
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Bosnia and Herzegovina may face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Both male and female forms of same-sex sexual activity are legal in Bosnia and Herzegovina. However, households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex couples.
Homosexuality in India is socially permitted by most of the traditional native philosophies of the nation, and legal rights continue to be advanced in mainstream politics and regional politics. Homosexual cohabitation is also legally permitted and comes with some legal protections and rights.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Fiji have evolved rapidly over the years. In 1997, Fiji became the second country in the world after South Africa to explicitly protect against discrimination based on sexual orientation in its Constitution. In 2009, the Constitution was abolished. The new Constitution, promulgated in September 2013, bans discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity or expression. However, same-sex marriage remains banned in Fiji and reports of societal discrimination and bullying are not uncommon.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) people in Cambodia face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Although same-sex sexual activity is legal in Cambodia, it provides no anti-discrimination protections for LGBT people, nor does it prohibit hate crimes based on sexual orientation and gender identity.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Cyprus have evolved in recent years, but LGBTQ people still face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Both male and female expressions of same-sex sexual activity were decriminalised in 1998, and civil unions which grant several of the rights and benefits of marriage have been legal since December 2015. Conversion therapy was banned in Cyprus in May 2023. However, adoption rights in Cyprus are reserved for heterosexual couples only.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Kazakhstan face significant challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Both male and female kinds of same-sex sexual activity are legal in Kazakhstan, but same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex married couples.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in the British Crown dependency of the Isle of Man have evolved substantially since the early 2000s. Private and consensual acts of male homosexuality on the island were decriminalised in 1992. LGBTQ rights have been extended and recognised in law since then, such as an equal age of consent (2006), employment protection from discrimination (2006), gender identity recognition (2009), the right to enter into a civil partnership (2011), the right to adopt children (2011) and the right to enter into a civil marriage (2016).

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Botswana face legal issues not experienced by non-LGBTQ citizens. Both female and male same-sex sexual acts have been legal in Botswana since 11 June 2019 after a unanimous ruling by the High Court of Botswana. Despite an appeal by the government, the ruling was upheld by the Botswana Court of Appeal on 29 November 2021.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in the British Virgin Islands face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal in the British Virgin Islands since 2001.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Malawi face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Both male and female expressions of same-sex sexual activity are illegal within the nation. The Penal Code prohibits "carnal knowledge against the order of nature", attempts to commit "carnal knowledge against the order of nature", and acts of "gross indecency". Homosexuality among men is punishable by up to 14 years in prison in the country, while homosexuality among women is also punishable by up to five years in prison. There are no protections for LGBT rights in the country.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Solomon Islands face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Male same-sex sexual activity is illegal, punishable by up to 14 years imprisonment, but the law is not enforced.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Bermuda, a British Overseas Territory, face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Homosexuality is legal in Bermuda, but the territory has long held a reputation for being homophobic and intolerant. Since 2013, the Human Rights Act has prohibited discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation.
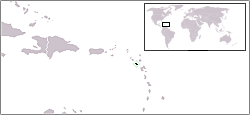
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in Montserrat face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal in Montserrat since 2001.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Mauritius have expanded in the 21st century, although LGBT Mauritians may still face legal difficulties not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Prior to 2023, sodomy was criminalized by Section 250 of the Criminal Code. However, Mauritius fully decriminalized homosexuality in October 2023. Although same-sex marriage is not recognized in Mauritius, LGBT people are broadly protected from discrimination in areas such as employment and the provision of goods and services, making it one of the few African countries to have such protections for LGBT people. The Constitution of Mauritius guarantees the right of individuals to a private life.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Seychelles face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal since 2016, and employment discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation is banned in Seychelles, making it one of the few African countries to have such protections for LGBT people. However, LGBT people may nonetheless face stigmatization among the broader population.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Niue face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Male same-sex sexual activity is illegal in Niue, although there is no recent instance of it being actively prosecuted. Same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex married couples.
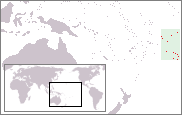
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in the Cook Islands face some legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents, but these challenges have gradually lessened in recent years. As of 1 June 2023, homosexual acts between men became legal in the Cook Islands after a vote by the Parliament of the Cook Islands. Female homosexual acts have never been illegal. Same-sex marriage is outlawed. Nevertheless, LGBT people do enjoy some limited legal protections, as employment discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation has been banned since 2013.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Samoa face legal challenges not faced by non-LGBT residents. Sexual contact between men is illegal, punishable by up to seven years’ imprisonment, but the law is not enforced.
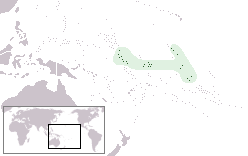
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Kiribati face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Male homosexuality is illegal in Kiribati with a penalty of up to 14 years in prison, but the law is not enforced. Female homosexuality is legal, but lesbians may face violence and discrimination. Despite this, employment discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation has been prohibited since 2015.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in Anguilla face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Same-sex sexual activity is legal in Anguilla, but same-sex couples cannot marry or obtain civil partnerships. Anguillian law does not forbid discrimination based on sexual orientation or gender identity.




















