
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom bonded to two organyl groups. They have the general formula R−O−R′, where R and R′ represent the organyl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the organyl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether". Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin.

In chemistry, an ester is a functional group derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.
In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction which introduces one or more halogens into a chemical compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transformation important, e.g. in the production of polymers, drugs. This kind of conversion is in fact so common that a comprehensive overview is challenging. This article mainly deals with halogenation using elemental halogens. Halides are also commonly introduced using salts of the halides and halogen acids. Many specialized reagents exist for and introducing halogens into diverse substrates, e.g. thionyl chloride.
In organic chemistry, butyl is a four-carbon alkyl radical or substituent group with general chemical formula −C4H9, derived from either of the two isomers (n-butane and isobutane) of butane.

Acetyl chloride is an acyl chloride derived from acetic acid. It belongs to the class of organic compounds called acid halides. It is a colorless, corrosive, volatile liquid. Its formula is commonly abbreviated to AcCl.
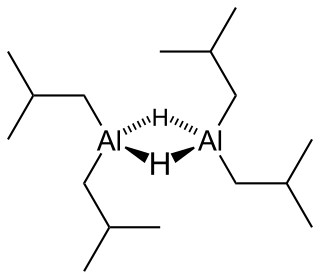
Diisobutylaluminium hydride (DIBALH, DIBAL, DIBAL-H or DIBAH) is a reducing agent with the formula (i-Bu2AlH)2, where i-Bu represents isobutyl (-CH2CH(CH3)2). This organoaluminium compound is a reagent in organic synthesis.
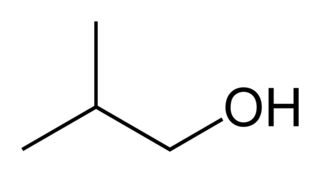
Isobutanol (IUPAC nomenclature: 2-methylpropan-1-ol) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2CHCH2OH (sometimes represented as i-BuOH). This colorless, flammable liquid with a characteristic smell is mainly used as a solvent either directly or as its esters. Its isomers are 1-butanol, 2-butanol, and tert-butanol, all of which are important industrially.
Isobutyl nitrite, C4H9NO2, is an alkyl nitrite, an ester of isobutanol and nitrous acid. Its chemical structure is (CH3)2CH-CH2-ONO.

Isoamyl alcohol is a colorless liquid with the formula C
5H
12O, specifically (H3C–)2CH–CH2–CH2–OH. It is one of several isomers of amyl alcohol (pentanol). It is also known as isopentyl alcohol, isopentanol, or (in the IUPAC recommended nomenclature) 3-methyl-butan-1-ol. An obsolete name for it was isobutyl carbinol.

Tebbe's reagent is the organometallic compound with the formula (C5H5)2TiCH2ClAl(CH3)2. It is used in the methylidenation of carbonyl compounds, that is it converts organic compounds containing the R2C=O group into the related R2C=CH2 derivative. It is a red solid that is pyrophoric in the air, and thus is typically handled with air-free techniques. It was originally synthesized by Fred Tebbe at DuPont Central Research.
![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Eschenmoser's salt</span> Ionic compound with the formula [(H3C–)2N–CH2]I](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/28/Eschenmosersalz.png/320px-Eschenmosersalz.png)
In organic chemistry, Eschenmoser's salt is the ionic, organic compound [(CH3)2NCH2]I. It is the iodide salt of the dimethylaminomethylene cation [(CH3)2NCH2]+.
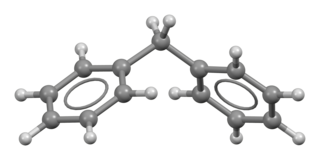
Diphenylmethane is an organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2CH2 (often abbreviated CH
2Ph
2). The compound consists of methane wherein two hydrogen atoms are replaced by two phenyl groups. It is a white solid.
Pivalic acid is a carboxylic acid with a molecular formula of (CH3)3CCO2H. This colourless, odiferous organic compound is solid at room temperature. Two abbreviations for pivalic acid are t-BuC(O)OH and PivOH. The pivalyl or pivaloyl group is abbreviated t-BuC(O).

Organoaluminium chemistry is the study of compounds containing bonds between carbon and aluminium. It is one of the major themes within organometallic chemistry. Illustrative organoaluminium compounds are the dimer trimethylaluminium, the monomer triisobutylaluminium, and the titanium-aluminium compound called Tebbe's reagent. The behavior of organoaluminium compounds can be understood in terms of the polarity of the C−Al bond and the high Lewis acidity of the three-coordinated species. Industrially, these compounds are mainly used for the production of polyolefins.
Isopropyl chloride is an organic compound with the chemical formula (CH3)2CHCl. It is a colourless to slightly yellow, volatile, flammable liquid with a sweet, ether-like (almost like petroleum) odour. It is used as an industrial solvent.
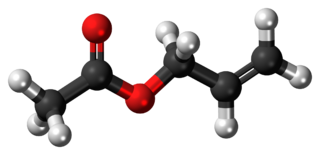
Allyl acetate is an organic compound with formula C3H5OC(O)CH3. This colourless liquid is a precursor to especially allyl alcohol, which is a useful industrial intermediate. It is the acetate ester of allyl alcohol.

Chlorodiisopropylphosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the formula [(CH3)2CH]2PCl. It is a colorless liquid that reacts with water and oxygen. The compound is used to prepare tertiary phosphines and phosphinite ligands.

Pentanoyl chloride is an acyl chloride derived from pentanoic acid. It is a colorless liquid that is used to attach the valeroyl group. It is usually produced by chlorination of valeric acid.
1,5-Hexadiene is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)2(CH=CH2)2. It is a colorless, volatile liquid. It is used as a crosslinking agent and precursor to a variety of other compounds.
Lauroyl chloride is the organic compound with the formula CH3(CH2)10COCl. It is the acid chloride of lauric acid. Lauroyl chloride is a standard reagent for installing the lauroyl group. It is mainly produced as a precursor to dilauroyl peroxide, which is widely used in free-radical polymerizations.










![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Eschenmoser's salt</span> Ionic compound with the formula [(H3C–)2N–CH2]I](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/28/Eschenmosersalz.png/320px-Eschenmosersalz.png)




