
Mushroom poisoning is poisoning resulting from the ingestion of mushrooms that contain toxic substances. Symptoms can vary from slight gastrointestinal discomfort to death in about 10 days. Mushroom toxins are secondary metabolites produced by the fungus.

Hypholoma fasciculare, commonly known as the sulphur tuft or clustered woodlover, is a common woodland mushroom, often in evidence when hardly any other mushrooms are to be found. This saprotrophic small gill fungus grows prolifically in large clumps on stumps, dead roots or rotting trunks of broadleaved trees.

Russula is a very large genus composed of around 750 worldwide species of ectomycorrhizal mushrooms. They are typically common, fairly large, and brightly colored – making them one of the most recognizable genera among mycologists and mushroom collectors. Their distinguishing characteristics include usually brightly coloured caps, a white to dark yellow spore print, brittle, attached gills, an absence of latex, and absence of partial veil or volva tissue on the stem. Microscopically, the genus is characterised by the amyloid ornamented spores and flesh (trama) composed of spherocysts. Members of the related genus Lactarius have similar characteristics but emit a milky latex when their gills are broken. The genus was described by Christian Hendrik Persoon in 1796.

Phallus indusiatus, commonly called the bamboo mushrooms, bamboo pith, long net stinkhorn, crinoline stinkhorn, bridal veil, or veiled lady, is a fungus in the family Phallaceae, or stinkhorns. It has a cosmopolitan distribution in tropical areas, and is found in southern Asia, Africa, the Americas, and Australia, where it grows in woodlands and gardens in rich soil and well-rotted woody material. The fruit body of the fungus is characterised by a conical to bell-shaped cap on a stalk and a delicate lacy "skirt", or indusium, that hangs from beneath the cap and reaches nearly to the ground. First described scientifically in 1798 by French botanist Étienne Pierre Ventenat, the species has often been referred to a separate genus Dictyophora along with other Phallus species featuring an indusium. P. indusiatus can be distinguished from other similar species by differences in distribution, size, color, and indusium length.

Shimeji is a group of edible mushrooms native to East Asia, but also found in northern Europe. Hon-shimeji is a mycorrhizal fungus and difficult to cultivate. Other species are saprotrophs, and buna-shimeji is now widely cultivated. Shimeji is rich in umami-tasting compounds such as guanylic acid, glutamic acid, and aspartic acid.

Inonotus hispidus, commonly known as shaggy bracket, is a fungus and a plant pathogen. This fungus has been used in eastern Asia as a popular remedy for many illnesses like cancer, diabetes, and other stomach ailments. In modern pharmacology, the Inonotus hispidus has aided in lowering blood glucose levels, showing anti-tumor responses and improving overall health in mice.

Flutazolam is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It was invented in Japan, and this is the main country in which it has been used medically. It has sedative, muscle relaxant, anticonvulsant, and anxiolytic effects similar to those produced by other benzodiazepine derivatives, and though it is around the same potency as diazepam, it produces a more marked sedation and impaired coordination. It is indicated for the treatment of insomnia. Its major active metabolite is n-desalkylflurazepam, also known as norflurazepam, which is also a principal metabolite of flurazepam. While flutazolam has a very short half-life of only 3.5 hours, n-desalkylflurazepam has a long half-life of between 47–100 hours.
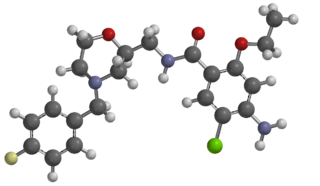
Mosapride is a gastroprokinetic agent that acts as a selective 5HT4 agonist. The major active metabolite of mosapride, known as M1, additionally acts as a 5HT3 antagonist, which accelerates gastric emptying throughout the whole of the gastrointestinal tract in humans, and is used for the treatment of gastritis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, functional dyspepsia and irritable bowel syndrome. It is recommended to be taken on an empty stomach (i.e. at least one hour before food or two hours after food).
Ammonia fungi are fungi that develop fruit bodies exclusively or relatively abundantly on soil that has had ammonia or other nitrogen-containing materials added. The nitrogen materials react as bases by themselves, or after decomposition. The addition of ammonia or urea causes numerous chemical and biological changes, for examples, the pH of soil litter is increased to 8–10; the high alkaline conditions interrupts the process of nutrient recycling. The mechanisms of colonization, establishment, and occurrence of fruiting bodies of ammonia fungi has been researched in the field and the laboratory.

Ergosterol peroxide (5α,8α-epidioxy-22E-ergosta-6,22-dien-3β-ol) is a steroid derivative. It has been isolated from a variety of fungi, yeast, lichens and sponges, and has been reported to exhibit immunosuppressive, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, trypanocidal and antitumor activities in vitro.
Cunninghamella elegans is a species of fungus in the genus Cunninghamella found in soil.

Omphalotus japonicus, commonly known as the tsukiyotake(月夜茸), is an orange to brown-colored gilled mushroom native to Japan and Eastern Asia. It is a member of the cosmopolitan genus Omphalotus, the members of which have bioluminescent fruit bodies which glow in darkness. A 2004 molecular study shows it to be most closely related to a clade composed of Omphalotus nidiformis of Australia, Omphalotus olivascens of Western North America and Omphalotus olearius of Europe.
Ecklonia kurome is a brown alga species in the genus Ecklonia found in the Sea of Japan.

Mallotus japonicus, also known as East Asian mallotus, the food wrapper plant or "Akamegashiwa" in Japanese, is a plant species in the genus Mallotus native to China. It is also found in Japan and Korea. This species was first described in 1865, its name was verified by AAS Systematic Botanists on October 2, 2015.

The diarylheptanoids are polyphenols and a relatively small class of plant secondary metabolites. Diarylheptanoids consist of two aromatic rings joined by a seven carbons chain (heptane) and having various substituents. They can be classified into linear (curcuminoids) and cyclic diarylheptanoids. The best known member is curcumin, which is isolated from turmeric and is known as food coloring E100. Some other Curcuma species, such as Curcuma comosa also produce diarylheptanoids.

Luteusin A is an azaphilone monoamine oxidase inhibitor produced by Talaromyces luteus.
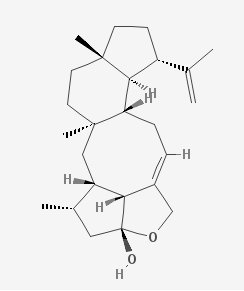
Variecolol is an immunosuppressant/antiviral compound isolated from ascomycete.

Cannabichromenic acid (CBCA) is minor cannabinoid and precursor of cannabichromene.

11-Hydroxycannabinol (11-OH-CBN) is the main active metabolite of cannabinol (CBN), one of the active components of cannabis, and has also been isolated from cannabis itself. It is more potent than CBN itself, acting as an agonist of CB1 with around the same potency as THC, but is a weak antagonist at CB2.















