
Multituberculata is an extinct taxon of rodent-like allotherian mammals that existed for approximately 166 million years, the longest fossil history of any mammal lineage. They eventually declined from the late Paleocene onwards, disappearing from the known fossil record in the late Eocene, though gondwanatheres lived into the Miocene, and may have been multituberculates. More than 200 species are known, ranging from mouse-sized to beaver-sized. These species occupied a diversity of ecological niches, ranging from burrow-dwelling to squirrel-like arborealism to jerboa-like hoppers. Multituberculates are usually placed as crown mammals outside either of the two main groups of living mammals—Theria, including placentals and marsupials, and Monotremata—but closer to Theria than to monotremes. Nonetheless, at least one study found a potential status as sister taxa to monotremes/Australosphenida.
Plagiaulacida is a group of extinct multituberculate mammals. Multituberculates were among the most common mammals of the Mesozoic, "the age of the dinosaurs". Plagiaulacids, an informal suborder, are the most basal of this order, and ranged from the Middle Jurassic Period to the Lower Cretaceous Period of the northern hemisphere.

Oligochaeta is a subclass of animals in the phylum Annelida, which is made up of many types of aquatic and terrestrial worms, including all of the various earthworms. Specifically, oligochaetes comprise the terrestrial megadrile earthworms, and freshwater or semiterrestrial microdrile forms, including the tubificids, pot worms and ice worms (Enchytraeidae), blackworms (Lumbriculidae) and several interstitial marine worms.
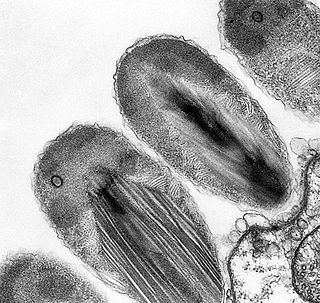
Verrucomicrobia is a phylum of Gram-negative bacteria that contains only a few described species. The species identified have been isolated from fresh water, marine and soil environments and human faeces. A number of as-yet uncultivated species have been identified in association with eukaryotic hosts including extrusive explosive ectosymbionts of protists and endosymbionts of nematodes residing in their gametes.

The Buxaceae are a small family of six genera and about 123 known species of flowering plants. They are shrubs and small trees, with a cosmopolitan distribution. A seventh genus, sometimes accepted in the past (Notobuxus), has been shown by genetic studies to be included within Buxus.

Eutamias is a genus of chipmunks within the tribe Marmotini of the squirrel family. It includes a single living species, the Siberian chipmunk. The genus is often treated as a subgenus of Tamias, which is now restricted to the eastern chipmunk of North America. Neotamias, which now includes the western North American chipmunks, has also been included in Eutamias.

Helicia is a genus of 110 species of trees and shrubs, constituting part of the plant family Proteaceae. They grow naturally in rainforests throughout tropical South and Southeast Asia, including India, Sri Lanka, Indochina, Peninsular Malaysia to New Guinea and as far south as New South Wales.

Enidae is a family of air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks.
The Synergistetes is a recently recognized phylum of anaerobic bacteria that show Gram-negative staining and have rod/vibrioid cell shape. Although Synergistetes have a diderm cell envelope, the genes for various proteins involved in lipopolysaccharides biosynthesis have not yet been detected in Synergistetes, indicating that they may have an atypical outer cell envelope. The Synergistetes inhabit a majority of anaerobic environments including animal gastrointestinal tracts, soil, oil wells, and wastewater treatment plants and they are also present in sites of human diseases such as cysts, abscesses, and areas of periodontal disease. Due to their presence at illness related sites, the Synergistetes are suggested to be opportunistic pathogens but they can also be found in healthy individuals in the microbiome of the umbilicus and in normal vaginal flora. Species within this phylum have also been implicated in periodontal disease, gastrointestinal infections and soft tissue infections. Other species from this phylum have been identified as significant contributors in the degradation of sludge for production of biogas in anaerobic digesters and are potential candidates for use in renewable energy production through their production of hydrogen gas. All of the known Synergistetes species and genera are presently part of a single class (Synergistia), order (Synergistiales) and family (Synergistaceae).

Eucyon is an extinct genus of medium omnivorous coyote-like canid that first appeared in the Western United States during the late Middle Miocene 10 million years ago. It was the size of a jackal and weighed around 15kg. Its species E. zhoui was one of a number of North American mammals which invaded East Asia around 5–6 million years ago, followed by the genus going extinct 3 million years ago. This genus is proposed to have given rise to genus Canis 6 million years ago.
Ursavini is an extinct tribe of mammals of the family Ursidae (bears) endemic to North America, Europe, Africa, and Asia during Miocene through Pliocene, living from about 23—2.5 Mya, existing for roughly 20.5 million years.
Ursavus is an extinct genus of bear that existed in North America, Europe, and Asia during the Miocene period, about 23–5.3 million years ago (Mya), existing for roughly 17.7 million years . The genus apparently dispersed from Asia into North America about 20 Mya, becoming the earliest member of the subfamily Ursinae in the New World. Qiu points out that if a questionable 29 million-year-old specimen of Ursavus reported in North America is validated, Ursavus may have evolved in North America and dispersed westward into Asia. The higher number of fossils in Europe grading toward eastern Asia make the westward dispersal unlikely.

Coccus is a genus of scale insects in the family Coccidae. Several species, such as Coccus viridis, a major pest of coffee, are major agricultural pests. The type species is Coccus hesperidumLinnaeus.
Lentisphaerae is a phylum of bacteria closely related to Chlamydiae and Verrucomicrobia.

Cynipini is a tribe of gall wasps. These insects induce galls in plants of the beech and oak family, Fagaceae. They are known commonly as the oak gall wasps.
Teratura is a genus of Asian bush crickets belonging to the tribe Meconematini.
Anelytra is an Asian genus of bush crickets in the tribe Agraeciini, belonging to the 'conehead' subfamily Conocephalinae.
The Jurasaidae are a family of Coleoptera known from 3 rare species in the Brazilian Atlantic rainforest; all known species have neotenic females and normal males.
Prosellodrilus is a genus of annelids belonging to the family Lumbricidae.









