
Eduard Čech was a Czech mathematician. His research interests included projective differential geometry and topology. He is especially known for the technique known as Stone–Čech compactification and the notion of Čech cohomology. He was the first to publish a proof of Tychonoff's theorem in 1937.
Feng Kang was a Chinese mathematician. He was elected an academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in 1980. After his death, the Chinese Academy of Sciences established the Feng Kang Prize in 1994 to reward young Chinese researchers who made outstanding contributions to computational mathematics.
Olgierd Cecil Zienkiewicz was a British academic of Polish descent, mathematician, and civil engineer. He was born in Caterham, England. He was one of the early pioneers of the finite element method. Since his first paper in 1947 dealing with numerical approximation to the stress analysis of dams, he published nearly 600 papers and wrote or edited more than 25 books.
In the numerical solution of partial differential equations, a topic in mathematics, the spectral element method (SEM) is a formulation of the finite element method (FEM) that uses high-degree piecewise polynomials as basis functions. The spectral element method was introduced in a 1984 paper by A. T. Patera. Although Patera is credited with development of the method, his work was a rediscovery of an existing method

Thomas Joseph Robert Hughes is a Professor of Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics and currently holds the Computational and Applied Mathematics Chair (III) at the Oden Institute at The University of Texas at Austin. Hughes has been listed as an ISI Highly Cited Author in Engineering by the ISI Web of Knowledge, Thomson Scientific Company.
Ray William Clough,, was Byron L. and Elvira E. Nishkian Professor of structural engineering in the department of civil engineering at the University of California, Berkeley and one of the founders of the finite element method (FEM). His article in 1956 was one of the first applications of this computational method. He coined the term “finite elements” in an article in 1960. He was born in Seattle.
In mathematics, the Babuška–Lax–Milgram theorem is a generalization of the famous Lax–Milgram theorem, which gives conditions under which a bilinear form can be "inverted" to show the existence and uniqueness of a weak solution to a given boundary value problem. The result is named after the mathematicians Ivo Babuška, Peter Lax and Arthur Milgram.
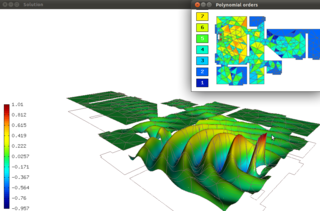
Hermes2D is a C++/Python library of algorithms for rapid development of adaptive hp-FEM solvers. hp-FEM is a modern version of the finite element method (FEM) that is capable of extremely fast, exponential convergence.
hp-FEM is a generalization of the finite element method (FEM) for solving partial differential equations numerically based on piecewise-polynomial approximations. hp-FEM originates from the discovery by Barna A. Szabó and Ivo Babuška that the finite element method converges exponentially fast when the mesh is refined using a suitable combination of h-refinements and p-refinements .The exponential convergence of hp-FEM has been observed by numerous independent researchers.

Junuthula N. Reddy is a Distinguished Professor, Regent's Professor, and inaugural holder of the Oscar S. Wyatt Endowed Chair in Mechanical Engineering at Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, USA.[1] He is an authoritative figure in the broad area of mechanics and one of the researchers responsible for the development of the Finite Element Method (FEM). He has made significant seminal contributions in the areas of finite element method, plate theory, solid mechanics, variational methods, mechanics of composites, functionally graded materials, fracture mechanics, plasticity, biomechanics, classical and non-Newtonian fluid mechanics, and applied functional analysis. Reddy has over 620 journal papers and 20 books and has given numerous national and international talks. He served as a member of the International Advisory Committee at ICTACEM, in 2001 and keynote addressing in 2014.[2][3]
Ladislav Svante Rieger (1916–1963) was a Czechoslovak mathematician who worked in the areas of algebra, mathematical logic, and axiomatic set theory. He is considered to be the founder of mathematical logic in Czechoslovakia, having begun his work around 1957.

John E. Osborn was an American mathematician. He obtained B.S. (1958), M.S. (1963), and Ph.D. (1965) degrees at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. His Ph.D. adviser was Hans Weinberger. Osborn made fundamental contributions to computational mathematics, especially to the theory of numerical solution of partial differential equations, eigenvalue approximations, and the finite element method. He also co-authored several textbooks on differential equations and numerical computation with the goal of introducing computation into sophomore level differential equations courses.
In mathematics, a cyclically ordered group is a set with both a group structure and a cyclic order, such that left and right multiplication both preserve the cyclic order.
Thomas Yizhao Hou is the Charles Lee Powell Professor of Applied and Computational Mathematics in the Department of Computing and Mathematical Sciences at the California Institute of Technology. He is known for his work in numerical analysis and mathematical analysis.

Franco Brezzi is an Italian mathematician.
Zbyněk Šidák was a Czech mathematician. He is known for developing the Šidák correction.

Anders Szepessy is a Swedish mathematician.
Christoph Schwab is a German applied mathematician, specializing in numerical analysis of partial differential equations and boundary integral equations.

Michel Bercovier is a French-Israeli Professor (Emeritus) of Scientific Computing and Computer Aided Design (CAD) in The Rachel and Selim Benin School of Computer Science and Engineering at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. Bercovier is also the head of the School of Computer Science at the Hadassah Academic College, Jerusalem.

Barna A. Szabó is a Hungarian-American engineer and educator, noted for his contributions on the finite element method, particularly the conception and implementation of the p- and hp-versions of the Finite Element Method. He is a founding member and fellow of the United States Association for Computational Mechanics, an external member of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences and fellow of the St. Louis Academy of Sciences.








