
The Otranto Barrage was an Allied naval blockade of the Strait of Otranto between Brindisi in Italy and Corfu on the Greek side of the Adriatic Sea in the First World War. The operation consisted of over 200 vessels at the height of the blockade. The blockade was intended to prevent the Austro-Hungarian Navy from escaping into the Mediterranean and threatening Allied operations there. The blockade was effective in preventing surface ships from escaping the Adriatic, but it had little or no effect on the submarines based at Cattaro.

The Enemy Below is a 1957 American DeLuxe Color war film in CinemaScope about a battle between an American destroyer escort and a German U-boat during World War II. It stars Robert Mitchum and Curd Jürgens as the American and German commanding officers, respectively. Produced and directed by Dick Powell, the film was based on the 1956 novel of the same name by Denys Rayner, a British naval officer involved in antisubmarine warfare throughout the Battle of the Atlantic.

USS Cobia (SS/AGSS-245) is a Gato-class submarine, formerly of the United States Navy, named for the cobia.

USS Moody (DD-277) was a Clemson-class destroyer in the United States Navy in commission from 1919 to 1922 and from 1923 to 1930. She was named for Secretary of the Navy (and future Supreme Court Justice} William Henry Moody.

Edward Ellsberg, OBE was an officer in the United States Navy and a popular author. He was widely known as "Commander Ellsberg".
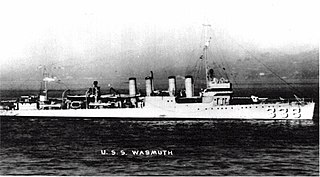
USS Wasmuth (DD-338/DMS-15) was a Clemson-class destroyer in the United States Navy following World War I.

Madge Evans was an American stage, film, radio, and television actress. She began her career as a child performer and model.

USS Harry F. Bauer (DD-738/DM-26/MMD-26) was a Robert H. Smith-class destroyer minelayer in the United States Navy. She was named for Lieutenant Commander Harry F. Bauer (1904–1942).

HMS M3, built by Armstrong Whitworth, Newcastle Upon Tyne was an M-class submarine of the Royal Navy.

The Navy of the Independent State of Croatia, was the navy of the Independent State of Croatia, an Axis puppet state controlled by the fascist Ustaše party. The NDH was created from parts of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia on 10 April 1941, four days after the World War II invasion of Yugoslavia by the Axis powers commenced. The RMNDH consisted of two commands, the Coast and Maritime Traffic Command, and the River and River Traffic Command, and had its headquarters in the NDH capital, Zagreb. The Coast and Maritime Traffic Command consisted of three naval commands along the Adriatic coast, which were each divided into a number of naval districts. The naval districts consisted mainly of naval and weather stations, and were only responsible for coast guard and customs duties. The River and River Traffic Command consisted of seven river stations, a naval infantry battalion, and a River Command Flotilla built around two former Yugoslav river monitors, which had been scuttled during the invasion but subsequently refloated.

Nereide was a Nautilus-class submarine in the Italian Royal Navy during World War I. She was built 1911–1913 at the navy yard at Venice and was sunk in 1915 by the Austro-Hungarian submarine U-5 under the command of Georg Ritter von Trapp. Nereide's captain, Carlo del Greco posthumously received the Medaglia d'Oro al Valore Militare for his actions when Nereide was sunk.

The Royal Navy, commonly known as the Royal Yugoslav Navy, was the naval warfare service branch of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. It was brought into existence in 1921, and initially consisted of a few former Austro-Hungarian Navy vessels surrendered at the conclusion of World War I and transferred to the new nation state under the terms of the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye. The only modern sea-going warships transferred to the new state were twelve steam-powered torpedo boats, although it did receive four capable river monitors for use on the Danube and other large rivers. Significant new acquisitions began in 1926 with a former German light cruiser, followed by the commissioning of two motor torpedo boats (MTBs) and a small submarine flotilla over the next few years. When the name of the state was changed to Yugoslavia in 1929, the name of its navy was changed to reflect this. In the late 1920s, several of the original vessels were discarded.
SM UC-12 was a German Type UC I minelayer submarine or U-boat in the German Imperial Navy during World War I.

The Adriatic campaign of World War II was a minor naval campaign fought during World War II between the Greek, Yugoslavian and Italian navies, the Kriegsmarine, and the Mediterranean squadrons of the United Kingdom, France, and the Yugoslav Partisan naval forces. Considered a somewhat insignificant part of the naval warfare in World War II, it nonetheless saw interesting developments, given the specificity of the Dalmatian coastline.

Roma was an Italian pre-dreadnought battleship, laid down in 1903, launched in 1907 and completed in 1908. She was the third member of the Regina Elena class, which included three other vessels: Regina Elena, Napoli, and Vittorio Emanuele. Roma was armed with a main battery of two 305 mm (12 in) guns and twelve 203 mm (8 in) guns. She was quite fast for the period, with a top speed of nearly 21 knots.

Commander James Wiggins "Red" Coe (missing), January 8, 1946 was an American submariner. A submarine ace, Coe commanded USS Skipjack and Cisco during operations in the Pacific theatre of World War II. After a number of successful patrols, Coe and the Cisco failed to return from patrol in November 1943, and her captain and crew were presumed dead in 1946.

Made on Broadway is a 1933 American pre-Code comedy film directed by Harry Beaumont and written by Courtney Terrett. The film stars Robert Montgomery, Sally Eilers, Madge Evans, Eugene Pallette, C. Henry Gordon and Jean Parker. The film was released on May 19, 1933, by Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer.

Renaudin was one of six Bisson-class destroyers built for the French Navy during the early 1910s. Completed in 1913, the ship was assigned to the 1st Naval Army in the Mediterranean Sea. During the First World War, she escorted the battle fleet during the Battle of Antivari in August 1914 and escorted multiple convoys to Montenegro for the rest of the year. Renaudin helped to sink a crippled Austro-Hungarian destroyer during the 1st Battle of Durazzo in late 1915 and protected the evacuation of the Royal Serbian Army from Durazzo, Albania, in February 1916. The ship was sunk by an Austro-Hungarian submarine the following month with the loss of 50 crewmen.

The Albona class were mine warfare ships used by the Italian Regia Marina and Royal Yugoslav Navy. Fourteen ships were originally laid down between 1917 and 1918 for the Austro-Hungarian Navy as the MT.130 class. However, the end of World War I and the dissolution of Austria-Hungary left them incomplete until 1920, when three ships were finished for the Regia Marina. These ships were armed with two 76 mm (3 in) guns. An additional five ships were completed for the KM in 1931 as the Malinska or Marjan class, and were armed with a single 66 mm (2.6 in). All of the completed ships could carry 24 to 39 naval mines. The remaining ships were never completed.

T5 was a sea-going torpedo boat operated by the Royal Yugoslav Navy between 1921 and 1941. Originally 87 F, a 250t-class torpedo boat of the Austro-Hungarian Navy built in 1914–1915, she was armed with two 66 mm (2.6 in) guns and four 450 mm (17.7 in) torpedo tubes, and could carry 10–12 naval mines. She saw active service during World War I, performing convoy, patrol, escort and minesweeping tasks, anti-submarine operations and shore bombardment missions. In 1917 the suffixes of all Austro-Hungarian torpedo boats were removed, and thereafter she was referred to as 87. She was part of the escort force for the Austro-Hungarian dreadnought Szent István during the action that resulted in the sinking of that ship by Italian torpedo boats in June 1918, and rescued many of her crew.



















