
Harpers Ferry is a historic town in Jefferson County, West Virginia, in the lower Shenandoah Valley. The town's population was 269 at the 2020 United States census. Situated at the confluence of the Potomac and Shenandoah rivers, where Maryland, Virginia, and West Virginia meet, it is the easternmost town in West Virginia.

John Daniel Imboden, American lawyer, Virginia state legislator, and a Confederate army general. During the American Civil War, he commanded an irregular cavalry force. After the war, he resumed practicing law, became a writer, and was active in land development founding the town of Damascus, Virginia.

Harpers Ferry National Historical Park, originally Harpers Ferry National Monument, is located at the confluence of the Potomac and Shenandoah rivers in and around Harpers Ferry, West Virginia. The park includes the historic center of Harpers Ferry, notable as a key 19th-century industrial area and as the scene of John Brown's failed abolitionist uprising. It contains the most visited historic site in the state of West Virginia, John Brown's Fort.

The Fayetteville Rifle was a 2 banded rifle produced at the Confederate States Arsenal in Fayetteville, North Carolina. The machinery which produced these weapons was primarily that captured at the United States Arsenal at Harpers Ferry, Virginia, which was previously used to produce the US Model 1855 Rifle.

The Fayetteville Arsenal in Fayetteville, North Carolina was built in 1838 because during the War of 1812 the United States government realized that the existing distribution of weapons and ammunition factories was not adequate for the defense of the country. A program was begun to provide more Federal arsenals which would be distributed so that no area of the country would be too far away from an arms depot. Bladen County Representative James McKay introduced House Resolution #374 for inclusion of an arsenal at Fayetteville.

Josiah Gorgas was a Confederate general in the American Civil War and was later president of the University of Alabama.

Dixon Stansbury Miles was a career United States Army officer who served in the Mexican–American War and the Indian Wars. He was mortally wounded as he surrendered his Union garrison in the Battle of Harpers Ferry during the American Civil War.
Edwards Lucas was a nineteenth-century politician, lawyer and military officer from western Virginia, who served in the War of 1812, the Virginia House of Delegates and the U.S. House of Representatives before becoming superintendent of the military arsenal at Harpers Ferry (1837-1841) and then its paymaster until his death. His younger brother William Lucas would also later hold the redistricted congressional seat.

During the American Civil War, Arkansas was a Confederate state, though it had initially voted to remain in the Union. Following the capture of Fort Sumter in April 1861, Abraham Lincoln called for troops from every Union state to put down the rebellion, and Arkansas along with several other southern states seceded. For the rest of the civil war, Arkansas played a major role in controlling the Mississippi River, a major waterway.

Colonel Stonewall Jackson's operations against the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad in 1861 were aimed at disrupting the critical railroad used heavily by the opposing Union Army as a major supply route. A second goal was to capture the maximum number of locomotives and cars for use in the Confederate States of America. During this point in the war, the state of Maryland's stance was not yet determined. The B&O Railroad, then owned by the state of Maryland, ran through Maryland and along the Potomac River Valley in its pass through the Appalachian Mountains, but took a crucial turn at Harpers Ferry and passed south, through Virginia and Martinsburg while crossing the Shenandoah Valley. The railroad then continued on through much of present-day West Virginia, which then was still part of Virginia, meaning that a major portion of the route went through a state which later seceded.

The Harpers Ferry Armory, more formally known as the United States Armory and Arsenal at Harpers Ferry, was the second federal armory created by the United States government; the first was the Springfield Armory. It was located in Harpers Ferry, Virginia, which since 1863 has been part of West Virginia. It was both an arsenal, manufacturing firearms, and an armory, a storehouse for firearms. Along with the Springfield Armory, it was instrumental in the development of machining techniques to make interchangeable parts of precisely the same dimensions.

The Richmond rifle was a rifled musket produced by the Richmond Armory in Richmond, Virginia, for use by the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War.

Heritage Square is a place in Fayetteville, North Carolina. Owned and maintained by The Woman's Club of Fayetteville, Heritage Square includes the Sandford House, built in 1797; the Oval Ballroom, a freestanding single room built in 1818; and the Baker-Haigh-Nimocks House, constructed in 1804. The buildings located on Heritage Square are listed in the National Register of Historic Places as the "Fayetteville Woman's Club and Oval Ballroom" and "Nimocks House."

Elliott Daingerfield (1859–1932) was an American artist who lived and worked in North Carolina. He is considered one of North Carolina's most prolific artists.

John Brown's raid on Harpers Ferry was an effort by abolitionist John Brown, from October 16 to 18, 1859, to initiate a slave revolt in Southern states by taking over the United States arsenal at Harpers Ferry, Virginia. It has been called the dress rehearsal for, or tragic prelude to, the American Civil War.
Alfred Madison Barbour was a Virginia lawyer, one-term delegate in the Virginia House of Delegates and also in the Virginia Secession Convention of 1861. He may be best known for his role as Superintendent of the Harpers Ferry Armory in Harpers Ferry, Virginia during John Brown's raid. Although Barbour voted against secession, he became a major in the Confederate States Army and served as a quartermaster during the American Civil War.
Kenton Harper was an American newspaper editor, soldier, Indian agent, plantation owner, banker and politician. An officer of the Virginia militia then U.S. Army during the Mexican–American War, Harper later became a Confederate general officer during the American Civil War, and reportedly helped nickname Stonewall Jackson.
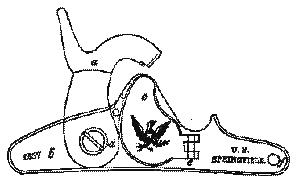
The Springfield Model 1855 was a rifled musket widely used in the American Civil War. It exploited the advantages of the new conical Minié ball, which could be deadly at over 1,000 yards (910 m). It was a standard infantry weapon for Union and Confederates alike, until the Springfield Model 1861 supplanted it, obviating the use of the insufficiently weather resistant Maynard tape primer.

Cross Creek Cemetery is a cemetery located in Fayetteville, North Carolina, near a creek of that name that "meanders for more than a mile from downtown Fayetteville to the Cape Fear River." It was established in 1785. The cemetery is organized into five numbered sections and is managed by a cemetery office within Fayetteville–Cumberland County Parks & Recreation.

Julius Adolphus De Lagnel, was a Confederate States Army officer, who was appointed and confirmed as a brigadier general, during the American Civil War, but who declined the appointment. He was second in command to Brigadier General Josiah Gorgas in the Confederate Ordnance Bureau and at times was an inspector of arsenals. Before the war, he served in the United States Army from March 8, 1847, until May 17, 1861. After the war, he was engaged in Pacific steamship service.

















