
Harmaline is a fluorescent indole alkaloid from the group of harmala alkaloids and beta-carbolines. It is the partly hydrogenated form of harmine.

Clorgiline (INN), or clorgyline (BAN), is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) structurally related to pargyline which is described as an antidepressant. Specifically, it is an irreversible and selective inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A). Clorgiline was never marketed, but it has found use in scientific research. It has been found to bind with high affinity to the σ1 receptor (Ki = 3.2 nM) and with very high affinity to the I2 imidazoline receptor (Ki = 40 pM).

Voacangine is an alkaloid found predominantly in the root bark of the Voacanga africana tree, as well as in other plants such as Tabernanthe iboga, Tabernaemontana africana, Trachelospermum jasminoides, Tabernaemontana divaricata and Ervatamia yunnanensis. It is an iboga alkaloid which commonly serves as a precursor for the semi-synthesis of ibogaine. It has been demonstrated in animals to have similar anti-addictive properties to ibogaine itself. It also potentiates the effects of barbiturates. Under UV-A and UV-B light its crystals fluoresce blue-green, and it is soluble in ethanol.
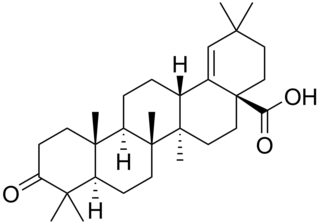
Moronic acid is a natural triterpene. Moronic acid can be extracted from Rhus javanica, a sumac plant traditionally believed to hold medicinal applications. The molecule has also been extracted from mistletoe.

Scoulerine, also known as discretamine and aequaline, is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid (BIA) that is derived directly from (S)-reticuline through the action of berberine bridge enzyme. It is a precursor of other BIAs, notably berberine, noscapine, (S)-tetrahydropalmatine, and (S)-stylopine, as well as the alkaloids protopine, and sanguinarine. It is found in many plants, including opium poppy, Croton flavens, and certain plants in the genus Erythrina.

Tryptoline, also known as tetrahydro-β-carboline and tetrahydronorharmane, is a natural organic derivative of beta-carboline. It is an alkaloid chemically related to tryptamines. Derivatives of tryptoline have a variety of pharmacological properties and are known collectively as tryptolines.

Mitraphylline, an oxindole derivative, is an active alkaloid in the leaves of the tree Mitragyna speciosa, commonly known as kratom. As a non-narcotic constituent, it also occurs to a significant amount in the bark of Uncaria tomentosa along with a number of isomeric alkaloids.

7-Hydroxymitragynine (7-OH) is a terpenoid indole alkaloid from the plant Mitragyna speciosa, commonly known as kratom. It was first described in 1994 and is a natural product derived from mitragynine present in the kratom leaf. 7-OH binds to opioid receptors like mitragynine, but research suggests that 7-OH binds with greater efficacy.

Maslinic acid is a compound derived from dry olive-pomace oil which is a byproduct of olive oil extraction. It is a member of the group of triterpenes known as oleananes.

Polygodial is chemical compound found in dorrigo pepper, mountain pepper, horopito, canelo, paracress, water-pepper, and Dendrodoris limbata.
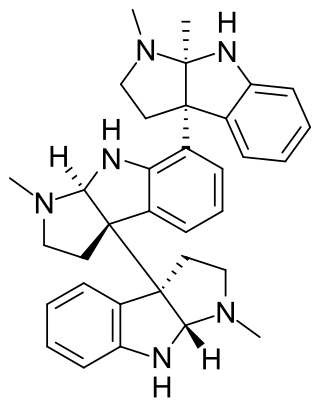
Hodgkinsine is an alkaloid found in plants of the genus Psychotria, particularly Psychotria colorata, although it is also found in Psychotria lyciiflora and probably other species in this family,

Glaucine(1,2,9,10-TetraMethoxyAporphine, Bromcholitin, Glauvent, Tusidil, Tussiglaucin) is an aporphine alkaloid found in several different plant species in the family Papaveraceae such as Glaucium flavum, Glaucium oxylobum and Corydalis yanhusuo, and in other plants like Croton lechleri in the family Euphorbiaceae.

Kavain is the main kavalactone found mostly in the roots of the kava plant.

Phellodendrine is an alkaloid isolated originally from Phellodendron amurense (Rutaceae).
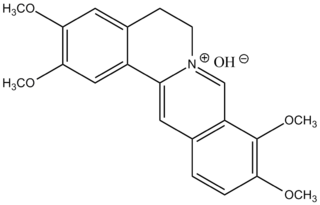
Palmatine is a protoberberine alkaloid found in several plants including Phellodendron amurense, Coptis Chinensis and Corydalis yanhusuo, Tinospora cordifolia, Tinospora sagittata, Phellodendron amurense, Stephania yunnanensis.

Matrine is an alkaloid found in plants from the genus Sophora. It has a variety of pharmacological effects, including anti-cancer effects, as well as κ-opioid and μ-opioid receptor agonism.

Paeonol is a phenolic compound found in peonies such as Paeonia suffruticosa, in Arisaema erubescens, and in Dioscorea japonica. It is a chemical compound found in some traditional Chinese medicines.

Kopsanone is an alkaloid isolated from Aspidosperma.
Guineesine is a compound isolated from long pepper and black pepper.

Tabernaemontanine is a naturally occurring monoterpene indole alkaloid found in several species in the genus Tabernaemontana including Tabernaemontana divaricata.



















