
Nyarlathotep is a character in the works of H. P. Lovecraft and other writers. The character is commonly known in association with its role as a malign deity in the Lovecraft Mythos fictional universe, where it is known as the Crawling Chaos. First appearing in Lovecraft's 1920 prose poem of the same name, he was later mentioned in other works by Lovecraft and by other writers and in the tabletop role-playing games making use of the Cthulhu Mythos. Later writers describe him as one of the Outer Gods.
Cthugha is a deity in the Cthulhu Mythos genre of horror fiction, the creation of August Derleth. In Derleth's version of the Cthulhu Mythos, Cthugha is a Great Old One, an elemental spirit of fire opposed to the Elder Gods. Derleth set its homeworld as the star Fomalhaut, which had featured in Lovecraft's poetry. He first appeared in Derleth's short story "The House on Curwen Street" (1944).

Mi-Go are a fictional race of extraterrestrials created by H. P. Lovecraft and used by others in the Cthulhu Mythos setting. The word Mi-Go comes from "Migou", a Tibetan word for yeti. The aliens are fungus-based lifeforms which are extremely varied due to their prodigious surgical, biological, chemical, and mechanical skill. The variants witnessed by Akeley in "The Whisperer in Darkness" look like winged humanoid crabs, and do not resemble yeti.
The Pnakotic Manuscripts is a fictional manuscript in the Cthulhu Mythos. The tome was created by H. P. Lovecraft and first appeared in his short story "Polaris" (1918). They are mentioned in many of Lovecraft's stories, including "The Other Gods" (1933), The Dream-Quest of Unknown Kadath (1926), The Whisperer in Darkness, At the Mountains of Madness (1936), "Through the Gates of the Silver Key", The Shadow Out of Time (1936) and "The Haunter of the Dark". The manuscripts are also referred to by other Mythos authors, such as Lin Carter and Brian Lumley.

Azathoth is a deity in the Cthulhu Mythos and Dream Cycle stories of writer H. P. Lovecraft and other authors. He is the ruler of the Outer Gods.
Nightgaunts are a fictional race in the Cthulhu Mythos and is also part of H. P. Lovecraft's Dream Cycle. The creatures appear in the poem "Night-Gaunts" and the novella The Dream-Quest of Unknown Kadath, both by Lovecraft.
This is a complete list of works by H. P. Lovecraft. Dates for the fiction, collaborations and juvenilia are in the format: composition date / first publication date, taken from An H. P. Lovecraft Encyclopedia by S. T. Joshi and D. E. Schultz, Hippocampus Press, New York, 2001. For other sections, dates are the time of composition, not publication. Many of these works can be found on Wikisource.
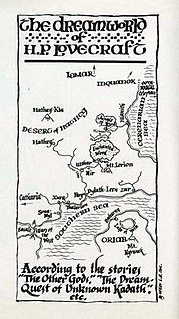
The Dream Cycle is a series of short stories and novellas by author H. P. Lovecraft (1890–1937). Written between 1918 and 1932, they concern themselves with the "Dreamlands", a vast, alternate dimension that can only be entered via dreams.
Randolph Carter is a recurring fictional character in H. P. Lovecraft's fiction and is, presumably, an alter ego of Lovecraft himself. The character first appears in "The Statement of Randolph Carter", a short story Lovecraft wrote in 1919 based on one of his dreams. An American magazine called The Vagrant published the story in May 1920.

The Dream-Quest of Unknown Kadath is a novella by American writer H. P. Lovecraft. Begun probably in the autumn of 1926, the draft was completed on January 22, 1927 and it remained unrevised and unpublished in his lifetime. It is both the longest of the stories that make up his Dream Cycle and the longest Lovecraft work to feature protagonist Randolph Carter. Along with his 1927 novel The Case of Charles Dexter Ward, it can be considered one of the significant achievements of that period of Lovecraft's writing. The Dream-Quest combines elements of horror and fantasy into an epic tale that illustrates the scope and wonder of humankind's ability to dream.

The Elder Sign is an icon in the Cthulhu Mythos, whose stories describe it as a form of protection against evil forces. Although not described in Lovecraft's work, he illustrated it in correspondence as a line with five branches. Mythos writer August Derleth described the Elder Sign as a warped, five-pointed star with a flaming pillar in its center, and it is this interpretation which has become the most popular in subsequent Mythos literature.
"Celephaïs" is a fantasy story by American horror fiction writer H. P. Lovecraft, written in early November 1920 and first published in the May 1922 issue of the Rainbow. The title refers to a fictional city that later appears in Lovecraft's Dream Cycle, including his novella The Dream-Quest of Unknown Kadath (1926).
The following characters appear in H.P. Lovecraft's story cycle — the Cthulhu Mythos.
Kingsport is a fictional town in the writings of H. P. Lovecraft and used by subsequent writers in his tradition. The town first appeared in Lovecraft's short story "The Terrible Old Man" (1921).
"The Dreams in the Witch House" is a horror short story by American writer H. P. Lovecraft, part of the Cthulhu Mythos cycle. Written in January/February 1932, it was first published in the July 1933 issue of Weird Tales.

The Lurker at the Threshold is a horror novel by American writer August Derleth, based on short fragments written by H. P. Lovecraft, who died in 1937, and published as a collaboration between the two authors. According to S. T. Joshi, of the novel's 50,000 words, 1,200 were written by Lovecraft.

"The Other Gods" is a fantasy short story written by American author H. P. Lovecraft, on August 14, 1921. It was first published in the November 1933 issue of The Fantasy Fan.

The Doom That Came to Sarnath and Other Stories is a collection of fantasy and horror stories by H. P. Lovecraft, edited by Lin Carter. It was first published in paperback by Ballantine Books as the twenty-sixth volume of its Ballantine Adult Fantasy series in February 1971. It was the second collection of Lovecraft's works assembled by Carter for the series, the first being The Dream-Quest of Unknown Kadath. The stories were written between 1919 and 1935, and originally published in various fantasy magazines, notably Weird Tales.
"I, Cthulhu" is a short humorous story by fantasy author Neil Gaiman featuring H. P. Lovecraft's Cthulhu who is dictating an autobiography to a human slave, Whateley. The story reveals much about Cthulhu's 'birth' and early life.
H. P. Lovecraft created a number of deities throughout the course of his literary career, including the "Great Old Ones" and aliens, such as the "Elder Things", with sporadic references to other miscellaneous deities whereas the "Elder Gods" are a later creation of other prolific writers such as August Derleth, who was credited with formalizing the Cthulhu Mythos.









