
The flatworms, flat worms, Platyhelminthes, Plathelminthes, or platyhelminths are a phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, unsegmented, soft-bodied invertebrates. Unlike other bilaterians, they are acoelomates, and have no specialized circulatory and respiratory organs, which restricts them to having flattened shapes that allow oxygen and nutrients to pass through their bodies by diffusion. The digestive cavity has only one opening for both ingestion and egestion ; as a result, the food cannot be processed continuously.

In evolutionary biology, parasitism is a symbiotic relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or in another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism, trophically transmitted parasitism, vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation.

In biology and medicine, a host is an organism that harbours a parasitic, a mutualistic, or a commensalist guest (symbiont), the guest typically being provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include animals playing host to parasitic worms, cells harbouring pathogenic (disease-causing) viruses, a bean plant hosting mutualistic (helpful) nitrogen-fixing bacteria. More specifically in botany, a host plant supplies food resources to micropredators, which have an evolutionarily stable relationship with their hosts similar to ectoparasitism. The host range is the collection of hosts that an organism can use as a partner.

Ostracods, or ostracodes, are a class of the Crustacea, sometimes known as seed shrimp. Some 70,000 species have been identified, grouped into several orders. They are small crustaceans, typically around 1 mm (0.039 in) in size, but varying from 0.2 to 30 mm in the case of Gigantocypris. Their bodies are flattened from side to side and protected by a bivalve-like, chitinous or calcareous valve or "shell". The hinge of the two valves is in the upper (dorsal) region of the body. Ostracods are grouped together based on gross morphology. While early work indicated the group may not be monophyletic; and early molecular phylogeny was ambiguous on this front, recent combined analyses of molecular and morphological data found support for monophyly in analyses with broadest taxon sampling

Maxillopoda is a diverse class of crustaceans including barnacles, copepods and a number of related animals. It does not appear to be a monophyletic group, and no single character unites all the members.

Cymothoa exigua, or the tongue-eating louse, is a parasitic isopod of the family Cymothoidae. This parasite enters fish through the gills. The female attaches to the tongue and the male attaches on the gill arches beneath and behind the female. Females are 8–29 millimetres (0.3–1.1 in) long and 4–14 mm (0.16–0.55 in) wide. Males are approximately 7.5–15 mm (0.3–0.6 in) long and 3–7 mm (0.12–0.28 in) wide. The parasite severs the blood vessels in the fish's tongue, causing the tongue to fall off. It then attaches itself to the remaining stub of the tongue and becomes the fish's new tongue.

The Pentastomida are an enigmatic group of parasitic arthropods commonly known as tongue worms due to the resemblance of the species of the genus Linguatula to a vertebrate tongue. They are traditionally seen as crustaceans, even if that position has been questioned.
Traditionally, the Myodocopa and Podocopa have been classified as subclasses within the class Ostracoda, although there is some question about how closely related the two groups actually are. The Myodocopa are defined by possession of a poorly calcified carapace, and 8–9 articles in the exopod of the second antenna. The ventral margin of the carapace is not concave, and the valves do not overlap to a great extent.
Cylindroleberididae is a family of ostracods that shows remarkable morphological diversity. The defining feature is the possession of gills: 7–8 leaf-like pairs at the posterior of the body. Other features common to all species in the family include a "baleen-comb" on both the maxilla and the fifth limb, a sword-shaped coxal endite on the mandible, and the triaenid bristles on the basal endites of the mandible.

Cestoda is a class of parasitic worms in the flatworm phylum (Platyhelminthes). Most of the species—and the best-known—are those in the subclass Eucestoda; they are ribbon-like worms as adults, known as tapeworms. Their bodies consist of many similar units, known as proglottids, which are essentially packages of eggs which are regularly shed into the environment to infect other organisms. Species of the other subclass, Cestodaria, are mainly fish parasites.
Human parasites include various protozoa and worms that may infect humans that cause parasitic diseases.
Halipegus eccentricus is a monoecious, digenea parasitic trematode commonly found in true frogs in North America. It was first described in 1939.

Phoresis, or phoresy, is rooted in the Greek words phoras (bearing) and phor (thief). It is used to describe a non-permanent, commensalistic interaction in which one organism attaches itself to another solely for the purpose of travel. Phoresis has been observed directly in ticks and mites since the 1700s and indirectly in fossils 320 million years old, but is not restricted to arthropods or animals. Plants with seeds that disperse by attaching themselves to animals are also considered to be phoretic. The term, originally defined in 1896 as a relationship in which the host acts as a vehicle for its passenger, clashed with other terminology being developed at the time, so constraints on the length of time, feeding and ontogeny are now considered. Phoresis is used as a strategy for dispersal, seasonal migration, transport to new host/habitat escaping ephemeral habitats, and reducing inbreeding depression. In addition to the benefits afforded to individuals and species, its presence can add to the ecological diversity and complexity of an ecosystem.
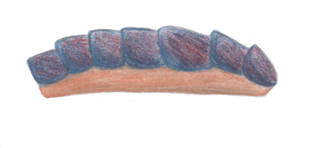
Kulindroplax perissokomos is a Silurian mollusk, known from a single fossil from the Wenlock Series Lagerstätte fauna of England. It lived during the Homerian Age. It is considered a basal aplacophoran. Unlike all modern aplacophorans, which are shell-less, Kulindroplax has a chiton-like shell, and it is considered a transitional fossil in the evolution of molluscs.
Pauline avibella is a fossil ostracod from the Silurian with unusually well preserved soft parts, including limbs, eyes, gills and alimentary system.
Pauline is a fossil genus of ostracods from the Silurian. Genus contains two species: Pauline avibella found in 425-million-year-old rocks in the Herefordshire Lagerstätte in England near the Welsh Border and Pauline nivisis, known from the Lower Silurian Pentamerus Bjerge Formation of north Greenland.
Luprisca incuba is an extinct species of ostracod —a group related to crabs, shrimps and lobsters. It was described as a new species in 2014, following discovery and analysis of fossilised specimens in mudstone rocks from New York State, USA. A team of researchers from the universities of Yale and Kansas, Oxford and the Japan Agency of Marine Science and Technology made the discovery.

Aquilonifer spinosus is an extinct species of arthropod from the Silurian period. It is known from a single fossil specimen found in the Wenlock Series Lagerstätte of Herefordshire, England, in rocks about 430 million years old. The 1 cm long specimen is a stem-group mandibulate, not directly related to any living species. The many-legged, eyeless adult has ten unusual tethered appendages, interpreted as juveniles attached to the parent, in a unique form and previously unknown brooding behaviour.
Offacolus is an extinct genus of euchelicerate, a group of chelicerate arthropods. Its only species, O. kingi, has been found in deposits from the Silurian period in the Wenlock Series Lagerstätte of Herefordshire, England. It is classified as a basal ("primitive") genus in the monotypic family Offacolidae in the clade Euchelicerata, along with Dibasterium and Prosomapoda. The genus is named after Offa, a king from the ancient kingdom of Mercia, and colus, a person who dwelled among the Offa's Dyke. The species name honors Robert Joseph King, a British mineralogist who found the fossils of Offacolus.

Inquicus fellatus is an extinct, bottle-shaped worm from the Chengjiang Biota, in what was once a marine environment from Early Cambrian Yunnan province. Its fossils are found attached to fossils of the worms Cricocosmia and Mafangscolex in either a parasitic or commensalistic relationship.











