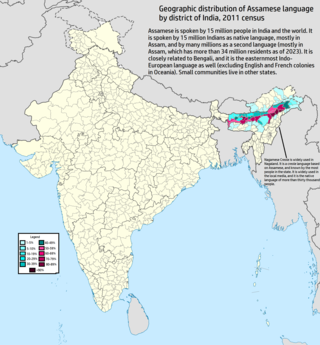
Assamese or Asamiya is an Indo-Aryan language spoken mainly in the north-eastern Indian state of Assam, where it is an official language. It serves as a lingua franca of the wider region and has over 15 million native speakers according to Ethnologue.

Kamarupi Prakrit is the postulated Middle Indo-Aryan (MIA) Prakrit language used in ancient Kamarupa. This language has been derived from Gauda-Kamarupi Prakrit and the historical ancestor of the Kamatapuri lects and the modern Assamese language; and can be dated prior to 1250 CE, when the proto-Kamta language, the parent of the Kamatapuri lects, began to develop. Though not substantially proven, the existence of the language that predated the Kamatapuri lects and modern Assamese is widely believed to be descended from it.

Cooch Behar district is a district of the Indian state of West Bengal.

The Khen dynasty of Assam was a late medieval dynasty of the erstwhile Kamata kingdom. After the fall of the Pala dynasty of Kamrupa, the western region was reorganized into the Kamata kingdom when Sandhya moved his capital from Kamarupanagara to Kamatapur in about 1257 due to the frequent clashes with the Kacharis from the east. Sandhya styled himself Kamateswara and the kingdom came to be known as "Kamata". The Khen dynasty at a later period took control of the kingdom.

The Kamata Kingdom emerged in western Kamarupa probably when Sandhya, a ruler of Kamarupanagara, moved his capital west to Kamatapur sometime after 1257 CE. Since it originated in the old seat of the Kamarupa kingdom, and since it covered most of the western parts of it, the kingdom is also sometimes called as Kamarupa-Kamata.
Kamtapur is an autonomous area in the Assam state of India administered by the Kamatapur Autonomous Council.
Goalpariya is a group of Indo-Aryan dialects spoken in the Goalpara region of Assam, India. Along with Kamrupi, they form the western group of Assamese dialects. The North Bengali dialect is situated to its west, amidst a number of Tibeto-Burman speech communities. The basic characteristic of the Goalpariya is that it is a composite one into which words of different concerns and regions have been amalgamated. Deshi people speak this language and there are around 20 lakhs people.
Magadhi Prakrit (Māgadhī) is of one of the three Dramatic Prakrits, the written languages of Ancient India following the decline of Pali. It was a vernacular Middle Indo-Aryan language, replacing earlier Vedic Sanskrit.

Rangpuri is an eastern Indo-Aryan language of the Bengali-Assamese branch, spoken in Rangpur Division in Bangladesh, northern West Bengal and western Goalpara of Assam in India. Many are bilingual in Bengali and Assamese in their respective regions. According to Glottolog, it forms the Central-Eastern Kamta group with the Kamta language. Together with Rajbanshi and Surjapuri they form the Kamta group of languages.

The Eastern Indo-Aryan languages, also known as Māgadhan languages, are spoken throughout the eastern region of the subcontinent, which includes Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand, Bengal region, Tripura, Assam, and Odisha; alongside other regions surrounding the northeastern Himalayan corridor. Bengali is official language of Bangladesh and the state of West Bengal, Tripura and the Barak valley of Assam while Assamese and Odia are the official languages of Assam and Odisha, respectively. The Eastern Indo-Aryan languages descend from Abahattha, which descends from Magadhan Apabhraṃśa and ultimately from Magadhi Prakrit.

The Nashya Shaikh or Nashya Sekh is a Muslim community found in northern parts of the state of West Bengal in India. They are culturally and linguistically similar to both people of northern Bangladesh and Goalpara of Assam. A small number of the community are also found in the neighboring state of Bihar, where they are known as the Bengali Shaikh. The group is descended from a set of tribals which were collectively referred to as Koches, who converted to Islam as they were unable to find a favourable position in Hindu society and came to be known as the Rajbanshi Muslims. They are homogeneous with the Koch people and are bilingual, speaking both Bengali and Surjapuri.

The Rajbanshi, also Rajbongshi and Koch-Rajbongshi, are peoples from Lower Assam, North Bengal, eastern Bihar, Terai region of eastern Nepal, Rangpur division of North Bangladesh and Bhutan who have in the past sought an association with the Koch dynasty. Koch-Rajbanshi people speak Kamatapuri, belong to Indo-Aryan languages likely due to language shift, and in the past they might have spoken Tibeto-Burman languages. The community is categorised as OBC in Assam and Bihar, and SC in West Bengal. In Nepal they are considered part of the Plains Janjati. In Bangladesh the community is classified as Plains ethnic group under 'Barman'. They are the largest Scheduled Caste community of West Bengal.
Surjapuri is an Indo-Aryan language of the Bengali-Assamese branch, spoken in Eastern India including North Bengal, West Bengal, and some eastern parts of Purnia division of Bihar, as well as Jhapa District in Nepal, Goalpara Division of Assam in India and Rangpur Division in Bangladesh. Among speakers in some regions, it is known as 'Deshi Bhasa'. It possesses similarities with Kamatapuri, Assamese, Bengali, and Maithili.
Gosanimari is both a village and an archaeological site in Dinhata I CD block, in the Dinhata subdivision of the Cooch Behar district of West Bengal, north-eastern India. The name of this site was taken from the modern grampanchyat name of the Dinhata subdivision.
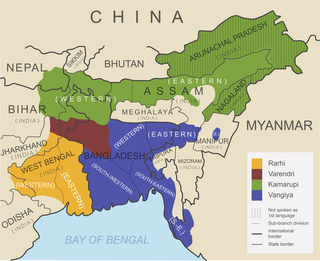
The Assamese-Bengali languages is a grouping of several languages in the eastern Indian subcontinent. This group belongs to the Eastern zone of Indo-Aryan languages. The languages in this group according to Glottolog includes Assamese, Bengali, Bishnupriya, Chakma, Chittagonian, Hajong, Kharia Thar, Kurmukar, Lodhi, Mal Paharia, Noakhailla, Rajbangshi, Rohingya, Sylheti, Tangchangya and Surjapuri.
Goalpara region, largely congruous to the historical undivided Goalpara district, is a region that is associated with the people and culture of Goalpara. It is bounded on the north by Bhutan, on the east by the Kamrup region, in the south by Meghalaya and in the west by Cooch Behar and Jalpaiguri in West Bengal and Rangpur in Bangladesh. The natural landmarks are: Sankosh and Brahmaputra rivers on the west, the Manas River on the east in the north bank, and a corresponding region in the south bank; the Garo Hills in the south and Bhutan Hills in the north.

Nilambar or Nīlambara was the last Khen ruler or Kamadeswar of the Kamata kingdom in Western Assam and North Bengal. He ruled from the city of Kamatapur.

Early Assamese or Proto-Eastern Kamarupa is an ancestor of the modern Assamese language. It is found in the literature from the 14th century to the end of 16th century in Kamata kingdom and rest the Brahmaputra valley of Assam.
Rajbanshi is a Bengali-Assamese language spoken in Nepal. It is related to, but distinct from Rangpuri/Kamta in Bangladesh and India, which is also known by the alternative name "Rajbanshi", with which it forms the KRNB cluster.
Sandhya was a king of Kamarupa in north-eastern India in the present-day state of Assam, India. He founded the Kamata Kingdom when he moved his capital west to Kamatapur sometime after 1257 CE.











