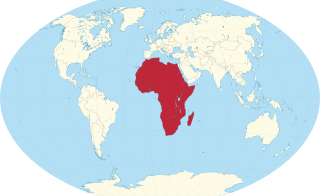
Africa is a continent comprising 63 political territories, representing the largest of the great southward projections from the main mass of Earth's surface. Within its regular outline, it comprises an area of 30,368,609 km2 (11,725,385 sq mi), excluding adjacent islands. Its highest mountain is Mount Kilimanjaro, its largest lake is Lake Victoria.

Hexactinellid sponges are sponges with a skeleton made of four- and/or six-pointed siliceous spicules, often referred to as glass sponges. They are usually classified along with other sponges in the phylum Porifera, but some researchers consider them sufficiently distinct to deserve their own phylum, Symplasma. Some experts believe glass sponges are the longest-lived animals on earth; these scientists tentatively estimate a maximum age of up to 15,000 years.

Eucalyptus microcorys, commonly known as tallowwood, is a species of medium to tall tree that is endemic to eastern Australia. It has rough, fibrous or string bark on the trunk and branches, lance-shaped to egg-shaped adult leaves, flower buds in groups of seven or nine, white to lemon-yellow flowers and conical fruit. It grows in forests near the coast of Queensland and New South Wales.

Eucalyptus obliqua, commonly known as messmate stringybark or messmate, but also known as brown top, brown top stringbark, stringybark or Tasmanian oak, is a species of tree that is endemic to south-eastern Australia. It has rough, stringy or fibrous bark on the trunk and larger branches, smooth greyish bark on the thinnest branches, lance-shaped to curved adult leaves, flower buds in groups of seven to fifteen or more, white flowers and cup-shaped or barrel-shaped fruit.
Sepia australis, the southern cuttlefish, is a species of cuttlefish which is found in the eastern South Atlantic Ocean and the western Indian Ocean off the coasts of Southern Africa, possibly extending into the waters off East Africa.

Eucalyptus pilularis, commonly known as blackbutt, is a species of medium-sized to tall tree that is endemic to eastern Australia. It has rough, finely fibrous greyish bark on the lower half of the trunk, smooth white, grey or cream-coloured bark above, lance-shaped to curved adult leaves, flower buds in groups of between seven and fifteen, white flowers and hemispherical or shortened spherical fruit.

The orange wall sponge is a species of sea sponge belonging to the order Trachycladida. It is found in the south Atlantic and Indo-Pacific oceans. Around the South African coast, it is known from the Cape Peninsula to Cape Agulhas.

Corymbia nesophila, commonly known as the Melville Island bloodwood, is a species of tree that is endemic to northern Australia. It has rough, tessellated bark on the trunk and branches, lance-shaped or curved adult leaves, flower buds in groups of seven, creamy white flowers and urn-shaped fruit.

Leucospermum pedunculatum is an evergreen, low shrub of 15–30 cm (5.9–11.8 in) high spreading from a single stern upright stem, from the family Proteaceae. The powdered or hairless line-shaped to somewhat sickle-shaped leaves are 3–6 cm (1.2–2.4 in) long and 2–5 mm (0.08–0.20 in) wide. The stalked, individually set flower heads are globe-shaped, 2½−3 cm in diameter consist of initially white to pale cream flowers that eventually turn carmine. From the center of the flowers emerge straight styles that jointly give the impression of a pincushion. It is called white-trailing pincushion in English. It flowers from August to January, peaking in September. It is an endemic species that is restricted to a narrow strip on the south coast of the Western Cape province of South Africa.
Haliclona submonilifera, or the bubble bead sponge, is a deep-water demosponge from the continental shelf and slope off south-west Africa.
Hamacantha is a genus of sponges in the family Hamacanthidae. This species in this genus differ from those in the other genera in this family through the presence of diancistras, distinctive microscleres. These are thought to aid in framing the skeleton by joining monactine megascleres. This genus contains 30 species in three subgenera.
Inflatella belli, or the gooseberry sponge, is a species of demosponge that appears to be restricted to the southern hemisphere, where it is widespread. It occurs from the coast of Namibia and the Indo-pacific, down to the Subantarctic and Antarctic regions.
Fibulia ramosa, or the columnar sponge, is a species of deep-sea demosponge from the southern hemisphere.
Mycale anisochela, the brain sponge, is a species of demosponge from South Africa and Namibia.
Polymastia bouryesnaultae, the knobbly sponge, is a small and cryptic species of demosponge from South Africa and Namibia.
Suberites dandelenae, the amorphous solid sponge, is a species of deep-sea demosponge from South Africa and Namibia.
Penares sphaera, the crater sponge, is a deep sea demosponge from southern Africa.
Tetilla capillosa, the furry sponge, is a species of demosponge from southern Africa.
Tetilla casula, the volcano sponge, is a species of demosponge from the south coast of South Africa.
Rossella antarctica is a relatively small species of glass sponge. It is widely distributed in the southern hemisphere, particularly in the Antarctic and sub-Antarctic regions.







