
Jeffrey Energy Center is a sub-bituminous coal-fired power plant located in Emmett Township, Pottawatomie County, seven miles (11 km) northwest of St. Marys, Kansas. Jeffrey EC is jointly owned by Westar Energy and Aquila Corp., both wholly owned subsidiaries of Evergy, Inc., Kansas City, Missouri. Jeffrey EC is composed of three separate 800-MW units providing a name-plate energy center capacity of 2.16 gigawatts. Unit 1 began operation in 1978, unit 2 in 1980 and unit 3 in 1983.

A fossil fuel power station is a thermal power station which burns a fossil fuel, such as coal, oil, or natural gas, to produce electricity. Fossil fuel power stations have machinery to convert the heat energy of combustion into mechanical energy, which then operates an electrical generator. The prime mover may be a steam turbine, a gas turbine or, in small plants, a reciprocating gas engine. All plants use the energy extracted from the expansion of a hot gas, either steam or combustion gases. Although different energy conversion methods exist, all thermal power station conversion methods have their efficiency limited by the Carnot efficiency and therefore produce waste heat.

Homer City Generating Station is a decommissioned 2-GW coal-burning power station near Homer City, in Indiana County, Pennsylvania, USA. It is owned by hedge funds and private equity firms and is operated by NRG Energy. Units 1 and 2, rated at 660 MWe, began operation in 1969. Unit 3, rated at 692 MWe nameplate capacity, was launched in 1977. It employed about 124 people.

The White Bluff Power Plant is a 1,800.0-megawatt (MW) coal-fired power station operated by Entergy Arkansas in Barraque Township, Arkansas. The plant is owned and operated by Entergy and has one of the tallest chimneys in the world at 305 metres (1,001 ft), which was built in 1980.

The Robert W. Scherer Power Plant is a coal-fired power plant in Juliette, Georgia, just north of Macon, Georgia, in the United States. The plant has four generating units, each capable of producing 930 megawatts, and is the most powerful coal-fired plant in North America. The plant is named after the former chairman and chief executive officer of Georgia Power.
The Acid Rain Program is a market-based initiative taken by the United States Environmental Protection Agency in an effort to reduce overall atmospheric levels of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, which cause acid rain. The program is an implementation of emissions trading that primarily targets coal-burning power plants, allowing them to buy and sell emission permits according to individual needs and costs. In 2011, the trading program that existed since 1995 was supplemented by four separate trading programs under the Cross-State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR). On August 21, 2012, the United States Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia issued its Opinion and Order in the appeal of the Cross State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR) for two independent legal reasons. The stay on CSAPR was lifted in October 2014, allowing implementation of the law and its trading programs to begin.

The Maritsa Iztok Complex is the largest energy complex in South Eastern Europe. Maritsa Iztok 1 and 3 located entirely within Stara Zagora Province in south-central Bulgaria while Maritsa Iztok 2 is split with eastern neighboring Sliven Province. It consists of three lignite-fired thermal power stations. The complex is located in a large lignite coal basin, which includes several mines, enrichment plants, a briquette plant and its own railway system. The development of the thermal power and mining complex at Maritsa Iztok began in 1952, but the lignite deposits used to be known well in the mid-19th century. The Maritsa Iztok mines and power plants are interdependent as the only market for coal is the power plants, while the power plants have no other supplier of coal but the mines.

The United States produced 5.2 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2020, the second largest in the world after greenhouse gas emissions by China and among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person. In 2019 China is estimated to have emitted 27% of world GHG, followed by the United States with 11%, then India with 6.6%. In total the United States has emitted a quarter of world GHG, more than any other country. Annual emissions are over 15 tons per person and, amongst the top eight emitters, is the highest country by greenhouse gas emissions per person.

China is both the world's largest energy consumer and the largest industrial country, and ensuring adequate energy supply to sustain economic growth has been a core concern of the Chinese Government since the founding of the People's Republic of China in 1949. Since the country's industrialization in the 1960s, China is currently the world's largest emitter of greenhouse gases, and coal in China is a major cause of global warming. However, from 2010 to 2015 China reduced energy consumption per unit of GDP by 18%, and CO2 emissions per unit of GDP by 20%. On a per-capita basis, China was only the world's 51st largest emitter of greenhouse gases in 2016. China is also the world's largest renewable energy producer, and the largest producer of hydroelectricity, solar power and wind power in the world. The energy policy of China is connected to its industrial policy, where the goals of China's industrial production dictate its energy demand managements.

Coal generated about 19.5% of the electricity at utility-scale facilities in the United States in 2022, down from 38.6% in 2014 and 51% in 2001. In 2021, coal supplied 9.5 quadrillion British thermal units (2,800 TWh) of primary energy to electric power plants, which made up 90% of coal's contribution to U.S. energy supply. Utilities buy more than 90% of the coal consumed in the United States. There were over 200 coal powered units across the United States in 2024. Coal plants have been closing since the 2010s due to cheaper and cleaner natural gas and renewables. Due to measures such as scrubbers air pollution from the plants kills far fewer people nowadays, but deaths in 2020 from PM 2.5 have been estimated at 1600. Environmentalists say that political action is needed to close them faster, to also reduce greenhouse gas emissions by the United States and better limit climate change.

The Chalk Point Generating Station is an electricity-generating plant, comprising oil and natural gas fired units, owned by NRG Energy, located near the town of Eagle Harbor, Maryland, United States, on the Patuxent River.

The Miami Fort Generating Station is a dual-fuel power generating facility. It is a major coal-fired electrical power station, supplemented with a small oil-fired facility. Miami Fort is located in Miami Township, Hamilton County, immediately east of the tripoint of Indiana, Kentucky, and Ohio. Miami Fort Station is named for the nearby Miami Fort.
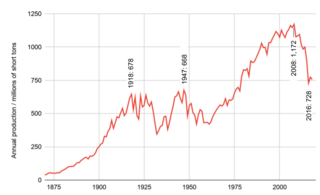
Coal mining is an industry in transition in the United States. Production in 2019 was down 40% from the peak production of 1,171.8 million short tons in 2008. Employment of 43,000 coal miners is down from a peak of 883,000 in 1923. Generation of electricity is the largest user of coal, being used to produce 50% of electric power in 2005 and 27% in 2018. The U.S. is a net exporter of coal. U.S. coal exports, for which Europe is the largest customer, peaked in 2012. In 2015, the U.S. exported 7.0 percent of mined coal.
The R. Gallagher Generating Station was a four-unit coal-burning power plant located along the Ohio River some two miles (3 km) downstream from New Albany, Indiana in southernmost Floyd County, Indiana. The total aggregate capacity (year-around) of the plant's four identical units was 560MW. Unit 2 began operating in 1958; unit 1 in 1959; unit 3 in 1960 and unit 4 in 1961. In early 2012, both Units 1 and 3 were retired. Units 2 and 4 continued to operate because Duke Energy installed baghouses, greatly reducing the pollution and meeting the current standards set by the EPA. The plant's 2012 output was 280 megawatts. The plant is connected to the grid by 138 and 230 kilovolt transmission lines.
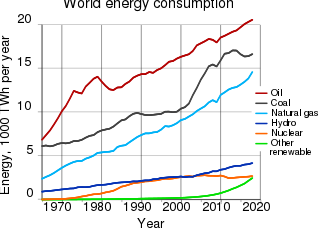
The environmental impact of the energy industry is significant, as energy and natural resource consumption are closely related. Producing, transporting, or consuming energy all have an environmental impact. Energy has been harnessed by human beings for millennia. Initially it was with the use of fire for light, heat, cooking and for safety, and its use can be traced back at least 1.9 million years. In recent years there has been a trend towards the increased commercialization of various renewable energy sources. Scientific consensus on some of the main human activities that contribute to global warming are considered to be increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases, causing a warming effect, global changes to land surface, such as deforestation, for a warming effect, increasing concentrations of aerosols, mainly for a cooling effect.
The John W. Turk Jr. Coal Plant is a base load 600-megawatt coal-fired power station in Fulton, Arkansas, operated by the American Electric Power subsidiary Southwestern Electric Power Company (SWEPCO). It provides power to customers in Arkansas, Louisiana, and Texas.
The United States state of Arkansas is a significant producer of natural gas and a minor producer of petroleum.

The Clean Power Plan was an Obama administration policy aimed at combating climate change that was first proposed by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in June 2014. The final version of the plan was unveiled by President Barack Obama on August 3, 2015. Each state was assigned an individual goal for reducing carbon emissions, which could be accomplished how they saw fit, but with the possibility of the EPA stepping in if the state refused to submit a plan. If every state met its target, the plan was projected to reduce carbon emissions from electricity generation 32% by 2030, relative to 2005 levels, as well as achieving various health benefits due to reduced air pollution.

Laramie River Station is a major coal-fired power plant, located in Platte County. It is operated by Basin Electric Power Cooperative and owned jointly by several of its member cooperatives. It is the second largest coal-fired power plant in Wyoming by capacity. The station currently employs 300 workers. Electricity produced at the station is distributed to across Wyoming, Nebraska and Colorado. Three similar units were launched in the early 1980s.
















