
A grain elevator is a facility designed to stockpile or store grain. In the grain trade, the term "grain elevator" also describes a tower containing a bucket elevator or a pneumatic conveyor, which scoops up grain from a lower level and deposits it in a silo or other storage facility.

Willis Haviland Carrier was an American engineer, best known for inventing modern air conditioning. Carrier invented the first electrical air conditioning unit in 1902. In 1915, he founded Carrier Corporation, a company specializing in the manufacture and distribution of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems.

William Henry "Whoop-La" White was an American baseball pitcher and manager from 1875 to 1889. He played all or parts of 10 seasons in Major League Baseball, primarily for the Cincinnati Reds in the National League (1878–1879) and the Cincinnati Red Stockings in the American Association (1882–1886). He had three 40-win, and one 40-loss, seasons in Cincinnati. During the 1882 and 1883 seasons, he led the American Association in wins, compiling an 83–34 win–loss record and a 1.84 earned run average (ERA).

John Cornelius Butler was a Republican politician from New York. He was most notable for his service as a member of the United States House of Representatives from 1941 to 1949 and 1951 to 1953.

Buffalo is the county seat of Erie County, and the second most populous city in the U.S. state of New York, after New York City. Originating around 1789 as a small trading community inhabited by the Neutral Nation near the mouth of Buffalo Creek, the city, then a town, grew quickly after the opening of the Erie Canal in 1825, with the city at its western terminus. Its position at the eastern end of Lake Erie strengthened the economy, based on grain milling and steel production along the southern shores and in nearby Lackawanna.

William Thornton Kemper Sr. was an American banker who was the patriarch of the Missouri Kemper family, which developed both Commerce Bancshares and United Missouri Bank to become a major banking family in the Midwest.

The Port of Albany–Rensselaer, widely known as the Port of Albany, is a port of entry in the United States with facilities on both sides of the Hudson River in Albany and Rensselaer, New York. Private and public port facilities have existed in both cities since the 17th century, with an increase in shipping after the Albany Basin and Erie Canal were built with public funds in 1825.

John Baker Manning was Mayor of the City of Buffalo, New York, serving during January 1883 – 1884, in the aftermath of the resignation of Grover Cleveland.

Concrete-Central Elevator is a historic grain elevator located on the Buffalo River at 175 Buffalo River Buffalo in Erie County, New York.

Wollenberg Grain and Seed Elevator was a historic grain and seed elevator located at Buffalo in Erie County, New York. It was built in 1912 and remained in service until 1987. It was notable as the sole surviving example of a wooden or so-called "country style" elevator. It was built in the style of the earliest elevators dating to the 1840s and had a capacity of 25,000 bushels.

The Cargill Pool Elevator is a grain storage facility in Buffalo harbor built in the 1920s and previously named the Saskatchewan Cooperative Elevator. The elevator is the only grain elevator in Buffalo that is located directly adjacent to Lake Erie.

The Great Northern Elevator was a grain storage facility at 250 Ganson Street in Buffalo, New York. The elevator was located on the City Ship Canal and at the time of its completion in 1897, the elevator was the world's largest. The elevator was the first to employ cylindrical steel bins for grain storage, and also one of the first to run on electricity. The brick curtain wall did not support the bins or the working house and was designed as weatherproofing only.

The Red Hook Grain Terminal is an abandoned grain elevator in the Red Hook neighborhood of Brooklyn, New York City, adjacent to the mouth of the Gowanus Canal. It is 12 stories tall, 70 feet (21 m) wide, and 429 feet (131 m) long, containing sixty 120-foot-tall (37 m) cement silos. As the neighborhood's tallest structure, it is highly visible from the elevated Gowanus Expressway and New York City Subway's IND Culver Line viaducts over the Gowanus Canal.
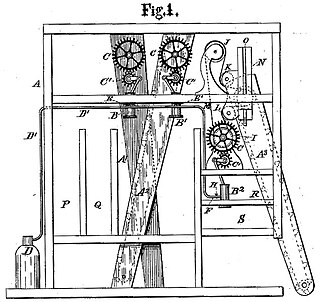
Robert Dunbar was a Scottish mechanical engineer. He designed the first steam-powered grain elevator in the world and the majority of the first grain elevators in Buffalo, New York City, and Canada.

George Armour was a Scottish American businessman and philanthropist known for his contributions to the global distribution process for commodities. He was credited with developing the grain elevator system, establishing grain trading standards as director and president of the Chicago Board of Trade (CBT), founding the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad (CBQ), Commercial Club of Chicago, YMCA of Chicago, Merchants' Loan & Trust Company (MLTC), the precursor to Continental Illinois, and the Chicago Academy of Fine Arts which later became the School of the Art Institute of Chicago and Art Institute of Chicago. He served as a director of several notable companies during his career.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Buffalo, New York, United States.

The Erie Basin Marina is a municipal inland harbor in Buffalo, New York. The marina is primarily for residential usage, containing a large array of boat docks, gardens, and a public observatory overlooking the city and waterfront. The marina's harbor discharges into the Niagara River and Lake Erie.

Isaac R. Harrington was a prominent businessman and entrepreneur in Burlington, Vermont and Buffalo, New York. He became active in politics as a Whig and served as mayor of Buffalo from 1841 to 1842.

PS Keystone State was a wooden-hulled American paddle steamer in service between 1849 and 1861. She was built in 1848 in Buffalo, New York, by Bidwell & Banta for ship-owner Charles M. Reed of Erie, Pennsylvania, and operated as part of his "Chicago Line". A luxuriously furnished palace steamer, she operated between Buffalo and Chicago, Illinois, while also making stops at various other ports. She was built for the passenger and package freight trade, frequently carrying both wealthy passengers and European immigrants who desired to settle in the Midwestern United States. Due to the Panic of 1857, Keystone State and several other paddle steamers were laid up. When the American Civil War began in 1861; she was refurbished, and put back into service.




















