
HMS Badger was an Acheron-class destroyer of the Royal Navy that served during the First World War and was sold for breaking in 1921. She was the eighth Royal Navy ship to be named Badger, after the mammal of the same name.

HMS Defender was an Acheron-class destroyer which was built in 1911, served throughout World War I and was broken up in 1921. She was the fifth ship of the name to serve in the Royal Navy.

HMS Acheron was the name ship of the Acheron-class destroyer of the British Royal Navy. She is named after the River Acheron, believed in Greek Mythology to be a branch of the River Styx. She was the fifth ship of the Royal Navy to bear the name.

HMS Phoenix was an Acheron-class destroyer of the British Royal Navy. She is named for the mythical bird, and was the fifteenth ship of the Royal Navy to bear the name. She was the only British warship ever to be sunk by the Austro-Hungarian Navy.

HMS Ariel was an Acheron-class destroyer built in 1911, which served during the First World War and sank in 1918 after striking a mine. Named after Shakespeare's "airy spirit", or the biblical spirit of the same name, she was the tenth and last ship of the name to serve in the Royal Navy.

HMS Attack was an Acheron-class destroyer built in 1911, which served during the First World War and was sunk in 1917 in the Mediterranean by a German U-boat. She was the third ship of the name to serve in the Royal Navy.

HMS Beaver was an Acheron-class destroyer of the Royal Navy that served during the First World War and was sold for breaking in 1921. She was the ninth Royal Navy ship to be named Beaver, after the mammal of the same name.

HMS Goshawk was an Acheron-class destroyer of the Royal Navy that served during World War I and was sold for breaking in 1921. She was the sixth Royal Navy ship to be named after the bird of prey, Accipiter gentilis.

HMS Druid was one of 20 Acheron-class destroyers built for the Royal Navy during the 1910s. Completed in 1912 the ship served during World War I and was sold for scrap in 1921.

HMS Jackal was an Acheron-class destroyer of the Royal Navy that served during the World War I and was sold for breaking in 1920. She was the seventh Royal Navy ship to be named Jackal, after the predatory mammal of the same name.

HMS Hornet was an Acheron-class destroyer of the Royal Navy that served during the First World War and was sold for breaking in 1921. She was the seventh Royal Navy ship to be named Hornet, after the insect.

The Battle of Imbros was a naval action that took place during the First World War. The battle occurred on 20 January 1918 when an Ottoman squadron engaged a flotilla of the British Royal Navy off the island of Imbros in the Aegean Sea. A lack of heavy Allied warships in the area allowed the Ottoman battlecruiser Yavûz Sultân Selîm and light cruiser Midilli to sortie into the Mediterranean and attack the Royal Navy monitors and destroyers at Imbros before assaulting the naval base at Mudros.

HMS Tigress was an Acheron-class destroyer of the Royal Navy that served during World War I. She was built under the 1910–11 shipbuilding programme by R. W. Hawthorn Leslie & Company of Hebburn, was launched on 20 December 1911 and was sold for breaking on 9 May 1921.

HMS Hind was an Acheron-class destroyer of the Royal Navy that served during World War I and was sold for breaking in 1921. She was the seventeenth Royal Navy ship to be named after the female deer.
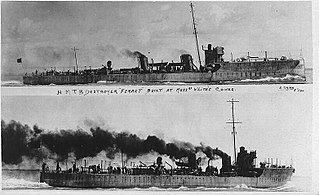
HMS Ferret was an Acheron-class destroyer of the Royal Navy that served during World War I and was sold for breaking in 1921. She was the sixteenth Royal Navy ship to be named after the domestic mammal Mustela putorius.

HMS Forester was an Acheron-class destroyer of the Royal Navy that served during World War I and was sold for breaking in 1921. She was the ninth Royal Navy ship to be named after the traditional craft of forester.

HMS Lapwing was an Acheron-class destroyer of the Royal Navy that served during World War I and was sold for breaking in 1921. She was the seventh Royal Navy ship to be named after Vanellus vanellus, the northern lapwing.

HMS Sandfly was an Acheron-class destroyer of the Royal Navy that served during World War I and was sold for breaking in 1921. She was the seventh Royal Navy ship to be named after the small biting fly of the same name.

HMS Laurel was a Laforey-class destroyer which served with the Royal Navy. Launched on 6 May 1913 as HMS Redgauntlet, the ship was renamed on 30 September under an Admiralty order to become one of the first alphabetical class destroyers. On commissioning, the vessel joined the 3rd Destroyer Flotilla and operated as part of the Harwich Force during the First World War. During Battle of Heligoland Bight, Laurel led a flotilla that pursued German torpedo boats, engaging with G194 and G196, and was damaged in action with the cruiser Mainz. The vessel also played a minor role in the Battles of Dogger Bank, Dover Strait and Jutland. With the cessation of hostilities, the ship was placed in reserve and scrapped on 1 November 1921.

HMS Liberty was a Laforey-class destroyer that served with the Royal Navy during the First World War. Launched on 15 September 1913 as HMS Rosalind, the ship was renamed on 30 September under an Admiralty order to become one of the first alphabetical class destroyers. On commissioning, the vessel joined the Third Destroyer Flotilla and operated as part of the Harwich Force. During Battle of Heligoland Bight, Liberty engaged with the German torpedo boats G194 and G196, and scored two hits on the cruiser Mainz. On 8 February 1917, the destroyer rammed and sank the German submarine UC-46. The vessel also played a minor role in the battles of Dogger Bank, Dover Strait and Jutland, as well as acting as a convoy escort and patrolling the Dover Barrage. With the cessation of hostilities, the ship was placed in reserve and sold to be broken up on 5 November 1921.





















