
The North American least shrew is one of the smallest mammals, growing to be only up to 3 inches long. It has a long pointed snout and a tail never more than twice the length of its hind foot. The dense fur coat is either grayish-brown or reddish-brown with a white belly. Its fur becomes lighter in the summer and darker in the winter. Although similar in appearance to several species of rodents, all shrews are members of the order Eulipotyphla and should not be mistaken for a member of the order Rodentia. The North American least shrew's eyes are small and its ears are completely concealed within its short fur, giving it very poor eyesight and hearing.
On Length and Shortness of Life is a text by the Ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle and one of the Parva Naturalia.

The Harivamsa is an important work of Sanskrit literature, containing 16,374 shlokas, mostly in the anustubh metre. The text is also known as the Harivamsa Purana. This text is believed to be a khila to the Mahabharata and is traditionally ascribed to Vyasa. The most celebrated commentary of the Mahabharata by Neelakantha Chaturdhara, the Bharata Bhava Deepa also covers the Harivamsa. According to a traditional version of the Mahabharata, the Harivamsa is divided into two parvas (books) and 12,000 verses. These are included with the eighteen parvas of the Mahabharata. The Critical Edition has three parvas and 5,965 verses.

Theileria is a genus of parasites that belongs to the phylum Apicomplexa, and is closely related to Plasmodium. Two Theileria species, T. annulata and T. parva, are important cattle parasites. T. annulata causes tropical theileriosis and T. parva causes East Coast fever. Theileria species are transmitted by ticks. The genomes of T. orientalis Shintoku, Theileria equi WA, Theileria annulata Ankara and Theileria parva Muguga have been sequenced and published.
Kauaiina is a genus of moths in the family Geometridae erected by Jules C. E. Riotte in 1978.
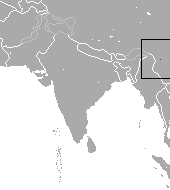
The pygmy brown-toothed shrew is a species of shrew in the order Eulipotyphla. It is distributed in China. C. parva was initially thought to be the same as Chodsigoa lamula, but it was found to be a separate species.

Bailya is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Pisaniidae.
Kauaiina ioxantha is a moth of the family Geometridae. It was first described by Edward Meyrick in 1899. It is endemic to the Hawaiian island of Kauai.
Kauaiina alakaii is a moth of the family Geometridae first described by Jules C. E. Riotte in 1979. It is endemic to the eastern part of the Hawaiian island of Kauai, where it was collected in the Alakai Swamp, after which it is named.
Kauaiina molokaiensis is a moth of the family Geometridae first described by Jules C. E. Riotte in 1979. It is endemic to the Hawaiian island of Molokai, where it was at an altitude of 1,290 meters above Puu Kolekole.
Kauaiina montgomeryi is a moth of the family Geometridae first described by Jules C. E. Riotte in 1978. It is endemic to the eastern part of the Hawaiian island of Maui.
Kauaiina howarthi is a moth of the family Geometridae first described by Jules C. E. Riotte in 1990. It is endemic to Hawaii.
Kauaiina rubropulverula is a moth of the family Geometridae first described by Jules C. E. Riotte in 1989. It is endemic to Hawaii.

Xanthorhoini is a tribe of geometer moths under subfamily Larentiinae. The tribe was described by Pierce in 1914.
Eois parva is a moth in the family Geometridae. It is found in Colombia and Costa Rica.
Epidesma parva is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Rothschild in 1912. It is found in Venezuela.
Choreutis parva is a moth in the family Choreutidae. It was described by Pagenstecher in 1884. It is found on the Moluccas.
Emmonsia parva is a filamentous, saprotrophic fungus and one of three species within the genus Emmonsia. The fungus is most known for its causal association with the lung disease, adiaspiromycosis which occurs most commonly in small mammals but is also seen in humans. The disease was first described from rodents in Arizona, and the first human case was reported in France in 1964. Since then, the disease has been reported from Honduras, Brazil, the Czech Republic, Russia, the United States of America and Guatemala. Infections in general are quite rare, especially in humans.





