
The Thomisidae are a family of spiders, including about 175 genera and over 2,100 species. The common name crab spider is often linked to species in this family, but is also applied loosely to many other families of spiders. Many members of this family are also known as flower spiders or flower crab spiders.

Wolf spiders are members of the family Lycosidae, from the Ancient Greek word "λύκος" meaning "wolf". They are robust and agile hunters with excellent eyesight. They live mostly in solitude and hunt alone, and do not spin webs. Some are opportunistic hunters pouncing upon prey as they find it or even chasing it over short distances. Some wait for passing prey in or near the mouth of a burrow.

The family Dipluridae, known as curtain-web spiders are a group of spiders in the infraorder Mygalomorphae, that have two pairs of booklungs, and chelicerae (fangs) that move up and down in a stabbing motion. A number of genera, including that of the Sydney funnel-web spider (Atrax), used to be classified in this family but have now been moved to Hexathelidae.

Deinopidae, also known as net casting spiders, is a family of cribellate spiders first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1850. It consists of stick-like elongated spiders that catch prey by stretching a web across their front legs before propelling themselves forward. These unusual webs will stretch two or three times their relaxed size, entangling any prey that touch them. The posterior median eyes have excellent night vision, allowing them to cast nets accurately in low-light conditions. These eyes are larger than the others, and sometimes makes these spiders appear to only have two eyes. Ogre-faced spiders (Deinopis) are the best known genus in this family. The name refers to the perceived physical similarity to the mythological creature of the same name. This genus also includes the humped-back spiders (Menneus).

Orb-weaver spiders are members of the spider family Araneidae. They are the most common group of builders of spiral wheel-shaped webs often found in gardens, fields and forest. "Orb" can in English mean "circular", hence the English name of the group. Araneids have eight similar eyes, hairy or spiny legs, and no stridulating organs.

Velvet spiders are a small group of spiders almost entirely limited to the Old World, with exception of a few species known from Brazil. The characteristics of this family of spiders are that they are entelegyne, eight-eyed araneomorph spiders that build unkempt webs. They are cribellate. Some species are nearly eusocial, lacking only a specialized caste system and a queen. They cooperate in brood rearing, unlike most other spiders except for some African agelenid spiders in the genus Agelena and a few others.

Archaeidae, also known as assassin spiders and pelican spiders, is a spider family with about ninety described species in five genera. It contains small spiders, ranging from 2 to 8 millimetres long, that prey exclusively on other spiders. They are unusual in that they have "necks", ranging from long and slender to short and fat. The name "pelican spider" refers to these elongated jaws and necks used to catch their prey. Living species of Archaeidae occur in South Africa, Madagascar and Australia, with the sister family Mecysmaucheniidae occurring in southern South America and New Zealand.

Euophryini is a tribe of jumping spiders. It has also been treated as the subfamily Euophryinae.

Lasiodora is a genus of tarantulas that was first described by Ludwig Carl Christian Koch in 1850. They are often very large; body lengths of up to 25 centimetres (9.8 in), including the legs, are not unusual.

Hemicloea is a genus of South Pacific flat spiders that was first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1870. Originally placed with the ground spiders, it was moved to the Trochanteriidae in 2018.

Cymbacha is a genus of crab spiders that was first described by Ludwig Carl Christian Koch in 1874.

Cryphoeca is a genus of araneomorph spiders in the family Cybaeidae, and was first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1870. The name means hidden, in reference to its preference for hiding under loose bark or in stone walls.
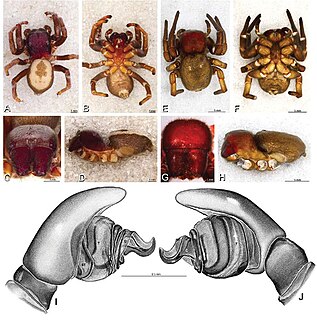
Dorceus is a genus of velvet spiders that was first described by C. L. Koch in 1846.
Cyllognatha is a genus of comb-footed spiders that was first described by Ludwig Carl Christian Koch in 1872.
Cetratus is a genus of South Pacific crab spiders that was first described by Władysław Kulczyński in 1911.
Corynethrix is a monotypic genus of South Pacific crab spiders containing the single species, Corynethrix obscura. It was first described by Ludwig Carl Christian Koch in 1876 based on a female specimen. They have been found in New South Wales and Queensland. A male has not yet been identified, and there is very little known about the biology and behavior of this species and its relatives.
Hedana is a genus of crab spiders that was first described by Ludwig Carl Christian Koch in 1874.

Pellenes nigrociliatus is a jumping spider species in the genus Pellenes.
Bomis is a genus of crab spiders that was first described by Ludwig Carl Christian Koch in 1874.













