
Incilius fastidiosus, or the Pico Blanco toad, is a species of toad from western Panama and southeastern Costa Rica. It inhabits premontane and lower montane rainforest. It is largely a fossorial species that breeds explosively in temporary pools after heavy rains in late April–May. Juveniles occur on rocky stream margins the year round.
Holdridge's toad, formerly Bufo holdridgei, is a species of toad endemic to Costa Rica. In October 2008, it was declared extinct by the International Union for Conservation of Nature in its Red List since the species had not been seen since 1987, despite years of extensive searches. However, the species was rediscovered in 2010 by a Costa Rican herpetologist and is now classified as critically endangered. It is believed that the species is most threatened by the presence of the chytrid fungus in its habitat.

The Gulf Coast toad is a species of toad native to eastern and southeastern Mexico and Central America as far south as Costa Rica.

Incilius bocourti is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is found in southwestern Guatemala and in Chiapas in the adjacent Mexico. Its phylogenetic position is uncertain; it might not to belong to this genus, being the sister taxon of Anaxyrus instead. It is named after Marie Firmin Bocourt, a French zoologist and artist.

Incilius campbelli is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It was first described in 1994. It is found in eastern Chiapas (Mexico), Guatemala, western Honduras, and Maya Mountains, Belize. Its natural habitats are lowland moist and premontane wet forests, and pristine forests in mountainous regions. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Incilius canaliferus, also known as the dwarf toad, is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is found along the Pacific slopes of western El Salvador, Guatemala, and southern Mexico. Its natural habitats are semi-deciduous forests near rivers and moderate-sized streams. Breeding takes place in ponds and streams. It also occurs in disturbed habitats, for example coffee plantations. Habitat loss and possibly water pollution are threats to this toad.

The evergreen toad is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae.
The jeweled toad is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is endemic to Mexico and known from the Pacific Coast between Acapulco and Jamiltepec . Its natural habitats are xeric and deciduous forests. It is a rare species threatened by habitat loss caused by agricultural expansion, wood extraction, and the expansion of plantations.

Incilius ibarrai is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is found in the central and southern highlands of Guatemala and adjacent Honduras. The specific name ibarrai honors Jorge Alfonso Ibarra (1921–2000), then-director of the Guatemalan National Natural History Museum.

Incilius luetkenii is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is found in the Mesoamerica along the Pacific versant from central Costa Rica to extreme southern Chiapas, Mexico, as well as dry interior valleys of Guatemala and Honduras and San Juan River drainage in Costa Rica on the Atlantic versant. It occurs in open areas, including disturbed pasturelands in lowland dry forest, and to a lesser extent, in lowland moist and premontane moist forests. It breeds in temporary pools. It is a common species that is not facing major threats. It is also worth mentioning that this species of toad are known for using their vocal behaviors in order to call for mating. This can sometimes lead to aggression between those who are male in the species.
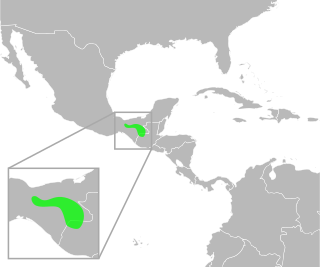
Incilius macrocristatus a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is found in Chiapas in southern Mexico and the adjacent Guatemala. Its natural habitats are cloud forests and pine-oak-Liquidambar forests. Breeding takes place in streams. It is a rare species that is threatened by habitat loss caused by agriculture and human settlement, and by water pollution.

Incilius mazatlanensis is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is endemic to Mexico and found in the Pacific coastal plain and slopes from southwestern Chihuahua and northern Sonora south to Colima.

The pine toad is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is endemic to Mexico and found on the Central Mexican Plateau.
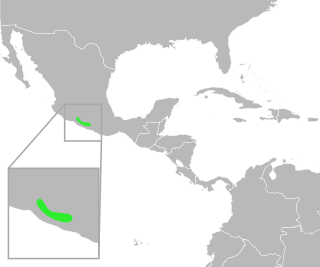
Incilius perplexus is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is endemic to southern Mexico and found in the Tepalcatepec River basin in the state of Michoacán and western Balsas River basin in the state of Guerrero. Its natural habitats are seasonal tropical forests near streams. It breeds in pools. It is threatened by habitat loss caused by infrastructure development and agricultural expansion.
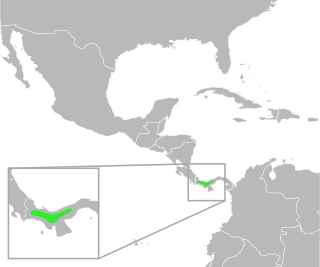
Incilius signifer is a species of toads in the family Bufonidae. It is endemic to Panama and known from the Pacific Coast to 800 m (2,600 ft) asl, west of the Canal Zone. Prior to its description in 2005, it was mixed with Incilius coccifer. Its natural habitats are tropical dry forests. It tolerates habitat modification but could be threatened by severe habitat modification.

Incilius spiculatus is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is endemic to Oaxaca, Mexico, and known from the northern slopes of the Sierra de Juárez and the adjacent Sierra Mixe. Its natural habitats are cloud forests and lowland rainforests. It breeds in streams. It is threatened by habitat loss.
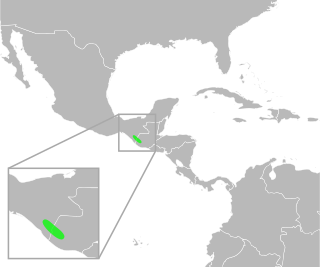
Incilius tacanensis is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is found in western Guatemala and eastern Chiapas (Mexico). Its name refers to Volcán Tacaná, its type locality. Its natural habitat is premontane tropical forest. It is assumed to be a stream breeder. It is a rare species threatened by habitat loss, and potentially, chytridiomycosis.

Incilius tutelarius is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is found in the Sierra Chimalapa and Sierra Madre de Chiapas in Guatemala and Chiapas, Mexico. Its natural habitats are cloud forests and pine-oak (broadleaf) forests. It is closely associated with streams, its breeding habitat. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Incilius epioticus is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is found on the Atlantic versant of the Cordillera de Talamanca in south-eastern Costa Rica and north-eastern Panama. Its natural habitats are primary and mature secondary forests, cloud forests, and highland oak forests. It is diurnal and found over dead leaves on the forest floor.

Incilius is a genus of toads in the true toad family, Bufonidae. They are sometimes known as the Central American toads or Middle American toads and are found in southern USA, Mexico, Central America, and northern Pacific South America. They are an ecologically and biogeographically diverse group of toads, including micro-endemic species such as Incilius spiculatus that are restricted to undisturbed cloud forests, and widespread lowland species such as Incilius valliceps that predominantly occur in disturbed habitats.



















