
Presidio is a city in Presidio County, Texas, United States. It is situated on the Rio Grande River, on the opposite side of the U.S.–Mexico border from Ojinaga, Chihuahua. The name originates from Spanish and means "fortress". The population was 4,169 at the 2000 census, and had increased to 4,426 as of the 2010 US census.

The city of Chihuahua or Chihuahua City is the state capital of the Mexican state of Chihuahua. As of 2020, the city of Chihuahua had a population of 925,762 inhabitants. while the metropolitan area had a population of 988,065 inhabitants.
Monclova, is a city and the seat of the surrounding municipality of the same name in the northern Mexican state of Coahuila. According to the 2015 census, the city had 231,107 inhabitants. Its metropolitan area has 381,432 inhabitants and a population density of 29.88 inhabitants per square kilometer. Monclova is the third-largest city and metropolitan area in the state in terms of population, after Torreón and Saltillo.

Chihuahua is a state in Northwest Mexico that is divided into 67 municipalities. According to the 2020 Mexican census, Chihuahua is the 12th most populous state with 3,741,869 inhabitants and the largest by land area spanning 247,798.08 square kilometres (95,675.37 sq mi).
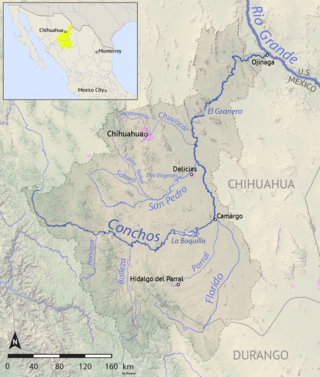
The Río Conchos is a large river in the Mexican state of Chihuahua. It joins the Río Bravo del Norte at the town of Ojinaga, Chihuahua.
Federal Highway 2 is a free part of the Mexican federal highway corridors that runs along the U.S. border. The highway is in two separate improved segments, starting in the west at Tijuana, Baja California, on the Pacific coast and ending in the east in Matamoros, Tamaulipas, on the Gulf of Mexico. Fed. 2 passes through the border states of Baja California, Sonora, Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo Leon and Tamaulipas. It has a total length of 1,987 kilometres (1,235 mi); 1,343 kilometres (835 mi) in the west and 644 kilometres (400 mi) in the east.

Cuauhtémoc is a city located in the west-central part of the Mexican state of Chihuahua. It serves as the seat of the municipality of Cuauhtémoc. The city lies 103 km (64 mi) west of the state capital of Chihuahua. As of 2015, the city of Cuauhtémoc had a population of 168,482. 3 languages are recognized as official in the city: Spanish, English, and Plautdietsch.
La Entrada al Pacífico is a trade corridor designated as "Trade Corridor 56" by the Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act. The corridor is an international project between Mexico and the United States as a route from the Pacific Ocean port of Topolobampo in the Mexican state of Sinaloa to the U.S. state of Texas and beyond by way of the Midland-Odessa area. There is also a proposed upgrade of the rail connection, which might be easier by not requiring the addition of new bridges and tunnels in the Barranca de Cobre region. Its canyons are comparable in depth to the Grand Canyon in the United States.

Chicoloapan de Juárez is the municipal seat and largest city in the municipality of Chicoloapan in State of Mexico, Mexico. It is located in the eastern part of the state, just east of Chimalhuacán and northeast of the Federal District, within the Greater Mexico City urban area.

Pablo Acosta Villarreal, commonly referred to as El Zorro de Ojinaga was a Mexican narcotics smuggler who controlled crime along a 200-mile stretch of U.S.-Mexico border. At the height of his power, he was smuggling 60 tons of cocaine per year for Colombian cartels in addition to the large quantities of marijuana and heroin that were the mainstay of his business. He was the mentor and business partner of Amado Carrillo Fuentes, the "Lord of the Skies", who took over after Acosta's death.
Garitas or retenes are federal inspection stations operated by the Mexican government. They are officially known as "garitas de revisión" (checkpoints). They are usually located within 50 kilometres (31 mi) of the national border with the United States, Belize, and Guatemala. They function as immigration checkpoints, where documents and cargo are to be inspected.

Ojinaga is a town and seat of the municipality of Ojinaga, in the northern Mexican state of Chihuahua. As of 2015, the town had a total population of 28,040. It is a rural border town on the U.S.-Mexico border, with the city of Presidio, Texas, directly opposite, on the U.S. side of the border. Ojinaga is situated where the Río Conchos drains into the Río Grande, an area called La Junta de los Rios. Presidio and Ojinaga are connected by the Presidio-Ojinaga International Bridge and the Presidio–Ojinaga International Rail Bridge.
The Presidio–Ojinaga International Bridge, also known simply as the Presidio Bridge and Puente Ojinaga, is an international bridge that crosses the Rio Grande between the cities of Presidio, Texas, and Ojinaga, Chihuahua, on the United States–Mexico border. It connects U.S. Route 67 to the north with Mexican Federal Highway 16 to the south. The bridge is privately owned and is tolled. It was completed and opened in 1985. The bridge is two lanes wide and 791 feet (241 m) long.

The Fifth Federal Electoral District of Chihuahua(V Distrito Electoral Federal de Chihuahua) is one of the 300 Electoral Districts into which Mexico is divided for the purpose of elections to the federal Chamber of Deputies and one of nine such districts in the state of Chihuahua.
Federal Highway 16 is a free part of the federal highways corridors of Mexico.

Chihuahua, officially the Estado Libre y Soberano de Chihuahua, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It is located in the northwestern part of Mexico and is bordered by the states of Sonora to the west, Sinaloa to the southwest, Durango to the south, and Coahuila to the east. To the north and northeast, it shares an extensive border with the U.S. adjacent to the U.S. states of New Mexico and Texas. The state was named after its capital city, Chihuahua City; the largest city is Ciudad Juárez.

The Samalayuca Dune Fields, more traditionally known as Los Médanos, or more recently referenced as Médanos de Samalayuca are a series of large but separated fields of sand dunes located in the northern part of the Mexican state of Chihuahua. The dune fields are scattered over a wide expanse of desert to the south, southwest and southeast of Ciudad Juárez. The dune fields are located in a 2000 km2 area known as the Samalayuca Desert.
José Luis Ortega Mata was a Mexican journalist and director of the Semanario de Ojinaga, a weekly newspaper based in Ojinaga, Chihuahua in northern Mexico.

The Cañón de Santa Elena Flora and Fauna Protection Area is a protected area for plants and wildlife in the Mexican municipalities of Manuel Benavides and Ojinaga, in the state of Chihuahua. It was founded on November 7, 1994 and has an area of 277,209 hectares.

The Battle of Ojinaga, also known as the Taking of Ojinaga, was one of the battles of the Mexican Revolution and was fought on January 11, 1914. The conflict put an end to the last stronghold of the Federal Army in Northern Mexico.














