
Dendrobranchiata is a suborder of decapods, commonly known as prawns. There are 540 extant species in seven families, and a fossil record extending back to the Devonian. They differ from related animals, such as Caridea and Stenopodidea, by the branching form of the gills and by the fact that they do not brood their eggs, but release them directly into the water. They may reach a length of over 330 millimetres (13 in) and a mass of 450 grams (1.0 lb), and are widely fished and farmed for human consumption.

Whiteleg shrimp, also known as Pacific white shrimp or King prawn, is a species of prawn of the eastern Pacific Ocean commonly caught or farmed for food.

The Indian prawn, is one of the major commercial prawn species of the world. It is found in the Indo-West Pacific from eastern and south-eastern Africa, through India, Malaysia and Indonesia to southern China and northern Australia. Adult shrimp grow to a length of about 22 cm (9 in) and live on the seabed to depths of about 90 m (300 ft). The early developmental stages take place in the sea before the larvae move into estuaries. They return to the sea as sub-adults.
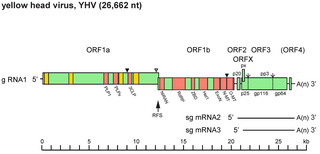
Okavirus is a genus of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which infect crustaceans. Host organisms are mostly shrimp. It is the only genus in the family Roniviridae. Viruses associated with the genus include: gill-associated virus (GAV) which causes reddening, biofouling with exoparasites, emaciation, and massive mortality; and yellow head virus (YHV) which causes yellow head, arrest of feeding, and massive mortality. The name is derived from the 'Oka' or lymphoid organ in which the viruses are commonly detected and in which pathology occurs during acute infections. Lymphoid organs are anatomical structures common to penaeid shrimp. There are three species in this genus.

The shrimp fishery is a major global industry, with more than 3.4 million tons caught per year, chiefly in Asia. Rates of bycatch are unusually high for shrimp fishing, with the capture of sea turtles being especially contentious.

A freshwater prawn farm is an aquaculture business designed to raise and produce freshwater prawns or shrimp for human consumption. Freshwater prawn farming shares many characteristics with, and many of the same problems as, marine shrimp farming. Unique problems are introduced by the developmental life cycle of the main species.
White spot syndrome (WSS) is a viral infection of penaeid shrimp. The disease is highly lethal and contagious, killing shrimp quickly. Outbreaks of this disease have wiped out the entire populations of many shrimp farms within a few days, in places throughout the world.

Shrimp farming is an aquaculture business that exists in either a marine or freshwater environment, producing shrimp or prawns for human consumption.

Macrobrachium rosenbergii, also known as the giant river prawn or giant freshwater prawn, is a commercially important species of palaemonid freshwater prawn. It is found throughout the tropical and subtropical areas of the Indo-Pacific region, from India to Southeast Asia and Northern Australia. The giant freshwater prawn has also been introduced to parts of Africa, Thailand, China, Japan, New Zealand, the Americas, and the Caribbean. It is one of the biggest freshwater prawns in the world, and is widely cultivated in several countries for food. While M. rosenbergii is considered a freshwater species, the larval stage of the animal depends on brackish water. Once the individual shrimp has grown beyond the planktonic stage and becomes a juvenile, it lives entirely in fresh water.

Penaeidae is a family of marine crustaceans in the suborder Dendrobranchiata, which are often referred to as penaeid shrimp or penaeid prawns. The Penaeidae contain many species of economic importance, such as the tiger prawn, whiteleg shrimp, Atlantic white shrimp, and Indian prawn. Many prawns are the subject of commercial fishery, and farming, both in marine settings, and in freshwater farms. Lateral line–like sense organs on the antennae have been reported in some species of Penaeidae. At 210 metres per second (760 km/h), the myelinated giant interneurons of pelagic penaeid shrimp have the world record for impulse conduction speed in any animal.

The Little Rann of Kutch is a salt marsh which is part of the Rann of Kutch in Kutch district, Gujarat, India.

Penaeus monodon, commonly known as the giant tiger prawn, Asian tiger shrimp, black tiger shrimp, and other names, is a marine crustacean that is widely reared for food.

Acetes is a genus of small shrimp that resemble krill, which is native to the western and central Indo-Pacific, the Atlantic coast of the Americas, Pacific coast of South America and inland waters of South America. Although most are from marine or estuarine habitats, the South American A. paraguayensis is a fresh water species. Several of its species are important for the production of shrimp paste in Southeast Asia, including A. japonicus, which is the world's most heavily fished species of wild shrimp or prawn in terms of total tonnage.

Palaemon serratus, also called the common prawn, is a species of shrimp found in the Atlantic Ocean from Denmark to Mauritania, and in the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea.

Penaeus esculentus is a species of prawn which is widely fished for consumption around Australia.

Shrimp are decapod crustaceans with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata. More narrow definitions may be restricted to Caridea, to smaller species of either group or to only the marine species. Under a broader definition, shrimp may be synonymous with prawn, covering stalk-eyed swimming crustaceans with long, narrow muscular tails (abdomens), long whiskers (antennae), and slender legs. Any small crustacean which resembles a shrimp tends to be called one. They swim forward by paddling with swimmerets on the underside of their abdomens, although their escape response is typically repeated flicks with the tail driving them backwards very quickly. Crabs and lobsters have strong walking legs, whereas shrimp have thin, fragile legs which they use primarily for perching.

Prawn is a common name for small aquatic crustaceans with an exoskeleton and ten legs, some of which can be eaten.

Kayamkulam Kayal, Kayamkulam Lake or Kayamkulam Estuary is a shallow brackish water lagoon streaching between Panmana and Karthikapally. It has an outlet to the Arabian sea at Kayamkulam barrage. The Kayal used to be connected to the sea most of the time except during dry season when a bar like formation separates it from the sea. Now the bar has been opened up permanently for construction of Kayamkulam Fishing Harbor. Kayamkulam boat race is conducted in Kayamkulam Kayal.

Rujak or Rojak is a salad dish of Javanese origin, commonly found in Indonesia, Malaysia and Singapore. The most popular variant in all three countries is a salad composed of a mixture of sliced fruit and vegetables served with a spicy palm sugar dressing. It is often described as tangy and spicy fruit salad due to its sweet, hot and spicy dressing made from ground chilli, palm sugar and peanuts.















