Laurel is a town in Sussex County, Delaware, United States. The population was 3,708 at the time of the 2010 census. Laurel is part of the Salisbury, Maryland-Delaware Metropolitan Statistical Area. It once hosted the Laurel Blue Hens of the Eastern Shore Baseball League.
Millsboro is a town in Sussex County, Delaware, United States. Millsboro is part of the Salisbury metropolitan area.
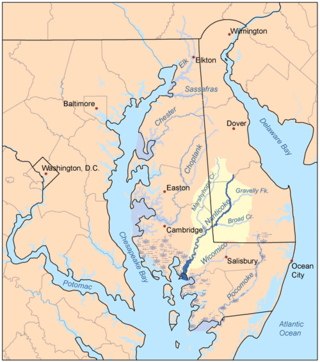
The Nanticoke people are a Native American Algonquian-speaking people, whose traditional homelands are in Chesapeake Bay area, including Delaware. Today they continue to live in the Northeastern United States, especially Delaware, and in Oklahoma. They also live in Ontario, Canada, where some ancestors resettled with Iroquois nations after the Revolutionary War.

Cathedral Parish School, also known as Wheeling Catholic Elementary and Diocese of Wheeling-Charleston Chancery, was a historic elementary school building located at Wheeling, Ohio County, West Virginia. It was built in 1896–1897, to service the St. Joseph Cathedral parish. A gymnasium addition was built in 1939. It is a three-story brick building, with an elevated first floor. It sits on a sandstone base. It features a center square tower with a pyramidal roof and Late Gothic Revival details.

Motor Square Garden, also known as East Liberty Market, is a building in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States, that is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
The Nanticoke Indian Association is a group of Nanticoke who have their headquarters in Millsboro, Delaware. They organized and were recognized by the state as a legal entity in 1881, known as the Independent Body. They were recognized as a Native American tribe by the state of Delaware in 1922.

The Grecian Shelter, designated a Croquet Shelter on the original plans of Prospect Park, is also referred to as the Prospect Park Peristyle or Peristyle. The building, a peristyle with Corinthian columns, is situated near the southern edge of Prospect Park in Brooklyn, New York. Constructed by McKim, Mead and White in 1905, this peristyle was built on the site of the 1860s-era Promenade Drive Shelter along the southwest shore of the Prospect Park Lake. The Prospect Park Peristyle is designed in the Renaissance architectural style. It consists of a raised platform located two steps above ground level; the platform is covered by a rectangular colonnade with 28 Corinthian marble columns, each with square piers. An entablature of terracotta runs atop the structure. The building was constructed as a temporary refuge from rain and sun.

Mount Harmon is an historic home, located at Earleville, Cecil County, Maryland, United States. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1974, and is currently open to the public.

The Field Matron's Cottage, also known as the Stone Building, was built circa 1925 on the Reno-Sparks Indian Colony in Sparks, Nevada. The cottage was built to support a Bureau of Indian Affairs program to instruct the 20 acres (8.1 ha) colony's Paiute and Washoe girls in sanitation and housekeeping skills. A "field matron" was provided by the Bureau from 1919 to as late as 1938. At first the matron lived in Reno, at some distance from the colony, but in 1926 funding was made available to build a dwelling on colony lands, allowing a closer relationship between the matron and the colony's inhabitants. The cottage included a library and an infirmary, and served as a community meeting place.

Harmony Church is a historic Methodist Episcopal church located at Millsboro, Sussex County, Delaware. It was built in 1891, and is a one-story, wood-frame building covered with asbestos siding and in the Late Gothic Revival style. It has a two-story wing and sits on a rock-faced, concrete block foundation. It features a two-story crenellated tower. The congregation was organized in 1818. The Indian Mission Church of the Nanticoke Indian Association was formed from Harmony Church after the hiring of an African American minister.

Indian Mission Church is a historic Methodist church located in Millsboro, Sussex County, Delaware. It was built in 1921, and is a one-story, wood-frame building covered with clapboard siding and in the Late Gothic Revival style. It features a two-story hipped roof tower and lancet windows. The congregation was organized in 1881 from the Harmony Church after the strongly Native American families of the Nanticoke Indian Association separated after the hiring of an African American minister.

Indian Mission School, also known as the Nanticoke Indian Center, is a historic school building located in Millsboro, Sussex County, Delaware. It was built in about 1948, after the original school was destroyed by fire. It is a one-story, stuccoed masonry building with a gable roof. It features a concrete block covered entrance. The school was organized after school reforms of the early 20th century mandated that the children of the strongly Native American families of the Nanticoke Indian Association be placed in the same schools as African-American students.

The Phoenix Indian School, or Phoenix Indian High School in its later years, was a Bureau of Indian Affairs-operated school in Encanto Village, in the heart of Phoenix, Arizona. It served lower grades also from 1891 to 1935, and then served as a high school thereafter. It opened in 1891 and closed in 1990 on the orders of the federal government. During its existence, it was the only non-reservation BIA school in Arizona.

Isaac Harmon Farmhouse is a historic farmhouse located near Millsboro, Sussex County, Delaware. It was built about 1845, and is a two-story, four-bay, single pile, wood frame dwelling clad in clapboard. It has a gable roof pierced by interior end brick chimneys. It was one of the first properties in the Indian River community to be owned by an Indian family. Isaac Harmon was one of the leaders in the Nanticoke Indian Association separatist movement of the 1880s.

Princess Ruth Keʻelikōlani Middle School is a school of the Hawaii Department of Education that occupies a historic building in Honolulu, Hawaiʻi, built on the grounds of Keōua Hale, the former palace of Princess Ruth Keʻelikōlani of Hawaiʻi.
The Island Field Site (7K-F-17) is a major archaeological site in Kent County, Delaware, United States. The site is located in South Bowers, just south of the Murderkill River near where it empties into Delaware Bay. The site was a major prehistoric Native American village site, which was most notable for its cemetery. The site was first identified in the 1920s during road work, and was excavated in the 1950s-60s, after which the area was eventually built up to include a museum. In 1986 members of the local Nanticoke tribe protested the display and removal for research of burial remains at the site.

The former East White Oak School also known as East White Oak Community Center, is a historic school building for African-American students located at Greensboro, Guilford County, North Carolina. It was built in 1916, and is a one-story, seven-bay, Colonial Revival style frame building. It features a portico supported by four solid wood columns. One-story additions were built in the 1920s or 1930s to form a square-shaped building. The school closed in 1946, and subsequently housed a YMCA and community center.

Trinity Episcopal Cathedral, located in Reno, Nevada, United States, https://trinityreno.org/ is the seat of the Diocese of Nevada. The congregation was established in 1870, and they held their first services in a schoolhouse. By 1873 they were able to buy the lot on which the school stood, and in December 1875 they completed a new church. The parish bought the property the present church building is located on in the 1920s. Local architect Frederic DeLongchamps designed a new church building, and the congregation was able to complete the lower level of the church in 1929. This served all the parish's needs until the present church was completed in 1949.