
Allen Newell was an American researcher in computer science and cognitive psychology at the RAND Corporation and at Carnegie Mellon University's School of Computer Science, Tepper School of Business, and Department of Psychology. He contributed to the Information Processing Language (1956) and two of the earliest AI programs, the Logic Theorist (1956) and the General Problem Solver (1957). He was awarded the ACM's A.M. Turing Award along with Herbert A. Simon in 1975 for their contributions to artificial intelligence and the psychology of human cognition.

Edward Albert Feigenbaum is a computer scientist working in the field of artificial intelligence, and joint winner of the 1994 ACM Turing Award. He is often called the "father of expert systems."
In artificial intelligence, symbolic artificial intelligence is the term for the collection of all methods in artificial intelligence research that are based on high-level symbolic (human-readable) representations of problems, logic and search. Symbolic AI used tools such as logic programming, production rules, semantic nets and frames, and it developed applications such as knowledge-based systems, symbolic mathematics, automated theorem provers, ontologies, the semantic web, and automated planning and scheduling systems. The Symbolic AI paradigm led to seminal ideas in search, symbolic programming languages, agents, multi-agent systems, the semantic web, and the strengths and limitations of formal knowledge and reasoning systems.
The expression computational intelligence (CI) usually refers to the ability of a computer to learn a specific task from data or experimental observation. Even though it is commonly considered a synonym of soft computing, there is still no commonly accepted definition of computational intelligence.

Robert Anthony Kowalski is an American-British logician and computer scientist, whose research is concerned with developing both human-oriented models of computing and computational models of human thinking. He has spent most of his career in the United Kingdom.

Timothy Wilking Finin is the Willard and Lillian Hackerman Chair in Engineering and is a Professor of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC). His research has focused on the applications of artificial intelligence to problems in information systems and has included contributions to natural language processing, expert systems, the theory and applications of multiagent systems, the semantic web, and mobile computing.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to artificial intelligence:
John Yen is Professor of Data Science and Professor-in-Charge of Data Science in the College of Information Sciences and Technology at Pennsylvania State University. He currently leads the Laboratory of AI for Cyber Security at Penn State. He was the founder and a former Director of the Cancer Informatics Initiative there.
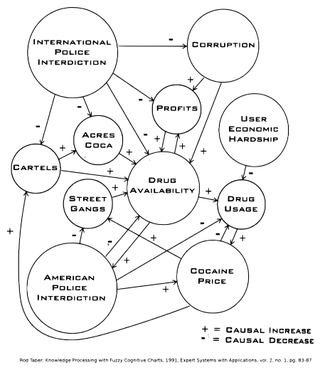
A fuzzy cognitive map (FCM) is a cognitive map within which the relations between the elements of a "mental landscape" can be used to compute the "strength of impact" of these elements. Fuzzy cognitive maps were introduced by Bart Kosko. Robert Axelrod introduced cognitive maps as a formal way of representing social scientific knowledge and modeling decision making in social and political systems, then brought in the computation.
An intelligent decision support system (IDSS) is a decision support system that makes extensive use of artificial intelligence (AI) techniques. Use of AI techniques in management information systems has a long history – indeed terms such as "Knowledge-based systems" (KBS) and "intelligent systems" have been used since the early 1980s to describe components of management systems, but the term "Intelligent decision support system" is thought to originate with Clyde Holsapple and Andrew Whinston in the late 1970s. Examples of specialized intelligent decision support systems include Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS), intelligent marketing decision support systems and medical diagnosis systems.

Brian R. Gaines is a British scientist, engineer, and Professor Emeritus at the University of Calgary.
Informatics is the study of computational systems. According to the ACM Europe Council and Informatics Europe, informatics is synonymous with computer science and computing as a profession, in which the central notion is transformation of information. In some cases, the term "informatics" may also be used with different meanings, e.g. in the context of social computing, or in context of library science.

Ronald Robert Yager is an American researcher in computational intelligence, decision making under uncertainty and fuzzy logic. He is currently Director of the Machine Intelligence Institute and Professor of Information Systems at Iona College.
Inductive programming (IP) is a special area of automatic programming, covering research from artificial intelligence and programming, which addresses learning of typically declarative and often recursive programs from incomplete specifications, such as input/output examples or constraints.
This glossary of artificial intelligence is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to the study of artificial intelligence, its sub-disciplines, and related fields. Related glossaries include Glossary of computer science, Glossary of robotics, and Glossary of machine vision.

Amir Hussain is a cognitive scientist, the director of Cognitive Big Data and Cybersecurity (CogBID) Research Lab at Edinburgh Napier University He is a professor of computing science. He is founding Editor-in-Chief of Springer Nature's internationally leading Cognitive Computation journal and the new Big Data Analytics journal. He is founding Editor-in-Chief for two Springer Book Series: Socio-Affective Computing and Cognitive Computation Trends, and also serves on the Editorial Board of a number of other world-leading journals including, as Associate Editor for the IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (Systems) and the IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine.

Ashok K. Goel is a professor of computer science and human-centered computing in the School of Interactive Computing at Georgia Institute of Technology, and the chief scientist with Georgia Tech's Center for 21st Century Universities. He conducts research into cognitive systems at the intersection of artificial intelligence and cognitive science with a focus on computational design and creativity. Goel is also the Principle Investigator and Executive Director of National Science Foundation's AI Institute for Adult Learning and Online Education and an editor emeritus of AAAI's AI Magazine.
Karen L. Myers is the director of SRI International's Artificial Intelligence Center, where she is also principal scientist.
Michael Genesereth is an American logician and computer scientist, who is most known for his work on computational logic and applications of that work in enterprise management, computational law, and general game playing. Genesereth is professor in the Computer Science Department at Stanford University and a professor by courtesy in the Stanford Law School. His 1987 textbook on Logical Foundations of Artificial Intelligence remains one of the key references on symbolic artificial intelligence. He is the author of the influential Game Description Language (GDL) and Knowledge Interchange Format (KIF), the latter of which led to the ISO Common Logic standard.








