
Saltopus is a genus of very small bipedal dinosauriform containing the single species Saltopus elginensis from the late Triassic period of Scotland. It is one of the most famous Elgin Reptiles.
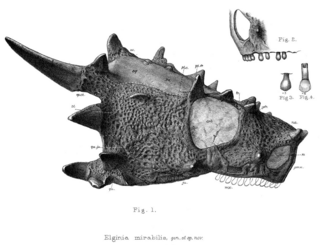
Elginia is an extinct genus of pareiasaurid known from the Late Permian of Scotland and China. It was named for the area around Elgin in Scotland, which has yielded many fossils referred to as the Elgin Reptiles.

The New Red Sandstone, chiefly in British geology, is composed of beds of red sandstone and associated rocks laid down throughout the Permian to the end of the Triassic, that underlie the Jurassic-Triassic age Penarth Group. The name distinguishes it from the Old Red Sandstone which is largely Devonian in age, and with which it was originally confused due to their similar composition.

The Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone is a tetrapod assemblage zone or biozone which correlates to the middle Abrahamskraal Formation, Adelaide Subgroup of the Beaufort Group, a fossiliferous and geologically important geological Group of the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa. The thickest outcrops, reaching approximately 2,000 metres (6,600 ft), occur from Merweville and Leeu-Gamka in its southernmost exposures, from Sutherland through to Beaufort West where outcrops start to only be found in the south-east, north of Oudshoorn and Willowmore, reaching up to areas south of Graaff-Reinet. Its northernmost exposures occur around the towns Fraserburg and Victoria West. The Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone is the second biozone of the Beaufort Group.
The Fremouw Formation is a Triassic-age rock formation in the Transantarctic Mountains of Antarctica. It contains the oldest known fossils of tetrapods from Antarctica, including synapsids, reptiles and amphibians. Fossilized trees have also been found. The formation's beds were deposited along the banks of rivers and on floodplains. During the Triassic, the area would have been a riparian forest at 70–75°S latitude.

Leptopleuron is an extinct genus of procolophonid that lived in the dry lands during the late Triassic in Elgin of northern Scotland and was the first to be included in the clade of Procolophonidae. First described by English paleontologist and biologist Sir Richard Owen, Leptopleuron is derived from two Greek bases, leptos for "slender" and pleuron for "rib," describing it as having slender ribs. The fossil is also known by a second name, Telerpeton, which is derived from the Greek bases tele for "far off" and herpeton for "reptile." In Scotland, Leptopleuron was found specifically in the Lossiemouth Sandstone Formation. The yellow sandstone it was located in was poorly lithified with wind coming from the southwest. The environment is also described to consist of barchan dunes due to the winds, ranging up to 20 m tall that spread during dry phases into flood plains. Procolophonoids such as Leptopleuron were considered an essential addition to the terrestrial ecosystem during the Triassic.

Brachyrhinodon is an extinct genus of sphenodontian from the Late Triassic Lossiemouth Sandstone of Scotland.
The Chañares Formation is a Carnian-age geologic formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin, located in La Rioja Province, Argentina. It is characterized by drab-colored fine-grained volcaniclastic claystones, siltstones, and sandstones which were deposited in a fluvial to lacustrine environment. The formation is most prominently exposed within Talampaya National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site within La Rioja Province.

Geikia is an extinct genus of dicynodont therapsids from the late Permian. The abundance and diversity of dicynodonts during this period, combined with incomplete or inadequately prepared specimens, have led to challenges in determining relationships within this taxon. Only two species, Geikia locusticeps and Geikia elginensis have been assigned to this genus. While this is the currently accepted classification, fossil record limitations have led to repeated debate on the genus assignments of these species.

Gordonia is an extinct genus of dicynodont therapsid from the Late Permian of Scotland. Fossils have been found from the Elgin sandstone of Cutties Hillock Sandstone in Elgin, Moray. These are among the many amniote fossils referred to as the Elgin Reptiles. Gordonia was named in 1893 with four species: G. traquairi, G. duffiana, G. huxleyana, and G. juddiana. Currently, the only recognized species is the type G. traquairi. All other species are considered synonyms of the type.

The Manda Formation is a Middle Triassic (Anisian?) or possibly Late Triassic (Carnian?) geologic formation in Tanzania. It preserves fossils of many terrestrial vertebrates from the Triassic, including some of the earliest dinosauromorph archosaurs. The formation is often considered to be Anisian in age according to general tetrapod biochronology hypotheses and correlations to the Cynognathus Assemblage Zone of South Africa. However, some recent studies cast doubt to this age, suggesting that parts deposits may actually be younger (Carnian) in age.
Paleontology in Virginia refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Virginia. The geologic column in Virginia spans from the Cambrian to the Quaternary. During the early part of the Paleozoic, Virginia was covered by a warm shallow sea. This sea would come to be inhabited by creatures like brachiopods, bryozoans, corals, and nautiloids. The state was briefly out of the sea during the Ordovician, but by the Silurian it was once again submerged. During this second period of inundation the state was home to brachiopods, trilobites and entire reef systems. During the mid-to-late Carboniferous the state gradually became a swampy environment.
Paleontology in Colorado refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Colorado. The geologic column of Colorado spans about one third of Earth's history. Fossils can be found almost everywhere in the state but are not evenly distributed among all the ages of the state's rocks. During the early Paleozoic, Colorado was covered by a warm shallow sea that would come to be home to creatures like brachiopods, conodonts, ostracoderms, sharks and trilobites. This sea withdrew from the state between the Silurian and early Devonian leaving a gap in the local rock record. It returned during the Carboniferous. Areas of the state not submerged were richly vegetated and inhabited by amphibians that left behind footprints that would later fossilize. During the Permian, the sea withdrew and alluvial fans and sand dunes spread across the state. Many trace fossils are known from these deposits.

The Usili Formation is a Late Permian geologic formation in Tanzania. It preserves fossils of many terrestrial vertebrates from the Permian, including temnospondyls, pareiasaurs, therapsids and the archosauromorph Aenigmastropheus.
Elgin Reptiles is the name given to the Permian and Triassic fossils found in the sandstone deposits in and around the town of Elgin, in Moray, Scotland. They are of historical and scientific importance, and many of the specimens are housed in the Elgin Museum, and some in the Hunterian in Glasgow, and the National Museum of Scotland in Edinburgh. The Elgin Reptiles include the dinosauriform Saltopus elginensis, the dicynodont Gordonia, and the pareiasaur Elginia. There are also many footprints and tail-drags associated with the same Permian and Triassic sandstone deposits.

The Teekloof Formation is a geological formation that forms part of the Beaufort Group, one of the five geological groups that comprises the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa. The Teekloof Formation is the uppermost formation of Adelaide Subgroup deposits West of 24ºE and contains Middle to Late Permian-aged deposits and four biozones of the Beaufort Group. It overlies the Abrahamskraal Formation. The Teekloof Formation does not underlie other units other than the younger Karoo dolerites and sills that relate to the emplacement of the Early Jurassic Drakensberg Group to the east. Outcrops and exposures of the Teekloof Formation range from Sutherland through the mountain escarpments between Fraserburg and Beaufort West. The northernmost localities of the Teekloof Formation are found by Loxton, Victoria West and Richmond.
The Ntawere Formation is a Middle Triassic (Anisian) geological formation in Zambia, preserving fossils of synapsids, archosaurs, and temnospondyls.
The Lashly Formation is a Late Triassic (Carnian) geologic formation in Victoria Land of Antarctica. The formation has provided fossil flora and indeterminate reptiles and dicynodonts.
Taoheodon is an extinct genus of dicynodont therapsid from the Sunjiagou Formation in the Shanxi province of China, dated to the Wuchiapingian age of the Late Permian. Its type and only known species is T. baizhijuni. Taoheodon was a close relative of the well known Dicynodon, and may represent a biogeographical link between the South African Dicynodon and similar dicynodonts found in Laos.
The Sunjiagou Formation is a geological formation in Shanxi, China. It is of Lopingian age. The lower and middle parts of the formation consists of intensely bioturbated fine grained sandstones and thinly interbedded mudstones, deposited in a shallow-shore lake depositional environment, while the upper part consists of fine grained sandstone, siltstone and mudstone. Alongside the Naobaogou Formation, it has provided an important vertebrate fauna.












