
The Heimathaus Twist is a cross-community cultural center in the municipality of Twist, Germany well known and for blues and folk music concerts nationwide.

The Heimathaus Twist is a cross-community cultural center in the municipality of Twist, Germany well known and for blues and folk music concerts nationwide.
The Heimathaus Twist is a complex of buildings and consists of four buildings in the traditional construction style of the Emsland county. The Handwerker-Haus (craftsman's house) is constructed in timber framing style and the second building is constructed as a brick building. Wooden beams from an old farm house were used from these houses. The timber-framed house and the wooden beams for the second building are from demolished farm houses in Heblermeer, a district in Twist, and were reconstructed in the center of Twist in 1980. The third build is a baking house that allows baking bread in a traditional way in a wood-fired oven. This house was constructed in 2003. In 2015 the Heimathaus Twist building was expended by another fourth building. This building is used for storage.
Since 1990 regularly different events have taken place regularly in the Heimathaus Twist amongst others readings, classic music, folk and jazz. Especially because of its blues concerts the Heimathaus Twist has gained great popularity within the blues fan community. The good reputation and high number of gigs with well known bands and musicians for instance headliners like Albert Hammond and Maggie Reilly , Chris Farlowe , Ten Years After , John Lee Hooker Jr . or Hamburg Blues Band lead to the nickname „Blues-Mekka im Moor“ (Blues Mecca in the bog). Because of the nearby border to the Netherlands many Dutch people form a big part of the core audience, for important events even people from London or Nice come to the concerts.
At concerts in Heimathaus Twist several Live-CDs have been recorded amongst others the concert of the Blues Company , Ten Years After and the concert of Lefthand Freddy and the Aces . Often these gigs are also broadcast by nationwide radio stations like Deutschlandfunk and Deutschlandradio Kultur.
Furthermore, the Heimathaus team also organizes bicycle tours to explore and discover the region around Twist and organizes special events for entertaining children.

In architecture, post and lintel is a building system where strong horizontal elements are held up by strong vertical elements with large spaces between them. This is usually used to hold up a roof, creating a largely open space beneath, for whatever use the building is designed. The horizontal elements are called by a variety of names including lintel, header, architrave or beam, and the supporting vertical elements may be called columns, pillars, or posts. The use of wider elements at the top of the post, called capitals, to help spread the load, is common to many traditions.

A barn is an agricultural building usually on farms and used for various purposes. In North America, a barn refers to structures that house livestock, including cattle and horses, as well as equipment and fodder, and often grain. As a result, the term barn is often qualified e.g. tobacco barn, dairy barn, cow house, sheep barn, potato barn. In the British Isles, the term barn is restricted mainly to storage structures for unthreshed cereals and fodder, the terms byre or shippon being applied to cow shelters, whereas horses are kept in buildings known as stables. In mainland Europe, however, barns were often part of integrated structures known as byre-dwellings. In addition, barns may be used for equipment storage, as a covered workplace, and for activities such as threshing.

Timber framing and "post-and-beam" construction are traditional methods of building with heavy timbers, creating structures using squared-off and carefully fitted and joined timbers with joints secured by large wooden pegs. If the structural frame of load-bearing timber is left exposed on the exterior of the building it may be referred to as half-timbered, and in many cases the infill between timbers will be used for decorative effect. The country most known for this kind of architecture is Germany, where timber-framed houses are spread all over the country.

A joist is a horizontal structural member used in framing to span an open space, often between beams that subsequently transfer loads to vertical members. When incorporated into a floor framing system, joists serve to provide stiffness to the subfloor sheathing, allowing it to function as a horizontal diaphragm. Joists are often doubled or tripled, placed side by side, where conditions warrant, such as where wall partitions require support.

Meppen is a town in and the seat of the Emsland district of Lower Saxony, Germany, at the confluence of the Ems, Hase, and Nordradde rivers and the Dortmund–Ems Canal (DEK). The name stems from the word Mappe, meaning "delta".

A cruck or crook frame is a curved timber, one of a pair, which support the roof of a building, historically used in England and Wales. This type of timber framing consists of long, generally naturally curved, timber members that lean inwards and form the ridge of the roof. These posts are then generally secured by a horizontal beam which then forms an "A" shape. Several of these "crooks" are constructed on the ground and then lifted into position. They are then joined together by either solid walls or cross beams which aid in preventing 'racking'.

A saltbox house is a gable-roofed residential structure that is typically two stories in the front and one in the rear. It is a traditional New England style of home, originally timber framed, which takes its name from its resemblance to a wooden lidded box in which salt was once kept.

A purlin is a longitudinal, horizontal, structural member in a roof. In traditional timber framing there are three basic types of purlin: purlin plate, principal purlin, and common purlin.

Twist is a municipality in the Emsland district, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated directly on the Dutch border.

The Fairbanks House in Dedham, Massachusetts is a historic house built c. 1637, making it the oldest surviving timber-frame house in North America that has been verified by dendrochronology testing. Puritan settler Jonathan Fairbanks constructed the farm house for his wife Grace and their family. The house was occupied and then passed down through eight generations of the family until the early 20th century. Over several centuries the original portion was expanded as architectural styles changed and the family grew.
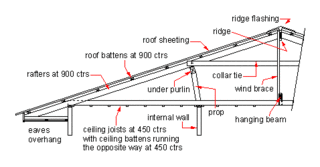
Domestic roof construction is the framing and roof covering which is found on most detached houses in cold and temperate climates. Such roofs are built with mostly timber, take a number of different shapes, and are covered with a variety of materials.

Belper North Mill, also known as Strutt's North Mill in Belper, is one of the Derwent Valley Mills, given UNESCO World Heritage Status in 2001.

A bressummer, breastsummer, summer beam is a load-bearing beam in a timber-framed building. The word summer derived from sumpter or French sommier, "a pack horse", meaning "bearing great burden or weight". "To support a superincumbent wall", "any beast of burden", and in this way is similar to a wall plate.

Icelandic turf houses are timber structures with turf walls and turf as a cover for the roof. Turf houses have been constructed since Iceland was settled in the 9th century. Turf houses were the product of a difficult climate, offering superior insulation compared to buildings solely made of wood or stone, and the relative difficulty in obtaining other construction materials in sufficient quantities.

First Period is an American architecture style originating between approximately 1626 and 1725, used primarily by British colonists during the settlement of the British colonies of North America, particularly in Massachusetts and Virginia. Among these cities, Essex County in Massachusetts has the highest amount of preserved First Period architecture buildings.

The Low German house or Fachhallenhaus is a type of timber-framed farmhouse found in northern Germany and the easternmost Netherlands, which combines living quarters, byre and barn under one roof. It is built as a large hall with bays on the sides for livestock and storage and with the living accommodation at one end.
The architecture of Iceland draws from Scandinavian influences and traditionally was influenced by the lack of native trees on the island. As a result, grass- and turf-covered houses were developed. Later on, the Swiss chalet style became a prevailing influence in Icelandic architecture as many timber buildings were constructed in this way. Stone and later concrete were popular building materials, the latter especially with the arrival of functionalism in the country. Contemporary architecture in Iceland is influenced by many sources, with styles varying greatly around the country.

The John Scott Farm is a historic farmstead near the community of Shandon, Ohio, United States. Established in the nineteenth century and still in operation in the twenty-first, the farmstead has been named a historic site because of its traditionally built agricultural structures.

The Winsen Museum Farm is an open-air museum in Winsen (Aller) in the north German state of Lower Saxony. It was started in 1982 and comprises a typical farmyard from the southern Lüneburg Heath around which other buildings, characteristic of the region, are grouped.

American historic carpentry is the historic methods with which wooden buildings were built in what is now the United States since European settlement. A number of methods were used to form the wooden walls and the types of structural carpentry are often defined by the wall, floor, and roof construction such as log, timber framed, balloon framed, or stacked plank. Some types of historic houses are called plank houses but plank house has several meanings which are discussed below. Roofs were almost always framed with wood, sometimes with timber roof trusses. Stone and brick buildings also have some wood framing for floors, interior walls and roofs.