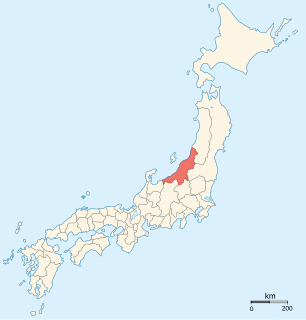
Niigata Prefecture is a prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshu. Niigata Prefecture has a population of 2,285,856 (2016) and is the fifth-largest prefecture of Japan by geographic area at 12,582 km2. Niigata Prefecture borders Toyama Prefecture and Nagano Prefecture to the southwest, Gunma Prefecture to the south, Fukushima Prefecture to the east, and Yamagata Prefecture to the northeast.

Gunma Prefecture is a prefecture of Japan located in the Kantō region. Its capital is Maebashi.

Sanjō is a city located in Niigata Prefecture, Japan. As of 30 September 2018, the city had an estimated population of 98,401 in 36,201 households, and a population density of 228 persons per km². The total area of the city was 431.97 square kilometres (166.78 sq mi).

The Hokuriku region was located in the northwestern part of Honshu, the main island of Japan. It lay along the Sea of Japan within the Chūbu region, which it is currently a part of. It is almost equivalent to Koshi Province and Hokurikudō area in pre-modern Japan. Due to its elongated shape, and the Noto Peninsula jutting out, the region is known as a 'rising dragon' 昇龍道. Since the Heian period until the Edo period the region was a core recipient of population, the population grew to be much larger proportionately than it is today, despite the rural character. With the growth of urban centers in the 20th century, particularly Tokyo and Chūkyō, the Hokuriku has steadily declined in importance to become relative backwaters. The region is also known for traditional culture that originated from elsewhere that has been long lost along the Taiheiyō Belt.

Yuzawa is a town located in Niigata Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 April 2018, the town had an estimated population of 8,074, and a population density of 23 persons per km². The total area of the town was 257.29 square kilometres (99.34 sq mi). The town is famous for its hot springs.

The Chūetsu earthquakes occurred in Niigata Prefecture, Japan, at 17:56 local time on Saturday, October 23, 2004. The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) named it the "Heisei 16 Niigata Prefecture Chuetsu Earthquake". Niigata Prefecture is located in the Hokuriku region of Honshu, the largest island of Japan. The initial earthquake had a magnitude of 6.6 and caused noticeable shaking across almost half of Honshu, including parts of the Tōhoku, Hokuriku, Chūbu, and Kantō regions.

The Joetsu Line is a major railway line in Japan, owned by the East Japan Railway Company. It connects Takasaki Station in Gunma Prefecture with Miyauchi Station in Niigata Prefecture, linking the northwestern Kanto region and the Sea of Japan coast of the Chūbu region. The name refers to the old provinces of Kōzuke (上野) and Echigo (越後), which the line connects.

Jōshin'etsu-kōgen National Park is a national park in the Chūbu region of the main island of Honshū, Japan formed around several active and dormant volcanoes. It spans the mountainous areas of Gunma, Nagano, and Niigata prefectures. The name refers to the two mountain ranges that make up the park. It was divided into two separate areas: the Southern Niigata/North Nagano Area and the East Nagano Area.

Takasaki is a city located in Gunma Prefecture, Japan. As of December 2015, the city had an estimated population of 371,750, and a population density of 810 persons per km2. Its total area is 459.16 square kilometres (177.28 sq mi). Takasaki is famous as the hometown of the Daruma doll, theoretically representing the Buddhist sage Bodhidharma and in modern practice a symbol of good luck.

Nagaoka is a city located in Niigata Prefecture, Japan. It is the second largest city in the prefecture, after the capital city of Niigata. As of 12 October 2018, the city had an estimated population of 271,444 in 107,374 households and a population density of 300 inhabitants per square kilometre (780/sq mi). The total area of the city was 891.06 square kilometres (344.04 sq mi).

The Shinetsu Main Line is a railway line, consisting of three geographically separated sections, operated by the East Japan Railway Company in Japan. It was originally one continuous line connecting Takasaki and Niigata via Nagano; however, with the opening of the Hokuriku Shinkansen, some sections were transferred to the third-sector railway companies or abandoned.

The Ban-etsu Expressway is a national expressway in the Tōhoku region of Japan. It is owned and operated by East Nippon Expressway Company.
Mikuni Kaidō (三国街道) was an ancient highway in Japan that stretched from Takasaki-juku on the Nakasendō to Teradomari-juku on the Hokuriku Kaidō.

National Route 18 is a national highway connecting Takasaki, Gunma and Joetsu, Niigata in Japan.

The Nagano Expressway is a 4-laned national expressway in Nagano Prefecture, Japan. It is owned and operated by East Nippon Expressway Company and Central Nippon Expressway Company.

Takasaki Station is a railway station located in Yashimachō, Takasaki, Gunma, Japan, operated by the East Japan Railway Company and the private railway operator Jōshin Dentetsu.

The Kita-Kantō Expressway is a 4-laned national expressway in Japan. It is owned and operated by East Nippon Expressway Company.

The Jōshin'etsu region is a region on the main Japanese island of Honshu, comprising parts of Gunma, Nagano, and Niigata Prefectures. It is a mountainous area with a large national park and numerous hot springs and ski resorts. It has long been a transportation corridor between the Kantō plain and coastal areas on the Japan Sea side of the island.