
Life expectancy at birth in 2013 was 74 for men and 79 for women. [1]

Life expectancy at birth in 2013 was 74 for men and 79 for women. [1]
In 2014 Sultan Qaboos University published research showing that 30% of the Omani population was overweight and 20% was obese. [2]
A ban on smoking in public places was introduced in 2010. Restaurants, malls and other public places were required to allot more than 50% of their space as non-smoking zones. [3] 70% of residents suffer from some kind of curable disease related to smoking. [4]

"Junk food" is a term used to describe food that is high in calories from macronutrients such as sugar and/or fat, and possibly sodium, making it hyperpalatable, but with insufficient dietary fiber, protein, or micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals. It is also known as HFSS food. The term junk food is a pejorative dating back to the 1950s. Many variations of junk food can be easily found in most supermarkets and fast-food restaurants. Due to easy accessibility, commercially-oriented packaging, and often-low prices, people are most likely to consume it.

Smoking bans, or smoke-free laws, are public policies, including criminal laws and occupational safety and health regulations, that prohibit tobacco smoking in certain spaces. The spaces most commonly affected by smoking bans are indoor workplaces and buildings open to the public such as restaurants, bars, office buildings, schools, retail stores, hospitals, libraries, transport facilities, and government buildings, in addition to public transport vehicles such as aircraft, buses, watercraft, and trains. However, laws may also prohibit smoking in outdoor areas such as parks, beaches, pedestrian plazas, college and hospital campuses, and within a certain distance from the entrance to a building, and in some cases, private vehicles and multi-unit residences.

A smoking ban in England, making it illegal to smoke in all enclosed workplaces in England, came into force on 1 July 2007 as a consequence of the Health Act 2006. Similar bans had already been introduced by the rest of the United Kingdom: in Scotland on 26 March 2006, Wales on 2 April 2007 and Northern Ireland on 30 April 2007. Plain tobacco packaging and a smoking ban in cars with passengers under 18 were introduced under Children and Families Act 2014.
Health in the United Kingdom refers to the overall health of the population of the United Kingdom. This includes overall trends such as life expectancy and mortality rates, mental health of the population and the suicide rate, smoking rates, alcohol consumption, prevalence of diseases within the population and obesity in the United Kingdom. Three of these – smoking rates, alcohol consumption and obesity – were above the OECD average in 2015.
As for many developing countries, health issues in Iran stem from a variety of reasons: namely, water and sanitation, diet and fitness, various addictions, mental fitness, communicable diseases, hygiene and the environment.

Health in Saudi Arabia refers to the overall health of the population of Saudi Arabia. Government prioritization of preventive healthcare and environmental health began in 1925 following the establishment of a public health department. The decision to create it came after a royal decree from King Abdul Aziz Al-Saud. The government announced plans to increase taxes on soft drinks and tobacco in December 2015.
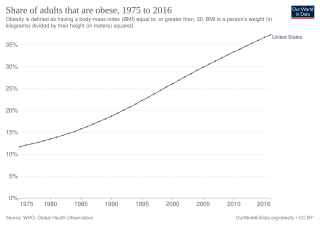
Obesity is common in the United States and is a major health issue associated with numerous diseases, specifically an increased risk of certain types of cancer, coronary artery disease, type 2 diabetes, stroke, and cardiovascular disease, as well as significant increases in early mortality and economic costs.

Inflight smoking refers to smoking tobacco on an aircraft while in flight. While once prevalent, it is now prohibited by almost all airlines and by many governments around the world. The bans on inflight smoking have been imposed in a piecemeal manner around the world beginning in the 1980s. The use of electronic cigarettes is also prohibited on many flights.
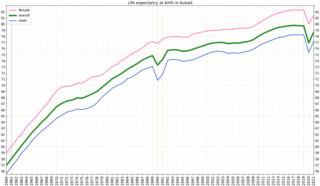
In Kuwait, life expectancy at birth in 2013 was 78 for men and 79 for women.
Smoking bans in private vehicles are enacted to protect passengers from secondhand smoke and to increase road traffic safety, e.g. by preventing the driver from being distracted by the act of smoking. Smoking bans in private vehicles are less common than bans extended to public transport or vehicles used during work, like trucks or police cars.

Smoking in Singapore is subjected to restrictions enacted through various legislations such as the Smoking Act, which was first enacted in 1970.

SmokinginCanada is banned in indoor public spaces, public transit facilities and workplaces, by all territories and provinces, and by the federal government. As of 2010, legislation banning smoking within each of these jurisdictions is mostly consistent, despite the separate development of legislation by each jurisdiction. Notable variations between the jurisdictions include: whether, and in what circumstances ventilated smoking rooms are permitted; whether, and up to what distance away from a building is smoking banned outside of a building; and, whether smoking is banned in private vehicles occupied by children.

After a significant decline in earlier decades, crude birth rates in Armenia slightly increased from 13.0 in the year 1998 to 14.2 in 2015; this timeframe also showed a similar trajectory in the crude death rate, which grew from 8.6 to 9.3. Life expectancy at birth at 74.8 years was the 4th-highest among the Post-Soviet states in 2014.
Montenegro is a country with an area of 13,812 square kilometres and a population of 620,029, according to the 2011 census. The country is bordered by Croatia, the Adriatic Sea, Bosnia, Herzegovina, Serbia, Kosovo and Albania. The most common health issues faced are non-communicable diseases accounting for 95% of all deaths. This is followed by 4% of mortality due to injury, and 1% due to communicable, maternal, perinatal and nutritional conditions. Other health areas of interest are alcohol consumption, which is the most prevalent disease of addiction within Montenegro and smoking. Montenegro has one of the highest tobacco usage rates across Europe. Life expectancy for men is 74 years, and life expectancy for women is 79.
Life expectancy in Bahrain at birth in 2013 was 76 for men and 78 for women. Compared to many countries in the region, the prevalence of AIDS and HIV is relatively low. Malaria and tuberculosis (TB) do not constitute major problems in Bahrain as neither disease is indigenous to the country. As a result, cases of malaria and TB have declined in recent decades with cases of contractions amongst Bahraini nationals becoming rare. The Ministry of Health sponsors regular vaccination campaigns against TB and other diseases such as hepatitis B.

The issue of smoking in association football is a historical controversy. Traditionally, football managers would smoke on the touch-line as well as players smoking away from the pitch. However, growing anti-smoking trends have led to a number of restrictions being put in place surrounding them. Smoking is now largely banned from stadiums around the world, but some individual players and managers have continued to smoke.