
The Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) is an international organisation that focuses on making scientific data on biodiversity available via the Internet using web services. The data are provided by many institutions from around the world; GBIF's information architecture makes these data accessible and searchable through a single portal. Data available through the GBIF portal are primarily distribution data on plants, animals, fungi, and microbes for the world, and scientific names data.

Petter Adolf Karsten was a Finnish mycologist, the foremost expert on the fungi of Finland in his day, and known in consequence as the "father of Finnish mycology".

Doidae is a small family of Lepidoptera with an exclusively New World distribution, with species occurring in Central America, the south-western United States, and northern South America.
The Catalogue of Life is an online database that provides an index of known species of animals, plants, fungi, and microorganisms. It was created in 2001 as a partnership between the global Species 2000 and the American Integrated Taxonomic Information System. The Catalogue is used by research scientists, citizen scientists, educators, and policy makers. The Catalogue is also used by the Biodiversity Heritage Library, the Barcode of Life Data System, Encyclopedia of Life, and the Global Biodiversity Information Facility. The Catalogue currently compiles data from 165 peer-reviewed taxonomic databases that are maintained by specialist institutions around the world. As of September 2022, the COL Checklist lists 2,067,951 of the world's 2.2m extant species known to taxonomists on the planet at present time.

Peucedanum is a genus of flowering plant in the carrot family, Apiaceae. Peucedanum boasts a global presence with diverse spread of morphological features. Peucedanum species are characterized by dorsally compressed mericarps, slightly prominent dorsal ribs, narrowly winged lateral ribs, and a broad commissure. However, the vast diversity of morphology, fruit forms, and phytochemical production makes classifying species in the Peucedanum challenging. Historically relevant in traditional medicine, Peucedanum's taxonomic complexity arises from its extensive diversity.

Monilinia is a genus of fungi in the family Sclerotiniaceae.
Sporormia is a genus of fungi in the family Sporormiaceae and part of the phylum Ascomycota. It is morphologically distinct from other genera in this family due to the orientation of cylindrical ascospores contained in a gelatinous sheath within the asci of the fruitbody. It is mostly known for being coprophilous but known to utilize wood as a substrate as well.
Cercidospora is a genus of fungi in the class Dothideomycetes. The relationship of this taxon to other taxa within the class is unknown. The genus was first described by Gustav Wilhelm Körber in 1865; it is synonymous with the name Prolisea described by Frederick Edward Clements in 1931.

Trichobolus is a genus of fungi in the Thelebolaceae family.

The Rhytismataceae are a family of fungi in the Rhytismatales order. It contains 55 genera and 728 species.
Bifusepta is a genus of fungi within the Rhytismataceae family. This is a monotypic genus, containing the single species Bifusepta tehonii.
Appendicospora is a genus of fungi in the family Apiosporaceae.

The Himalayan owl, also known as the Himalayan wood owl, is an owl of the forests of the Asia, from the Himalayas to Korea and Taiwan.

Cuphophyllus pratensis is a species of agaric in the family Hygrophoraceae. It has been given the recommended English name of meadow waxcap in the UK and in North America has variously been called the meadow waxy cap, salmon waxy cap, and butter meadowcap. The species has a widespread, mainly temperate distribution, occurring in grassland in Europe and in woodland elsewhere. The basidiocarps are edible and are occasionally collected and sold commercially.
The Atlas of Living Australia (ALA) is an online repository of information about Australian plants, animals, and fungi. Development started in 2006. The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) is an organisation significantly involved in the development of the ALA. The Atlas of Living Australia is the Australian node of the Global Biodiversity Information Facility. The ALA is being used to help assess suitability of revegetation projects by determining species vulnerability to climatic and atmospheric change.

iNaturalist is an American 501(c)(3) nonprofit social network of naturalists, citizen scientists, and biologists built on the concept of mapping and sharing observations of biodiversity across the globe. iNaturalist may be accessed via its website or from its mobile applications. iNaturalist includes an automated species identification tool, and users further assist each other in identifying organisms from photographs and even sound recordings. As of 9 July 2024, iNaturalist users had contributed approximately 197,660,888 observations of plants, animals, fungi, and other organisms worldwide, and 290,007 users were active in the previous 30 days.

The Interim Register of Marine and Nonmarine Genera (IRMNG) is a taxonomic database which attempts to cover published genus names for all domains of life, from 1758 in zoology up to the present, arranged in a single, internally consistent taxonomic hierarchy, for the benefit of Biodiversity Informatics initiatives plus general users of biodiversity (taxonomic) information. In addition to containing just over 500,000 published genus name instances as at May 2023, the database holds over 1.7 million species names, although this component of the data is not maintained in as current or complete state as the genus-level holdings. IRMNG can be queried online for access to the latest version of the dataset and is also made available as periodic snapshots or data dumps for import/upload into other systems as desired. The database was commenced in 2006 at the then CSIRO Division of Marine and Atmospheric Research in Australia and, since 2016, has been hosted at the Flanders Marine Institute (VLIZ) in Belgium.
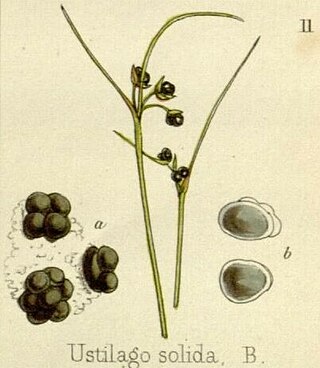
Cintractia is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Anthracoideaceae. It was first described by Marie Maxime Cornu in 1883.
Arthonia stereocaulina is a species of lichenicolous fungus in the family Arthoniaceae.











