
Penguins are a group of aquatic flightless birds from the family Spheniscidae of the order Sphenisciformes. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere: only one species, the Galápagos penguin, is found north of the Equator. Highly adapted for life in the ocean water, penguins have countershaded dark and white plumage and flippers for swimming. Most penguins feed on krill, fish, squid and other forms of sea life which they catch with their bills and swallow whole while swimming. A penguin has a spiny tongue and powerful jaws to grip slippery prey.

The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the status of the natural world and the measures needed to safeguard it. It is involved in data gathering and analysis, research, field projects, advocacy, and education. IUCN's mission is to "influence, encourage and assist societies throughout the world to conserve nature and to ensure that any use of natural resources is equitable and ecologically sustainable".

The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is an inventory of the global conservation status and extinction risk of biological species. A series of Regional Red Lists, which assess the risk of extinction to species within a political management unit, are also produced by countries and organizations.

Accipiter is a genus of birds of prey in the family Accipitridae. With 49 recognized species it is the most diverse genus in its family. Most species are called goshawks or sparrowhawks, although with the exception of the American goshawk almost all New World species are simply known as "hawks". They can be anatomically distinguished from their relatives by the lack of a procoracoid foramen. Two small and aberrant species usually placed here do possess a large procoracoid foramen and are also distinct as regards DNA sequence. They may warrant separation in the old genus Hieraspiza.

The conservation status of a group of organisms indicates whether the group still exists and how likely the group is to become extinct in the near future. Many factors are taken into account when assessing conservation status: not simply the number of individuals remaining, but the overall increase or decrease in the population over time, breeding success rates, and known threats. Various systems of conservation status are in use at international, multi-country, national and local levels, as well as for consumer use such as sustainable seafood advisory lists and certification. The two international systems are by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES).

NatureServe, Inc. is a non-profit organization based in Arlington County, Virginia, US, that provides proprietary wildlife conservation-related data, tools, and services to private and government clients, partner organizations, and the public. NatureServe reports being "headquartered in Arlington, Virginia, with regional offices in four U.S. locations and in Canada." In calendar year 2011 they reported having 86 employees, 6 volunteers, and 15 independent officers.

The Pantherinae is a subfamily of the Felidae; it was named and first described by Reginald Innes Pocock in 1917 as only including the Panthera species. The Pantherinae genetically diverged from a common ancestor between 9.32 to 4.47 million years ago and 10.67 to 3.76 million years ago.

A genet is a member of the genus Genetta, which consists of 17 species of small African carnivorans. The common genet is the only genet present in Europe and occurs in the Iberian Peninsula, Italy and France.

An IUCN Red List Critically Endangered species is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as facing an extremely high risk of extinction in the wild. As of December 2023, of the 157,190 species currently on the IUCN Red List, 9,760 of those are listed as Critically Endangered, with 1,302 being possibly extinct and 67 possibly extinct in the wild.
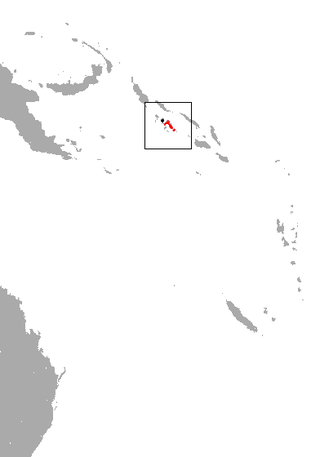
The New Georgian monkey-faced bat or New Georgian flying monkey is a recently described species of megabat endemic to the New Georgia and Vangunu Islands. It is presumably extinct on Kolombangara Island, and the remaining populations on other islands are threatened by habitat loss and hunting. Consequently, it is considered vulnerable by the IUCN. In 2013, Bat Conservation International listed this species as one of the 35 species of its worldwide priority list of conservation.

The Makira flying fox is a species of megabat in the genus Pteropus, found in the Solomon Islands. The species is currently decreasing and is endangered due to threats from logging and hunting. In 2013, Bat Conservation International listed this species as one of the 35 species of its worldwide priority list of conservation.

The World's 25 Most Endangered Primates is a list of highly endangered primate species selected and published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Species Survival Commission (SSC) Primate Specialist Group (PSG), the International Primatological Society (IPS), Global Wildlife Conservation (GWC), and Bristol Zoological Society (BZS). The IUCN/SSC PSG worked with Conservation International (CI) to start the list in 2000, but in 2002, during the 19th Congress of the International Primatological Society, primatologists reviewed and debated the list, resulting in the 2002–2004 revision and the endorsement of the IPS. The publication was a joint project between the three conservation organizations until the 2012–2014 list when BZS was added as a publisher. The 2018–2020 list was the first time Conservation International was not among the publishers, replaced instead by GWC. The list has been revised every two years following the biannual Congress of the IPS. Starting with the 2004–2006 report, the title changed to "Primates in Peril: The World's 25 Most Endangered Primates". That same year, the list began to provide information about each species, including their conservation status and the threats they face in the wild. The species text is written in collaboration with experts from the field, with 60 people contributing to the 2006–2008 report and 85 people contributing to the 2008–2010 report. The 2004–2006 and 2006–2008 reports were published in the IUCN/SSC PSG journal Primate Conservation,, since then they have been published as independent publications.

Nepenthes alzapan is a tropical pitcher plant native to the Philippine island of Luzon. It is known from only a handful of herbarium specimens collected in 1925 from submontane mossy forest at an elevation of 1800 m above sea level. It is closely allied to N. bellii and has similarly diminutive pitchers.
Himantolophus cornifer is a species of footballfish, a type of anglerfish. The fish is bathypelagic and can be found at depths ranging from 0 to 1,900 metres. It has been found in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic Oceans.
Odontella cornifer is a species of springtail in the family Odontellidae.












