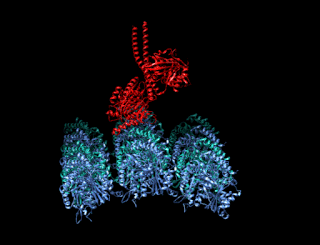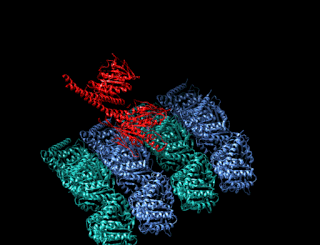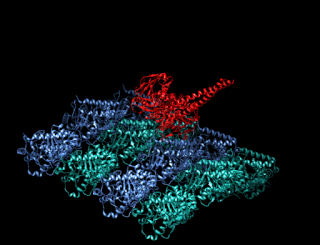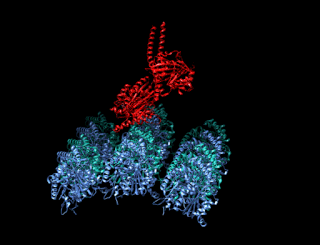
A kinesin is a protein belonging to a class of motor proteins found in eukaryotic cells.
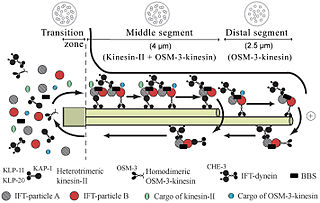
Intraflagellar transport or IFT is a bidirectional motility along axonemal microtubules that is essential for the formation (ciliogenesis) and maintenance of most eukaryotic cilia and flagella. It is thought to be required to build all cilia that assemble within a membrane projection from the cell surface. Plasmodium falciparum cilia and the sperm flagella of Drosophila are examples of cilia that assemble in the cytoplasm and do not require IFT. The process of IFT involves movement of large protein complexes called IFT particles or trains from the cell body to the ciliary tip and followed by their return to the cell body. The outward or anterograde movement is powered by kinesin-2 while the inward or retrograde movement is powered by cytoplasmic dynein 2/1b. The IFT particles are composed of about 20 proteins organized in two subcomplexes called complex A and B.

Kinesin-like protein KIF23 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF23 gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIF1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF1B gene.

Kinesin-1 heavy chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF5B gene.

Kinesin light chain 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLC1 gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIF22 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF22 gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIF2C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF2C gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIF3A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF3A gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIF20A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF20A gene.

Kinesin-associated protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIFAP3 gene. It is a non-motor, accessory subunit which co-oligomerizes with the motor subunits KIF3A and KIF3B or KIF3C, to form heterotrimeric kinesin-2 motor proteins. Kinesin-2 KAP subunits were initially characterized in echinoderms and mice.

Kinesin family member 3B (KIF3B) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF3B gene. KIF3B is an N-type protein that complexes with two other kinesin proteins to form two-headed anterograde motors. First, KIF3B forms a heterodimer with KIF3A (kinesin family member 3A;, that is membrane-bound and has ATPase activity. Then KIFAP3 binds to the tail domain to form a heterotrimeric motor. This motor has a plus end-directed microtubule sliding activity that exhibits a velocity of ∼0.3 μm/s a. There are 14 kinesin protein families and KIF3B is part of the Kinesin-2 family, of kinesins that can all form heterotrimeric complexes. Expression of the three motor subunits is ubiquitous. The KIG3A/3B/KAP3 motors can transport 90 to 160 nm in diameter organelles.

Kinesin heavy chain isoform 5A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF5A gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIFC1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIFC1 gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIF13A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF13A gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIF2A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF2A gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIF1A, also known as axonal transporter of synaptic vesicles or microtubule-based motor KIF1A, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF1A gene.

Kinesin-5 is a molecular motor protein that is essential in mitosis. Kinesin-5 proteins are members of kinesin superfamily, which are nanomotors that move along microtubule tracks in the cell. Named from studies in the early days of discovery, it is also known as kinesin family member 11, encoded by the KIF11 gene, or as BimC, Eg5 or N-2, based on the founding members of this kinesin family. The term kinesin-5 has been recommended based on a standardized nomenclature adopted by the scientific community.

Kinesin family member 15 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF15 gene.
Nobutaka Hirokawa is a Japanese neuroscientist and cell biologist famous for research on the Kinesin superfamily of motor proteins. He has been President and Chair of the Board of Trustees at the Human Frontier Science Program since 2012.




















