
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Mali face legal and societal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Although same-sex sexual activity is not illegal in Mali, LGBT people face widespread discrimination among the broader population. According to the 2007 Pew Global Attitudes Project, 98 percent of Malian adults believed that homosexuality is considered something society should not accept, which was the highest rate of non-acceptance in the 45 countries surveyed. The Constitution of Mali has outlawed same-sex marriage since 2023.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) face discrimination and legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Same-sex sexual activity is legal for both males and females in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, although LGBT individuals may still be targeted for prosecution under public indecency provisions on occasion.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Nigeria face severe challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. LGBT rights are generally infringed upon; both male and female expressions of homosexuality are illegal in Nigeria and punishable by up to 14 years of prison in the conventional court system. There is no legal protection for LGBT rights in Nigeria—a largely conservative country of more than 230 million people, split between a mainly Muslim north and a mainly Christian south. Very few LGBT persons are open about their sexual orientation, as violence against them is frequent. According to PinkNews, Nigerian authorities generally target the LGBT community. Many LGBT Nigerians are fleeing to countries with progressive law to seek protection.
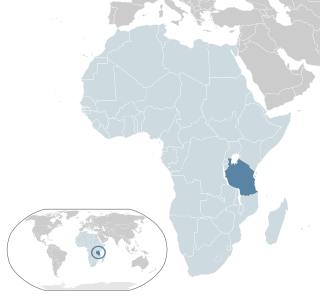
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Tanzania face severe challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Homosexuality in Tanzania is a socially taboo topic, and same-sex sexual acts are criminal offences, punishable with life imprisonment. The law also criminalises heterosexuals who engage in oral sex and anal intercourse.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in the British Virgin Islands face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal in the British Virgin Islands since 2001.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Dominica face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Homosexuality has been legal since 2024, when the High Court struck down the country's colonial-era sodomy law. Dominica provides no recognition to same-sex unions, whether in the form of marriage or civil unions, and no law prohibits discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation or gender identity.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Malawi face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Both male and female expressions of same-sex sexual activity are illegal within the nation. The Penal Code prohibits "carnal knowledge against the order of nature", attempts to commit "carnal knowledge against the order of nature", and acts of "gross indecency". Homosexuality among men is punishable by up to 14 years in prison in the country, while homosexuality among women is also punishable by up to five years in prison. There are no protections for LGBT rights in the country.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Zambia face significant challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Same-sex sexual activity is illegal for both men and women in Zambia. Formerly a colony of the British Empire, Zambia inherited the laws and legal system of its colonial occupiers upon independence in 1964. Laws concerning homosexuality have largely remained unchanged since then, and homosexuality is covered by sodomy laws that also proscribe bestiality. Social attitudes toward LGBT people are mostly negative and coloured by perceptions that homosexuality is immoral and a form of insanity. However, in recent years, younger generations are beginning to show positive and open minded attitudes towards their LGBT peers.

A sodomy law is a law that defines certain sexual acts as crimes. The precise sexual acts meant by the term sodomy are rarely spelled out in the law, but are typically understood and defined by many courts and jurisdictions to include any or all forms of sexual acts that are illegal, illicit, unlawful, unnatural and immoral. Sodomy typically includes anal sex, oral sex, manual sex, and bestiality. In practice, sodomy laws have rarely been enforced to target against sexual activities between individuals of the opposite sex, and have mostly been used to target against sexual activities between individuals of the same sex.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Bermuda, a British Overseas Territory, face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Homosexuality is legal in Bermuda, but the territory has long held a reputation for being homophobic and intolerant. Since 2013, the Human Rights Act has prohibited discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation.
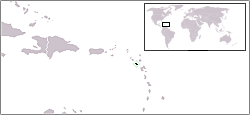
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in Montserrat face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal in Montserrat since 2001.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Togo face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Both male and female forms of same-sex sexual activity are illegal in Togo, with no legal recognition for same-sex marriage or adoption rights.
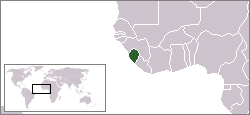
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Sierra Leone face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Male same-sex sexual activity is illegal in Sierra Leone and carries a possible penalty of life imprisonment, although this law is seldom enforced.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Niue face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Male same-sex sexual activity is illegal in Niue, although there is no recent instance of it being actively prosecuted. Same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex married couples.
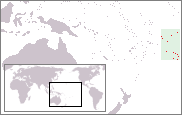
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in the Cook Islands face some legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents, but these challenges have gradually lessened in recent years. As of 1 June 2023, homosexual acts between men became legal in the Cook Islands after a vote by the Parliament of the Cook Islands. Female homosexual acts have never been illegal. Same-sex marriage is outlawed. Nevertheless, LGBT people do enjoy some limited legal protections, as employment discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation has been banned since 2013.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Grenada may face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. The penal code makes same-sex acts on Grenada proper illegal with a punishment up to 10 years in prison, it also does not address discrimination or harassment on the account of sexual orientation or gender identity, nor does it recognize same sex unions in any form, whether it be marriage or partnerships. Household headed by same-sex couples are also not eligible for any of the same rights given to opposite-sex married couples.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Samoa face legal challenges not faced by non-LGBT residents. Sexual contact between men is illegal, punishable by up to seven years’ imprisonment, but the law is not enforced.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Tuvalu face legal difficulties not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Sections 153, 154 and 155 of the Penal Code outlaw male homosexual intercourse with a penalty of up to 14 years in prison, but the law is not enforced. Employment discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation has been banned since 2017. Since 2023, the Constitution of Tuvalu has banned same-sex marriage.
This article gives a broad overview of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) history in Canada. LGBT activity was considered a crime from the colonial period in Canada until 1969, when Bill C-150 was passed into law. However, there is still discrimination despite anti-discrimination law. For a more detailed listing of individual incidents in Canadian LGBT history, see also Timeline of LGBT history in Canada.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in Anguilla face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Same-sex sexual activity is legal in Anguilla, but same-sex couples cannot marry or obtain civil partnerships. Anguillian law does not forbid discrimination based on sexual orientation or gender identity.



















