced similar classes on other British railways.
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 0-8-2 represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle.
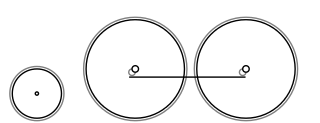
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-4-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles and no trailing wheels. In most of North America it became known as a Porter.

A 2-6-8-0 steam locomotive, in the Whyte notation for describing locomotive wheel arrangements, has two leading wheels, a set of six driving wheels, a set of eight driving wheels, and no trailing wheels. These locomotives usually employ the Mallet principle of articulation, with a swinging front engine and a rigidly attached rear engine.

The Great Northern Railway (GNR) No. 1 class Stirling Single is a class of steam locomotive designed for express passenger work. Designed by Patrick Stirling, they are characterised by a single pair of large driving wheels which led to the nickname "eight-footer". Originally the locomotive was designed to haul up to 26 passenger carriages at an average speed of 47 miles per hour (76 km/h). They could reach speeds of up to 85 mph.

The Great Northern Railway (GNR) Class C1 is a type of 4-4-2 steam locomotive. One, ex GNR 251, later LNER 2800, survives in preservation. Much like their small boiler cousins, they were capable of reaching speeds of up to 90 mph (145 km/h). They were also known as Large Atlantics.
During the 1880s and 1890s, William Dean constructed a series of experimental locomotives to test various new ideas in locomotive construction for the Great Western Railway.

The LNER Class A1/1 consisted of a single 4-6-2 "Pacific" express passenger locomotive rebuilt in 1945 from an A1 class locomotive, by Edward Thompson. It was intended as the prototype of a new design of pacific locomotives improving the A4 design of Thompson's predecessor Sir Nigel Gresley. No further examples were built due to Thompson's retirement in 1946.

The GWR 645 Class was a class of 0-6-0ST designed by George Armstrong and built at the Wolverhampton railway works of the Great Western Railway (GWR). Thirty-six were constructed between 1872-3, of which three were built for the South Wales Mineral Railway (SWMR), two for the Carmarthen and Cardigan Railway (C&CR) and the remainder for the GWR. In essence, they were saddle tank versions of his GWR 633 Class of 1871. From 1878, a further 72 of the class, partially enlarged, were added in the 1501 numbering sequence. Unlike the originals, the "1501"s had full-length saddle tanks from the start.
The Rhymney Railway P class was a class of 0-6-2T steam locomotive introduced into traffic in 1909 designed by the Rhymney Railway's engineer C. T. Hurry Riches. These were substantial sized tank locomotives, weighed 60 long tons and were 35 feet 0 inches (10.67 m) in length.

The GWR 455 Class, also called the "Metropolitan" or "Metro" Tanks, was a series of 140 2-4-0T locomotives built for the Great Western Railway, originally for their London suburban services, including running on the underground section of the Metropolitan Railway, the source of their nickname. Later on the class was seen on many other parts of the GWR system. Sixty "Metro" Tanks were built, from 1868 onwards, during the lifetime of their designer, Joseph Armstrong. His successor William Dean regarded the class so highly that he would add a further 80, the final 20 examples appearing as late as 1899. The "Metros" were all built at Swindon Works, in nine lots of ten or 20 engines each.
The William Dean 7 or Armstrong Class refers to a group of four prototype 4-4-0 double-frame locomotives built at the Swindon Works of the Great Western Railway in 1894.
The Great Northern O-1 was a class of 145 2-8-2 "Mikado"-type steam locomotives built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works between 1911 and 1919 and used by the Great Northern Railway until the late 1950s.














