
Southern California is a geographic and cultural region that generally comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. It includes the Los Angeles metropolitan area as well as the Inland Empire. The region generally contains ten of California's 58 counties: Los Angeles, San Diego, Orange, Riverside, San Bernardino, Kern, Ventura, Santa Barbara, San Luis Obispo, and Imperial counties.

Greater Los Angeles is the most populous metropolitan area in the U.S. state of California, encompassing five counties in Southern California extending from Ventura County in the west to San Bernardino County and Riverside County in the east, with Los Angeles County in the center, and Orange County to the southeast. The Los Angeles–Anaheim–Riverside combined statistical area (CSA) covers 33,954 square miles (87,940 km2), making it the largest metropolitan region in the United States by land area. The contiguous urban area is 2,281 square miles (5,910 km2), whereas the remainder mostly consists of mountain and desert areas. With an estimated population of over 18.3 million, it is the second-largest metropolitan area in the country, behind New York, as well as one of the largest megacities in the world.

Fontana is a city in San Bernardino County, California, United States. Founded by Azariel Blanchard Miller in 1913, it remained essentially rural until World War II, when entrepreneur Henry J. Kaiser built a large steel mill in the area. It is now a regional hub of the trucking industry, with the east–west Interstate 10 and State Route 210 crossing the city and Interstate 15 passing diagonally through its northwestern quadrant. The city is about 46 miles (74 km) east of Los Angeles.

The Pomona Valley is located in the Greater Los Angeles Area between the San Gabriel Valley and San Bernardino Valley in Southern California. The valley is approximately 30 miles (48 km) east of downtown Los Angeles.

The Cucamonga Valley is a region of southwestern San Bernardino County and northwestern Riverside County, in southern California. It is located below the San Gabriel Mountains in the Inland Empire region.

The San Bernardino Valley is a valley in Southern California located at the south base of the Transverse Ranges. It is bordered on the north by the eastern San Gabriel Mountains and the San Bernardino Mountains; on the east by the San Jacinto Mountains; on the south by the Temescal Mountains and Santa Ana Mountains; and on the west by the Pomona Valley. Elevation varies from 590 feet (180 m) on valley floors near Chino to 1,380 feet (420 m) near San Bernardino and Redlands. The valley floor is home to over 80% of the more than 4 million people in the Inland Empire region.
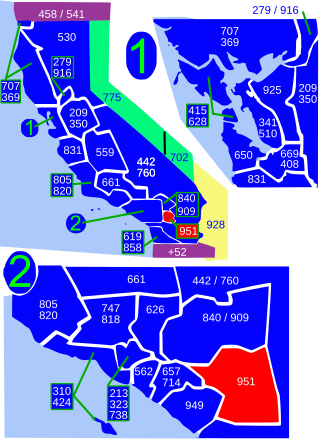
Area code 951 is a telephone area code in the North American Numbering Plan for western Riverside County in the southern part of the U.S. state of California. It was assigned in 2004 to a new numbering plan area that was created by an area code split of area code 909.

California's 35th congressional district is a U.S. congressional district in California. The district is currently represented by Democrat Norma Torres.

Route 15, consisting of the contiguous segments of State Route 15 (SR 15) and Interstate 15 (I-15), is a major north–south state highway and Interstate Highway in the U.S. state of California, connecting San Bernardino, Riverside, and San Diego Counties. The route consists of the southernmost 289.24 miles (465.49 km) of I-15, which extends north through Nevada, Arizona, Utah, Idaho, and Montana to the Canada–US border. It is a major thoroughfare for traffic between San Diego and the Inland Empire, as well as between Southern California, Las Vegas, Nevada, and the Intermountain West.
California's State Assembly districts are numbered 1st through 80th, generally in north-to-south order.

Fontana Unified School District is located in and serves most of the city of Fontana, California, a community in San Bernardino County about 50 miles east of Los Angeles. The district contains 45 schools, which serve students from K-12 to adult education. It was established in the 1920s and unified in 1956.
The Southern California Association of Governments (SCAG) is the Metropolitan Planning Organization (MPO) of six of the ten counties in Southern California, serving Imperial County, Los Angeles County, Orange County, Riverside County, San Bernardino County, and Ventura County. San Diego County's MPO is the San Diego Association of Governments, which is an unrelated agency.
The San Jose Hills are a part of the Transverse Ranges in eastern Los Angeles County, California, marking the border between the San Gabriel Valley and the Pomona Valley. It includes portions of Covina, West Covina, Walnut, Pomona, and San Dimas. To the south, the valley of San Jose Creek separates the San Jose Hills from the Puente Hills and Chino Hills.

Mount Jurupa is the highest point of the Jurupa Mountains, located in northwestern Riverside County, California. The summit is just south of the Riverside – San Bernardino county line. A hiking trail leads to its summit, which offers panoramic views of Riverside, Fontana, San Bernardino, and Moreno Valley.
Declezville is a formerly unincorporated community in southwestern San Bernardino County, in the Inland Empire region of southern California. Today, it is located within the city limits of Fontana.

Many of the existing freeways in Southern California's Inland Empire were completed in the late 1970s. The only exception is the segment of the Foothill Freeway, State Route 210 between San Dimas and San Bernardino, completed in July 2007. In general, most of the higher paying jobs are located in Los Angeles and Orange County. Thus, workers must commute daily up to two hours in each direction on the existing network. As the population increases, traffic congestion is also projected to increase. In 2007, Forbes magazine ranked the area first in its list of America's most unhealthy commutes, beating every other major metropolitan area in the country, as Inland area drivers breathe the unhealthiest air and have the highest rate of fatal auto accidents per capita.

Riverside County is a county located in the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 2,418,185, making it the fourth-most populous county in California and the 10th-most populous in the United States. The name was derived from the city of Riverside, which is the county seat.

Chino Creek is a major stream of the Pomona Valley, in the western Inland Empire region of Southern California. It is a tributary of the Santa Ana River.

Jurupa Valley is a city in the northwest corner of Riverside County, California, United States. It was the location of one of the earliest non-native settlements in the county, Rancho Jurupa. The Rancho was initially an outpost of the Mission San Gabriel Arcángel, then a Mexican land grant in 1838. The name is derived from a Native American village that existed in the area prior to the arrival of Europeans.
The Perris Block is the central block of three major fault-bounded blocks of the northern part of the Peninsular Ranges. The Perris Block lies between the Santa Ana Block to the west and the San Jacinto Block to the east. The Perris Block, was named by Walter A. English in 1925 for the city of Perris, located near the center of the block.
















