
The Namdapha flying squirrel is an arboreal, nocturnal flying squirrel endemic to Arunachal Pradesh in northeast India, where it is known from a single specimen collected in Namdapha National Park in 1981. No population estimate is available for B. biswasi, but the known habitat is tall Mesua ferrea jungles, often on hill slopes in the catchment area of Dihing River in northeastern India.

Callosciurus is a genus of squirrels collectively referred to as the "beautiful squirrels". They are found mainly in Southeast Asia, though a few species also occur in Nepal, northeastern India, Bangladesh and southern China. Several of the species have settled on islands. In total, the genus contains 15 species and numerous varieties and subspecies. The genera Glyphotes, Rubrisciurus, and Tamiops have sometimes been included in Callosciurus.

Pachliopta jophon, the Ceylon rose or Sri Lankan rose, is a butterfly found in Sri Lanka that belongs to the swallowtail family. It was earlier classified as a subspecies of Pachliopta hector, the crimson rose.
This article is a list of biological species, subspecies, and evolutionary significant units that are known to have become extinct during the Holocene, the current geologic epoch, ordered by their known or approximate date of disappearance from oldest to most recent.
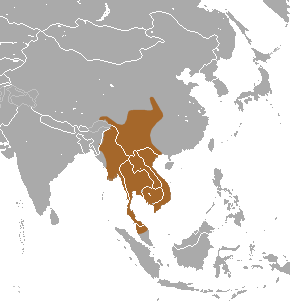
The Southeast Asian shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is found in Cambodia, India, China, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Thailand, and Vietnam.
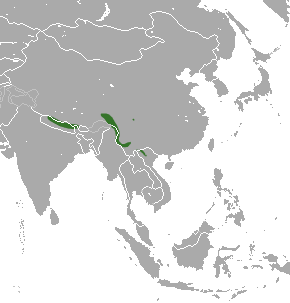
The long-tailed brown-toothed shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is found in China, India, Myanmar, Nepal, and Vietnam.

The East Asian tailless leaf-nosed bat or tail-less leaf-nosed bat is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae.

Partula taeniata, common name the Moorean viviparous tree snail, is a species of terrestrial gastropod in the Partulidae family. It is endemic to French Polynesia.
Heliodiaptomus pulcher is a species of copepod in the family Diaptomidae. It is endemic to India.
Neodiaptomus is a genus of freshwater copepods in the family Diaptomidae. It contains the following species, four of which are listed as vulnerable species on the IUCN Red List :
Tropodiaptomus is a genus of copepods in the family Diaptomidae. It includes the following species, many of which are narrow endemics and are included on the IUCN Red List :

Aquilaria malaccensis is a species of plant in the Thymelaeaceae family. It is found in Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand. It is threatened by habitat loss.

The Paradoxurinae are a subfamily of the viverrids that was denominated and first described by John Edward Gray in 1864. Pocock subordinated the oriental genera Paradoxurus, Paguma and Arctictis to this subfamily.
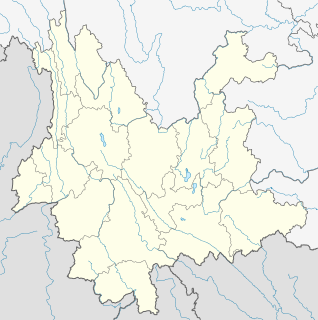
Fuxian Lake stretches out through Chengjiang, Jiangchuan and Huaning Counties in Yunnan Province, spanning an area of 212 square kilometers. The lake is ranked third-largest in Yunnan, after Dian Lake and Erhai Lake. Also the deepest lake in Yunnan, it is 155 meters deep at its greatest depth. It is also the third-deepest fresh water lake in China, after Tianchi and Kanas Lake.










