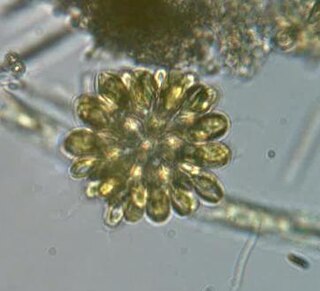
The synurids are a small group of heterokont algae, found mostly in freshwater environments, characterized by cells covered in silica scales.

Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg was a German naturalist, zoologist, comparative anatomist, geologist, and microscopist. Ehrenberg was an evangelist and was considered to be of the most famous and productive scientists of his time.
Wilhelm Friedrich Hemprich was a German naturalist and explorer.

Johann Christoph Friedrich Klug, was a German entomologist. He described the butterflies and some other insects of Upper Egypt and Arabia in Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg and Wilhelm Friedrich Hemprich's Symbolæ Physicæ. He was professor of medicine and entomology in the University of Berlin where he curated the insect collections from 1810 to 1856. At the same time he directed the Botanic Garden in Berlin which contains his collections. Klug worked mainly on Hymenoptera and Coleoptera. The plant genus Klugia was named in his honour as well as the butterflies Geitoneura klugii and Heliophisma klugii.

Fattail scorpion or fat-tailed scorpion is the common name given to scorpions of the genus Androctonus, one of the most dangerous groups of scorpion species in the world. The genus was first described in 1828 by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg.

The sebae anemone, also known as leathery sea anemone, long tentacle anemone, or purple tip anemone, is a species of sea anemone belonging to the family Stichodactylidae and native to the Indo-Pacific area.

The pulsating xenid is a species of soft coral in the family Xeniidae. The species was first described in 1834 by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg as Xenia fuscescens.

The sooty gull is a species of gull in the family Laridae, also known as the Aden gull or Hemprich's gull. It is found in Bahrain, Djibouti, Egypt, Eritrea, India, Iran, Israel, Jordan, Kenya, Lebanon, Maldives, Mozambique, Oman, Pakistan, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Somalia, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Tanzania, United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. As is the case with many gulls, it has traditionally been placed in the genus Larus. The sooty gull is named in honour of the German naturalist Wilhelm Hemprich who died in 1825 while on a scientific expedition to Egypt and the Middle East with his friend Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg.

Actinocyclus is a genus of sea slugs, dorid nudibranchs, shell-less marine gastropod molluscs in the family Actinocyclidae, and was first described by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg in 1831.

Rhodactis is genus of Mushroom corals which are characterized by large individual polyps that are often reminiscent of a mushroom. Rhodactis are related to stony corals but do not produce a stony skeleton.

Lophoceros is a genus of birds in the hornbill family, Bucerotidae, which are native to Africa.
The genus Bacterium was a taxon described in 1828 by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg. The type species was later changed from Bacterium triloculare to Bacterium coli as it was lost. In 1951 and then in 1954 it was recognised as a nomen generum rejiciendum, which means a generic name to be rejected; this also applied to its family Bacteriaceae.

Lobophyllia hemprichii, commonly called lobed brain coral, lobed cactus coral or largebrain root coral, is a species of large polyp stony coral in the family Lobophylliidae. It is found in the Indo-Pacific Ocean. In its specific name Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg honoured his late partner the Prussian naturalist Wilhelm Hemprich; they were among the first to study the marine life of the Red Sea.

Acropora millepora is a species of branching stony coral native to the western Indo-Pacific where it is found in shallow water from the east coast of Africa to the coasts of Japan and Australia. It was first described in 1834 by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg as Heteropora millepora.

Anemonia is a genus of sea anemones belonging to the family Actiniidae.

Acropora hemprichii is a species of acroporid coral that was first described by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg in 1834. It lives in reefs at depths of 3 to 15 m for between 13 and 24 years. The species is listed as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, and has a decreasing population. It is common with a wide range, and is listed on Appendix II of CITES.
Gyrosmilia is a monotypic genus of large polyp stony coral. It is represented by a single species, Gyrosmilia interrupta. It was first described by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg in 1834 as Manicina interrupta.
Anthopleura stellula is a species of sea anemone in the family Actiniidae. It was first described in 1834 by Wilhelm Hemprich and Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg as Actinia (Isacmaea) stellula. It is found in the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea, and is unusual among sea anemones in that it can divide itself in two transversely.

Heterodactyla hemprichii is a species of sea anemone in the family Thalassianthidae, and was first formally described in 1834 by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg.

Favites halicora is a species of coral belonging to the family Merulinidae. The species was first described in 1834 by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg as Astraea halicora.
















