Related Research Articles

The Hopi are Native Americans who primarily live in northeastern Arizona. The majority are enrolled in the Hopi Tribe of Arizona and live on the Hopi Reservation in northeastern Arizona; however, some Hopi people are enrolled in the Colorado River Indian Tribes of the Colorado River Indian Reservation at the border of Arizona and California.

The Kaw Nation is a federally recognized Native American tribe in Oklahoma and parts of Kansas.
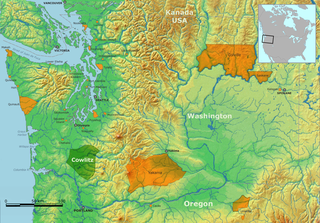
The term Cowlitz people covers two culturally and linguistically distinct indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest; the Lower Cowlitz or Cowlitz proper, and the Upper Cowlitz / Cowlitz Klickitat or Taitnapam. Lower Cowlitz refers to a southwestern Coast Salish people, which today are enrolled in the federally recognized tribes: Cowlitz Indian Tribe, Quinault Indian Nation, and Confederated Tribes of the Chehalis Reservation. The Upper Cowlitz or Taitnapam, is a Northwest Sahaptin speaking people, part of the Confederated Tribes and Bands of the Yakama Nation.

The Quileute are a Native American people in western Washington state in the United States, with 808 enrolled members as of 3/14/2018. They are a federally recognized tribe: the Quileute Tribe of the Quileute Reservation.

The Hoh or Chalá·at are a Native American tribe in western Washington state in the United States. The tribe lives on the Pacific Coast of Washington on the Olympic Peninsula. The Hoh moved onto the Hoh Indian Reservation, 47°44′31″N124°25′17″W at the mouth of the Hoh River, on the Pacific Coast of Jefferson County, after the signing of the Quinault Treaty on July 1, 1855. The reservation has a land area of 1.929 square kilometres and a 2000 census resident population of 102 persons, 81 of whom were Native Americans. It lies about halfway between its nearest outside communities of Forks, to its north, and Queets, to its south. The river is central to their culture. The main resources they used included cedar trees, salmon, and the nearby vegetation. They also traded and bartered with other tribes closer to Eastern Washington, near the Plateaus and Great Plains.

The Daybreak Star Indian Cultural Center is a Native American cultural center in Seattle, Washington, described by its parent organization United Indians of All Tribes as "an urban base for Native Americans in the Seattle area." Located on 20 acres in Seattle's Discovery Park in the Magnolia neighborhood, the center developed from activism by Bernie Whitebear and other Native Americans, who staged a generally successful self-styled "invasion" and occupation of the land in 1970. Most of the former Fort Lawton military base had been declared surplus by the U.S. Department of Defense. "The claim [Whitebear and others made] to Fort Lawton was based on rights under 1865 U.S.-Indian treaties promising reversion of surplus military lands to their original owners."

The Coeur d'Alene Tribe are a Native American tribe and one of five federally recognized tribes in the state of Idaho.
The Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians is one of three federally recognized tribes of Choctaw people, and the only one in the state of Mississippi. On April 20, 1945, this tribe was organized under the Indian Reorganization Act of 1934. Their reservation included lands in Neshoba, Leake, Newton, Scott, Jones, Attala, Kemper, and Winston counties. The Mississippi Choctaw regained stewardship of their mother mound, Nanih Waiya mounds and cave in 2008. The Mississippi Band of Choctaw have declared August 18 as a tribal holiday to celebrate their regaining control of the sacred site. The other two Choctaw groups are the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma, the third largest tribe in the United States, and the Jena Band of Choctaw Indians, located in Louisiana.
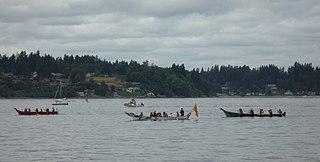
The Intertribal Canoe Journey is a celebrated event of the Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast. Organizers call it the Canoe Journey or Intertribal Canoe Journey, and colloqually Tribal Journeys. It is also referred to by its destination, i.e. Paddle to Muckleshoot.

Lawney L. Reyes was an American Sin-Aikst artist, curator, and memoirist, based in Seattle, Washington.

Bernie Whitebear, birth name Bernard Reyes, was an American Indian activist in Seattle, Washington, a co-founder of the Seattle Indian Health Board (SIHB), the United Indians of All Tribes Foundation, and the Daybreak Star Cultural Center, established on 20 acres of land acquired for urban Indians in the city.
The Quinault Treaty was a treaty agreement between the United States and the Native American Quinault and Quileute tribes located in the western Olympic Peninsula north of Grays Harbor, in the recently formed Washington Territory. The treaty was signed on 1 July 1855, at the Quinault River, and on 25 January 1856 at Olympia, the territorial capital. It was ratified by Congress on 8 March 1859, and proclaimed law on April 11, 1859.

The Quileute Indian Reservation is an Indian reservation for the Quileute people located on the northwestern Olympic Peninsula in Clallam County, Washington, United States. The reservation is at the mouth of the Quillayute River on the Pacific coast.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to United States federal Indian law and policy:

The Quinault Indian Nation, formerly known as the Quinault Tribe of the Quinault Reservation, is a federally recognized tribe of Quinault, Queets, Quileute, Hoh, Chehalis, Chinook, and Cowlitz peoples. They are a Southwestern Coast Salish people of indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast. Their tribe is located in Washington state on the Pacific coast of the Olympic Peninsula. These peoples are also represented in other tribes in Washington and Oregon.

The Swinomish Indian Tribal Community, also known as the Swinomish Tribe, is a federally recognized tribe located on Puget Sound in Washington state. Swinomish is a legal successor to signatories of the 1855 Treaty of Point Elliott. Its Reservation is located 65 miles North of Seattle, Washington on Fidalgo Island.The tribe's population is primarily composed of Swinomish, Lower Skagit, Kikiallus, and Samish peoples and their descendants. Other populations on the reservation include the Suquamish and Upper Skagit.
The Cowlitz Indian Tribe is a federally recognized tribe of Cowlitz people. They are a tribe of Southwestern Coast Salish and Sahaptan indigenous people of the Pacific Northwest located in Washington.

The Chow Chow Bridge was an early, wooden cable-stayed bridge crossing the Quinault River on the Quinault Indian Reservation near Taholah, Grays Harbor County, Washington. It was built for the first time in 1952 and finally removed in 1988. Frank Milward designed the bridge for Aloha Lumber Company.

The Quinault Cultural Center and Museum is a museum of culture in Taholah, Washington, owned and funded by the Quinault Indian Nation. It contains artifacts, arts, and crafts of the Quinault, housed in a converted retail building. Some of the art forms have been influenced by Polynesian cultural motifs, brought home by World War II veterans.

Fawn Sharp is a Native American politician, attorney, and policy advocate who served as president of the National Congress of American Indians (NCAI) from 2019 to 2023. Prior to this position, Sharp served as president of the Quinault Indian Nation, as president of the Affiliated Tribes of Northwest Indians, and as vice president of the National Congress of American Indians.
References
- Lawney L. Reyes, Bernie Whitebear: An Urban Indian's Quest for Justice, University of Arizona, 2006. ISBN 0-8165-2521-8. ISBN 978-0-8165-2521-8.