
Oscillatoria is a genus of sugar making microscopic creatures.
Oocystaceae is a family of green algae, in the order Chlorellales. The type genus is Oocystis.

Kirchneriella is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae. It is found in freshwater habitats, as phytoplankton or metaphyton.

Scytonema is a genus of photosynthetic cyanobacteria that contains over 100 species. It grows in filaments that form dark mats. Many species are aquatic and are either free-floating or grow attached to a submerged substrate, while others species grow on terrestrial rocks, wood, soil, or plants. Scytonema is a nitrogen fixer, and can provide fixed nitrogen to the leaves of plants on which it is growing. Some species of Scytonema form a symbiotic relationship with fungi to produce a lichen.

Planktothrix is a diverse genus of filamentous cyanobacteria observed to amass in algal blooms in water ecosystems across the globe. Like all Oscillatoriales, Planktothrix species have no heterocysts and no akinetes. Planktothrix are unique because they have trichomes and contain gas vacuoles unlike typical planktonic organisms. Previously, some species of the taxon were grouped within the genus Oscillatoria, but recent work has defined Planktothrix as its own genus. A tremendous body of work on Planktothrix ecology and physiology has been done by Anthony E. Walsby, and the 55.6 kb microcystin synthetase gene which gives these organisms the ability to synthesize toxins has been sequenced. P. agardhii is an example of a type species of the genus. P. agardhii and P. rubescens are commonly observed in lakes of the Northern Hemisphere where they are known producers of potent hepatotoxins called microcystins.
Ernst Johann Lemmermann was a German botanist who specialized in the field of phycology.

The Pseudanabaenaceae are a family of cyanobacteria.
Anathece is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Synechococcaceae.
Eucapsis is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Merismopediaceae.
Geitlerinema is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Coleofasciculaceae.
Gloeocapsopsis is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Chroococcaceae.

Aphanothece is a polyphyletic genus with 63 accepted species. The name is derived from the Greek words, ‘aphanes’ and ‘theke’ which mean “invisible" and “box or sheath” respectively. This genera is cosmopolitan, found in soils, thermal springs and other benthic, freshwater, marine, hypersaline, and moist terrestrial environments. Morphology can vary, with both microscopic and macroscopic colonies large enough to be collected and preserved in herbarium records.

Chamaesiphon is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Chamaesiphonaceae.
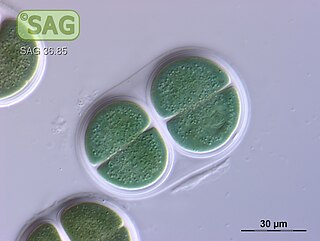
Chroococcus is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Chroococcaceae.
Cyanodictyon is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Synechococcaceae.
Jaaginema is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Pseudanabaenaceae.
Komvophoron is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Borziaceae.
Lemmermanniella is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Synechococcaceae.
Limnococcus is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Chroococcaceae.
Phormidium aerugineo-caeruleum is a species of cyanobacteria in the genus Phormidium.







