
Aspartate transaminase (AST) or aspartate aminotransferase, also known as AspAT/ASAT/AAT or (serum) glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase, is a pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)-dependent transaminase enzyme that was first described by Arthur Karmen and colleagues in 1954. AST catalyzes the reversible transfer of an α-amino group between aspartate and glutamate and, as such, is an important enzyme in amino acid metabolism. AST is found in the liver, heart, skeletal muscle, kidneys, brain, red blood cells and gall bladder. Serum AST level, serum ALT level, and their ratio are commonly measured clinically as biomarkers for liver health. The tests are part of blood panels.
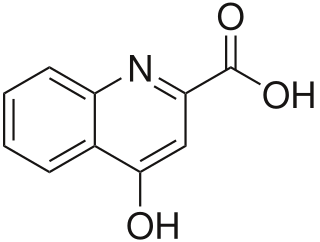
Kynurenic acid is a product of the normal metabolism of amino acid L-tryptophan. It has been shown that kynurenic acid possesses neuroactive activity. It acts as an antiexcitotoxic and anticonvulsant, most likely through acting as an antagonist at excitatory amino acid receptors. Because of this activity, it may influence important neurophysiological and neuropathological processes. As a result, kynurenic acid has been considered for use in therapy in certain neurobiological disorders. Conversely, increased levels of kynurenic acid have also been linked to certain pathological conditions.

In enzymology, 4-aminobutyrate transaminase, also called GABA transaminase or 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase, or GABA-T, is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
In enzymology, an adenosylmethionine-8-amino-7-oxononanoate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alanine-glyoxylate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an aromatic-amino-acid-glyoxylate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a diaminobutyrate-2-oxoglutarate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a diaminobutyrate-pyruvate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glycine-oxaloacetate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glycine transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a kynurenine-oxoglutarate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a methionine-glyoxylate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a serine-glyoxylate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a serine-pyruvate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Serine—pyruvate aminotransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AGXT gene.

Aspartate aminotransferase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GOT2 gene. Glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase is a pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzyme which exists in cytoplasmic and inner-membrane mitochondrial forms, GOT1 and GOT2, respectively. GOT plays a role in amino acid metabolism and the urea and Kreb's cycle. Also, GOT2 is a major participant in the malate-aspartate shuttle, which is a passage from the cytosol to the mitochondria. The two enzymes are homodimeric and show close homology. GOT2 has been seen to have a role in cell proliferation, especially in terms of tumor growth.

Kynurenine—oxoglutarate transaminase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CCBL1 gene. It is one of the Kynurenine—oxoglutarate transaminases.
4-aminobutyrate---pyruvate transaminase is an enzyme with systematic name 4-aminobutanoate:pyruvate aminotransferase. This enzyme is a type of GABA transaminase, which degrades the neurotransmitter GABA. The enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Kynurenine/alpha-aminoadipate aminotransferase, mitochondrial, also known as alpha-aminoadipate aminotransferase and kynurenine aminotransferase 2, is a mitochondrial enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AADAT gene. It converts alpha-aminoadipate to alpha-ketoadipate. It is also one of the Kynurenine—oxoglutarate transaminases.

Kynurenine aminotransferase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the KYAT3 gene. It is one of the Kynurenine—oxoglutarate transaminases.










