
In archaeology and the field of lithic reduction, a burin is a type of stone tool, a handheld lithic flake with a chisel-like edge which prehistoric humans used for carving or finishing wood or bone tools or weapons, and sometimes for engraving images.
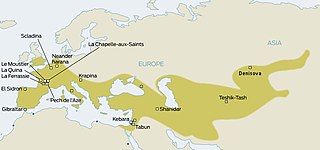
The Mousterian is an archaeological industry of stone tools, associated primarily with the Neanderthals in Europe, and to the earliest anatomically modern humans in North Africa and West Asia. The Mousterian largely defines the latter part of the Middle Paleolithic, the middle of the West Eurasian Old Stone Age. It lasted roughly from 160,000 to 40,000 BP. If its predecessor, known as Levallois or Levallois-Mousterian, is included, the range is extended to as early as c. 300,000–200,000 BP. The main following period is the Aurignacian of Homo sapiens.

The Aterian is a Middle Stone Age stone tool industry centered in North Africa, from Mauritania to Egypt, but also possibly found in Oman and the Thar Desert. The earliest Aterian dates to c. 150,000 years ago, at the site of Ifri n'Ammar in Morocco. However, most of the early dates cluster around the beginning of the Last Interglacial, around 150,000 to 130,000 years ago, when the environment of North Africa began to ameliorate. The Aterian disappeared around 20,000 years ago.

Nubiology is the scientific study of ancient Nubia. The term was coined by Kazimierz Michałowski.

Wādī Ḥalfā is a city in the Northern state of Sudan on the shores of Lake Nubia near the border with Egypt. It is the terminus of a rail line from Khartoum and the point where goods are transferred from rail to ferries going down the lake. As of 2007, the city had a population of 15,725. The city is located amidst numerous ancient Nubian antiquities and was the focus of much archaeological work by teams seeking to save artifacts from the flooding caused by the completion of the Aswan Dam.

The Levallois technique is a name given by archaeologists to a distinctive type of stone knapping developed around 250,000 to 400,000 years ago during the Middle Palaeolithic period. It is part of the Mousterian stone tool industry, and was used by the Neanderthals in Europe and by modern humans in other regions such as the Levant.

Prehistoric Egypt and Predynastic Egypt was the period of time starting at the first human settlement and ending at the First Dynasty of Egypt around 3100 BC.
Jebel Sahaba is a prehistoric cemetery site in the Nile Valley, near the northern border of Sudan with Egypt in Northeast Africa. It is associated with the Qadan culture. It was discovered in 1964 by a team led by Fred Wendorf.

The Tabun Cave is an excavated site located at Nahal Me'arot Nature Reserve, Israel and is one of the Human Evolution sites at Mount Carmel, which were proclaimed as having universal value by UNESCO in 2012.
The Paleo-Arctic Tradition is the name given by archaeologists to the cultural tradition of the earliest well-documented human occupants of the North American Arctic, which date from the period 8000–5000 BC. The tradition covers Alaska, and expands far into the east, west, and the Southwest Yukon Territory of Canada.
Uan Muhuggiag is an archaeological site in Libya that was occupied by pastoralists between the early Holocene and mid-Holocene; the Tashwinat mummy, which was found at Uan Muhuggiag, was dated to 5600 BP and presently resides in the Assaraya Alhamra Museum in Tripoli.

The Mushabian culture is an archaeological culture suggested to have originated among the Iberomaurusians in North Africa, though once thought to have originated in the Levant.
Broken Mammoth, Alaska is an archeological site located in the Tanana River Valley, Alaska, in the United States. The site was occupied approximately 11,000 to 12,000 years ago making this one of the oldest known sites in Alaska. Charles E. Holmes discovered the site in 1989 and investigation of the site began in 1990 and excavations are ongoing to this day.

Dishna (Arabic: دشنا, from Coptic: ⲧⲉϣⲛⲏ, lit. 'the tree garden') is a settlement west of Qena situated on the north bank of the river Nile in Qena Governorate, Egypt.
Sebilian is a pre-historic archaeological culture in Nubia spanning the period c. 13,000–10,000 B.C.
The Swan Point Archeological Site is located in eastern central Alaska, in the Tanana River watershed. It is one of a collection of sites in the area that have yielded the oldest evidence of human habitation in the state, in addition to megafauna no longer found in Alaska, such as wapiti (elk), bison, and woolly mammoth. Finds co-located with human artifacts at the site have given radiocarbon dates of 14,000 years, indicating the site was occupied around 12,000 BCE. Swan Point is the oldest archaeological site in the Americas whose age is not disputed.

Taforalt, or Grotte des Pigeons, is a cave in the province of Berkane, Aït Iznasen region, Morocco, possibly the oldest cemetery in North Africa. It contained at least 34 Iberomaurusian adolescent and adult human skeletons, as well as younger ones, from the Upper Palaeolithic between 15,100 and 14,000 calendar years ago. There is archaeological evidence for Iberomaurusian occupation at the site between 23,200 and 12,600 calendar years ago, as well as evidence for Aterian occupation as old as 85,000 years.
Khormusan industry was a Paleolithic archeological industry in Nubia dated at 42,000 to 18,000 BP.
R12 is a middle Neolithic cemetery located in the Northern Dongola Reach on the banks of the Seleim Nile palaeochannel of modern-day Sudan. The site is dated to between 5000 and 4000 BC. Centro Veneto di Studi Classici e Orientali excavated the site, within the concession of the Sudan Archaeological Research Society and after an agreement with it, between 2000 and 2003 over three digging seasons. The first was in 2000 and 33 graves were discovered. The second was in 2001 and another 33 graves were discovered. The third was in 2003 and the last 100 graves were discovered. There are 166 graves total at the site. Contents of the graves include ceramics, animal bones, grinding stones, human skeletons, and plant remains.
Wadi Kubbaniya is a Late Paleolithic site in Upper Egypt. Archaeologists initially believed that the site held evidence for some of the earliest examples of agriculture. When Wadi Kubbaniya was discovered, there were traces of barley that were originally thought to be evidence of farming. It is now believed that this is most likely not the case. The site has been dated to between 19,000 and 17,000 years ago using radiocarbon dating. This site was a part of a settlement system that people would come back to during its prime seasons of summer and winter.










