
HMS Attentive was one of two Adventure-class scout cruisers built for the Royal Navy during the first decade of the 20th century. Completed in 1905 the ship was placed in reserve until she was commissioned in 1907 as part of the Home Fleet. She then spent the next seven years moving on and off of active service in British waters. The ship sank one destroyer and damaged two others in collisions. Attentive was assigned to coastal defence duties when the First World War began in 1914, and spent most of the war assigned to the Dover Patrol. She played a minor role in the Zeebrugge Raid in early 1918 and was then assigned to escort convoys to Gibraltar. The ship was sent to the White Sea later in the year to support the unsuccessful North Russia intervention in the Russian Civil War. Attentive paid off at the end of 1918 and was sold for scrap in 1920.

HMS Charger was a Charger-class destroyer which served with the Royal Navy. She was launched by Yarrow Shipbuilders at Poplar, London on 15 September 1894, served in home waters and was sold off in 1912.

HMS Waveney was a Hawthorn Leslie-type River-class destroyer ordered by the Royal Navy under the 1902–1903 Naval Estimates. Named after the River Waveney in eastern England, she was the first ship of the Royal Navy to carry this name.

HMS Boyne was a Hawthorn Leslie type River-class destroyer ordered by the Royal Navy under the 1903 – 1904 Naval Estimates. Named after the River Boyne in Ireland, the site of a British military victory in 1689, she was the fifth ship to carry this name since it was introduced in 1692 for a two deck ship-of-the-line.

HMS Doon was a Hawthorn Leslie type River-class destroyer ordered by the Royal Navy under the 1903 – 1904 Naval Estimates. Named after the River Doon in western Scotland, she was the first ship to carry this name in the Royal Navy.

HMS Welland was a Yarrow-built River-class destroyer ordered by the Royal Navy under the 1902 – 1903 Naval Estimates. Named after the River Welland that drains into the Wash on the English east coast, she was the first ship to carry this name in the Royal Navy.
HMS Ouse was a Laird type River-class destroyer ordered by the Royal Navy under the 1903 – 1904 Naval Estimates. Named after the River Ouse in north east England near the city of York, she was the first ship to carry this name in the Royal Navy.

HMS Arun was a Laird Type River-class destroyer ordered by the Royal Navy under the 1902–1903 Naval Estimates. Named after the River Arun in southern England she was the first ship to carry this name in the Royal Navy.

HMS Blackwater was a Laird-type River-class destroyer ordered by the Royal Navy under the 1902–1903 Naval Estimates. Named after the River Blackwater in southern England near London she was the first ship to carry this name in the Royal Navy.
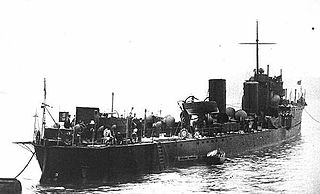
HMS Itchen was a Laird-type River-class destroyer ordered by the Royal Navy under the 1901–1902 Naval Estimates. Named after the River Itchen in southern England near Southampton, she was the first ship to carry this name in the Royal Navy.
HMS Liffey was a Laird-type River-class destroyer ordered by the Royal Navy under the 1903 – 1904 Naval Estimates. Named after the River Liffey flowing through Dublin, she was the third and final ship to carry this name since it was introduced in 1813 for a 50-gun 4th rate sold in 1827.
HMS Moy was a Laird Type River-class destroyer of the Royal Navy. Named after the River Moy in Ireland, she was the first ship to carry this name in the Royal Navy.
HMS Ness was a White Type River-class destroyer ordered by the Royal Navy under the 1903 – 1904 Naval Estimates. Named after the River Ness in northern Scotland, flowing through Inverness, she was the first ship to carry this name in the Royal Navy.
HMS Nith was a White Type River Class Destroyer ordered by the Royal Navy under the 1903–1904 Naval Estimates. Named after the River Nith in southern Scotland, on the West Coast, she was the first ship to carry this name in the Royal Navy.

HMS Ribble was a Yarrow-type River-class destroyer ordered by the Royal Navy under the 1901 – 1902 Naval Estimates. Named after the River Ribble in northern England, she was the first ship to carry this name in the Royal Navy.

HMS Usk was a Yarrow type River Class destroyer ordered by the Royal Navy under the 1901 – 1902 Naval Estimates. Named after the River Usk in Wales flowing through Newport, she was the first ship to carry this name in the Royal Navy.

HMS Ettrick was a River-class destroyer ordered by the Royal Navy under the 1901 – 1902 Naval Estimates. Named after Ettrick Water in the Scottish Borders area south of Edinburgh, she was the first ship to carry this name in the Royal Navy. She was launched in 1903 and served during World War I. She was torpedoed by UC-61 in 1917.
HMS Cherwell was a Palmer Type River-class destroyer ordered by the Royal Navy under the 1902 – 1903 Naval Estimates. Named after the River Cherwell in south central England near Oxford, she was the first ship to carry this name in the Royal Navy.

HMS Kennet was a Thornycroft type River Class Destroyer ordered by the Royal Navy under the 1902 – 1903 Naval Estimates. Named after the River Kennet in south west England, she was the first ship to carry this name in the Royal Navy.
HMS Ure was a Palmer Type River Class Destroyer ordered by the Royal Navy under the 1903 – 1904 Naval Estimates. Named after the River Ure in Yorkshire, England, she was the first ship to carry this name in the Royal Navy.












