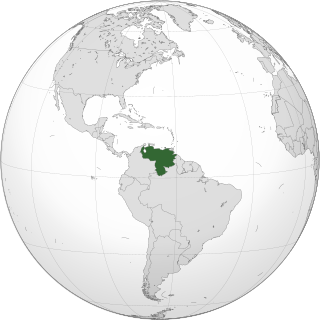
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Venezuela face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Both male and female types of same-sex sexual activity are legal in Venezuela, but same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex married couples. Also, same-sex marriage and de facto unions are constitutionally banned since 1999.
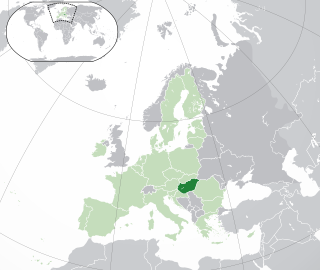
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) people in Hungary face legal and social challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Homosexuality is legal in Hungary for both men and women. Discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and sex is banned in the country. However, households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for all of the same legal rights available to heterosexual married couples. Registered partnership for same-sex couples was legalised in 2009, but same-sex marriage remains banned. The Hungarian government has passed legislation that restricts the civil rights of LGBT Hungarians – such as ending legal recognition of transgender Hungarians and banning LGBT content and displays for minors. This trend continues under the Fidesz government of Viktor Orbán. In June 2021, Hungary passed an anti-LGBT law on banning "homosexual and transexual propaganda" effective since 1 July. The law has been condemned by seventeen member states of the European Union. In July 2020, the European Commission started legal action against Hungary and Poland for violations of fundamental rights of LGBTQI people, stating: "Europe will never allow parts of our society to be stigmatized."
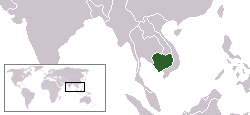
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) people in Cambodia face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Although same-sex sexual activity is legal in Cambodia, it provides no anti-discrimination protections for LGBT people, nor does it prohibit hate crimes based on sexual orientation and gender identity.

New Zealand lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights are some of the most extensive in the world. The protection of LGBT rights is advanced, relative to other countries in Oceania, and among the most liberal in the world, with the country being the first in the region to legalise same-sex marriage.
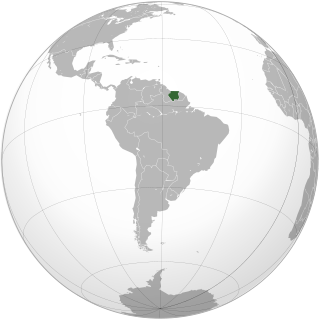
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Suriname may face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Both male and female expressions of same-sex sexual activity are legal in Suriname. Since 2015, hate speech and discrimination in employment and the provision of goods and services on the basis of sexual orientation has been banned in the country. Same-sex marriage and civil unions are not recognised by law. Nevertheless, Suriname is legally bound to the January 2018 Inter-American Court of Human Rights ruling, which held that same-sex marriage is a human right protected by the American Convention on Human Rights.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people in Japan have fewer legal protections than in most other developed countries, although some developments towards stronger rights have been made in the 2020s. Same-sex sexual activity was criminalised only briefly in Japan's history between 1872 and 1881, after which a localised version of the Napoleonic Penal Code was adopted with an equal age of consent. Same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples are ineligible for the legal protections available to opposite-sex couples, although since 2015 some cities and prefectures, covering over 60% of the population by 2023, offer "partnership certificates" to recognise the relationships of same-sex couples and provide some legal benefits. Japan is the only country in the G7 that does not legally recognize same-sex unions nationally in any form. In March 2021 and May 2023, the Sapporo and Nagoya District Courts ruled that not recognising same-sex marriage was a violation of the Constitution respectively. While in June 2022, the Osaka District Court ruled that not recognising same-sex marriage was not a violation of the Constitution, in November 2022, the Tokyo District Court ruled that the absence of same-sex marriage legislation was an unconstitutional state of affairs but did not violate the Constitution, though the court's ruling has no immediate legal effect. In June 2023, the Fukuoka District Court ruled that the ban on same-sex marriage was constitutional. A second ruling in September 2023 concluded that same-sex relationships should not be excluded from Japan's marriage system.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Albania face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents, although LGBT people are protected under comprehensive anti-discrimination legislation. Both male and female same-gender sexual activities have been legal in Albania since 1995, but households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-gender couples, with same-sex unions not being recognized in the country in any form.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Armenia face legal and social challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents, due in part to the lack of laws prohibiting discrimination on the grounds of sexual orientation and gender identity and in part to prevailing negative attitudes about LGBT persons throughout society.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Malta rank among the highest in the world. Throughout the late 20th and early 21st centuries, the rights of the LGBTQ community received more awareness and same-sex sexual activity was legalized on 29 January 1973. The prohibition was already dormant by the 1890s.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Moldova face legal and social challenges and discrimination not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same rights and benefits as households headed by opposite-sex couples. Same-sex unions are not recognized in the country, so consequently same-sex couples have little to no legal protection. Nevertheless, Moldova bans discrimination based on sexual orientation in the workplace, and same-sex sexual activity has been legal since 1995.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Rwanda face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. While neither homosexuality nor homosexual acts are illegal, homosexuality is considered a taboo topic, and there is no significant public discussion of this issue in any region of the country and LGBT people still face stigmatization among the broader population. No anti-discrimination laws are afforded to LGBT citizens, and same-sex marriages are not recognized by the state, as the Constitution of Rwanda provides that "[o]nly civil monogamous marriage between a man and a woman is recognized". LGBT Rwandans have reported being harassed, blackmailed, and even arrested by the police under various laws dealing with public order and morality.

Oceania is, like other regions, quite diverse in its laws regarding LGBT rights. This ranges from significant rights, including same-sex marriage – granted to the LGBT+ community in New Zealand, Australia, Guam, Hawaii, Easter Island, Northern Mariana Islands, Wallis and Futuna, New Caledonia, French Polynesia and the Pitcairn Islands – to remaining criminal penalties for homosexual activity in six countries and one territory. Although acceptance is growing across the Pacific, violence and social stigma remain issues for LGBT+ communities. This also leads to problems with healthcare, including access to HIV treatment in countries such as Papua New Guinea and the Solomon Islands where homosexuality is criminalised.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Lesotho face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Lesotho does not recognise same-sex marriages or civil unions, nor does it ban discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation or gender identity.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Micronesia may face legal difficulties not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex married couples, as same-sex marriage and civil unions are not recognized. Discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation has been illegal since 2018.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Samoa face legal challenges not faced by non-LGBT residents. Sexual contact between men is illegal, punishable by up to seven years’ imprisonment, but the law is not enforced.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in North Macedonia face discrimination and some legal and social challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Both male and female same-sex sexual activity have been legal in North Macedonia since 1996, but same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex married couples.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) rights in the U.S. state of Alaska have evolved significantly over the years. Since 1980, same-sex sexual conduct has been allowed, and same-sex couples can marry since October 2014. The state offers few legal protections against discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity, leaving LGBTQ people vulnerable to discrimination in housing and public accommodations; however, the U.S. Supreme Court's ruling in Bostock v. Clayton County established that employment discrimination against LGBTQ people is illegal under federal law. In addition, four Alaskan cities, Anchorage, Juneau, Sitka and Ketchikan, representing about 46% of the state population, have passed discrimination protections for housing and public accommodations.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Palau do not possess the same legal protections as non-LGBT residents, and may face social challenges that are not experienced by others. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal in Palau since 23 July 2014, when the current Penal Code took effect, but households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex married couples. Same-sex marriage is constitutionally banned, and there are no anti-discrimination laws concerning sexual orientation and gender identity.
Sexual encounters in private between two adults are legal. Although homosexuality was decriminalized, LGBT Dominicans still endure discrimination and violence due to their sexual orientation and/or gender identity. In a 2014 poll, almost three quarters, 73%, of people in the Dominican Republic alone have said that members of the LGBT community have experienced some sort of violence or discrimination. Members of the LGBT Community in the Dominican Republic are victims of hate crimes, extortion by the police, and discrimination when it comes to resources and employment services. They also face discrimination when seeking treatment from health care systems. Between 2006 and August 2015, there have been 32 reports of possible hate crimes against transgender people.:5
Fiji does not recognise same-sex marriage, civil unions or any other form of recognition for same-sex couples.


















