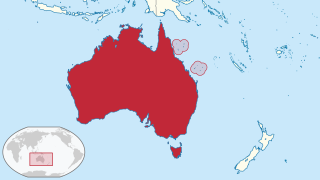
The Coral Sea Islands Territory is an external territory of Australia which comprises a group of small and mostly uninhabited tropical islands and reefs in the Coral Sea, northeast of Queensland, Australia. The only inhabited island is Willis Island. The territory covers 780,000 km2 (301,160 sq mi), most of which is ocean, extending east and south from the outer edge of the Great Barrier Reef and includes Heralds Beacon Island, Osprey Reef, the Willis Group and fifteen other reef/island groups. Cato Island is the highest point in the Territory.

The Turks and Caicos Islands are a British Overseas Territory consisting of the larger Caicos Islands and smaller Turks Islands, two groups of tropical islands in the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean and northern West Indies. They are known primarily for tourism and as an offshore financial centre. The resident population was 31,458 in 2012, of whom 23,769 lived on Providenciales in the Caicos Islands; July 2020 estimates put the population at 55,926. It is the third largest of the British overseas territories by population.

Villa Clara is one of the provinces of Cuba. It is located in the central region of the island bordering with the Atlantic at north, Matanzas Province by west, Sancti Spiritus Province by east, and Cienfuegos Province on the South. Villa Clara shares with Cienfuegos and Sancti Spiritus on the south the Escambray Mountain Range. Its main cities are Santa Clara, Remedios, Sagua La Grande, Camajuani, Caibarién, Ranchuelo, Placetas, and Manicaragua.

The Cay is a teen novel written by Theodore Taylor. It was published in 1969.

Southwest Cay, also known as Vietnamese: Đảo Song Tử Tây; Pugad Island ; Mandarin Chinese: 南子島/南子岛; pinyin: Nánzi Dǎo, is an islet on the northwestern edge of the Spratly Islands in the South China Sea. It is part of the atoll North Danger Reef, and just 1.75 miles (2.82 km) southwest of Northeast Cay. With an area of 12 hectares, it is the sixth largest of the naturally occurring Spratly Islands, and the second largest of the Vietnamese-occupied islands. Southwest Cay has the archipelago's highest point, at 4 meters above sea level. It was once a breeding place for birds, and was covered with trees and guano; export of guano had been carried out "on a considerable scale".

Guanaja is one of the Bay Islands of Honduras and is in the Caribbean. It is about 70 kilometres (43 mi) off the north coast of Honduras, and 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) from the island of Roatan. One of the cays off Guanaja, also called Guanaja or Bonacca or Low Cay, is near the main island, and contains most of the approximately 5,538 people who live in Guanaja. The densely populated cay has been described as the Venice of Honduras because of the waterways that run through it. The other two main settlements on Guanaja are Mangrove Bight and Savannah Bight. Smaller settlements includes Pelican Reef, East End and North East Bight.

Samana Cay is a now -uninhabited island in the Bahamas believed by some researchers to have been the location of Christopher Columbus's first landfall in the Americas on October 12, 1492.

Moore's Island is one of the districts of the Bahamas, on the Abaco Islands.

The fork-tailed flycatcher is a passerine bird of the tyrant flycatcher family, and is the member of a genus typically referred to as kingbirds. Named for their distinguishingly long forked tail, fork-tailed flycatchers are seen in lightly-forested or grassland areas; ranging from southern Mexico, to south past Argentina. They are most frequently observed sitting on conspicuous perches waiting for flying arthropods to fly past, they then sally out, eat their prey, and return to their perch. Northern populations near southern Mexico tend to be permanent residents, while fork-tailed flycatchers that live further south are migrants with a reputation to wander as far north as the eastern seaboard of the United States.

Northeast Cay, also known as Parola Island, with a land area of 12.7 hectares, is the fifth largest of the naturally occurring Spratly Islands and the third largest of the Philippine-occupied islands. It is part of the North Danger Reef and is located to the northwest of Dangerous Ground.

The following is an alphabetical list of articles related to the territory of the United States Virgin Islands.

The Prickly Pear Cays, sometimes spelt as Prickley Pear Cays, are a small pair of uninhabited islands about six miles from Road Bay, Anguilla, in the Leeward Islands of the Caribbean. They are divided by a narrow boat channel between Prickly Pear East and Prickly Pear West. Prickly Pear Cays were classified as 'wildlands' by the "Eastern Caribbean Natural Area Management Programme" (ECNAMP). In addition, Prickly Pear Cays are one of six marine protected areas of Anguilla.

The Tizard Bank, 10°15′N114°30′E, in Chinese known as 郑和群礁 and Zhenghe Qunjiao, is a partially sunken atoll and one of the significant maritime features of the north-western part of the Spratly Islands. It is claimed by the People's Republic of China, the Republic of China and Vietnam, and various parts of it are occupied by these states.

Saba Island is a rocky Caribbean island in the United States Virgin Islands, situated three miles south of the Cyril E. King Airport and 2.6 miles west of Water Island. It is a steep, 200 feet high island with a sandy beach on the northern side. Turtledove Cay is connected by a shallow sandbar. Saba Island has salt ponds on both the eastern and western sides, which is popular bird observation posts, and has numerous rocky cliffs with sea birds on its southern shores. Besides for bird observation, the island is visited by scuba divers and snorkelers. In addition to coral reefs, the waters here are home to numerous ship wrecks, such as the Witshoal II, Witconcrete II, Grainton, and Witservice IV.

Cas Cay is a fifty-acre (200,000-square-metre) undeveloped island, situated a mile south of Red Hook on the eastern side of Saint Thomas in the United States Virgin Islands. It is under the protection of the Department of Natural Resources. Ferries here depart from Compass Point Marina, right east of Nadir.

Steven Cay is a small scrub-covered and rocky Caribbean island, about 28 feet high and situated 0.5 miles west of Cruz Bay on Saint John in the United States Virgin Islands. It is a popular destination for snorkelers and scuba divers,.

Cinnamon Cay is a cay in the United States Virgin Islands, situated approximately 0.7 miles east of Trunk Cay in the Cinnamon Bay, and 100 yards from the shore at Cinnamon Bay Beach on Saint John island. It has a height of 32 feet. The islet is uninhabited, but regularly visited by scuba-divers, snorkelers and kayakers. Cinnamon Bay Watersports offers kayaks and snorkeling equipment for travelers to the cay. Cinnamon Cay is mostly covered with grass and cactus, and is located within the Virgin Islands National Park.

















