Related Research Articles
Opposition to legal rights for lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer (LGBTQ) people exists throughout the world. LGBTQ rights opponents may be opposed to the decriminalization of homosexuality; laws permitting civil unions or partnerships or supporting LGBT parenting and adoption, LGBT military members, access to assisted reproductive technology, and access to gender-affirming surgery and gender-affirming hormone therapy for transgender individuals.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Fiji have evolved rapidly over the years. In 1997, Fiji became the second country in the world after South Africa to explicitly protect against discrimination based on sexual orientation in its Constitution. In 2009, the Constitution was abolished. The new Constitution, promulgated in September 2013, bans discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity or expression. However, same-sex marriage remains banned in Fiji and reports of societal discrimination and bullying are not uncommon.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Kenya face significant challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Sodomy is a felony per Section 162 of the Kenyan Penal Code, punishable by 21 years' imprisonment, and any sexual practices are a felony under section 165 of the same statute, punishable by five years' imprisonment. On 24 May 2019, the High Court of Kenya refused an order to declare sections 162 and 165 unconstitutional. The state does not recognise any relationships between persons of the same sex; same-sex marriage is banned under the Kenyan Constitution since 2010. There are no explicit protections against discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity. Adoption is restricted to heterosexual couples only.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Cyprus have evolved in recent years, but LGBTQ people still face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Both male and female expressions of same-sex sexual activity were decriminalised in 1998, and civil unions which grant several of the rights and benefits of marriage have been legal since December 2015. Conversion therapy was banned in Cyprus in May 2023. However, adoption rights in Cyprus are reserved for heterosexual couples only.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Trinidad and Tobago face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same rights and benefits as that of opposite-sex couples.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) people in Bhutan face legal challenges that are not faced by non-LGBTQ people. Bhutan does not provide any anti-discrimination laws for LGBT people, and same-sex unions are not recognised. However, same-sex sexual activity was decriminalised in Bhutan on 17 February 2021.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Dominica face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Homosexuality has been legal since 2024, when the High Court struck down the country's colonial-era sodomy law. Dominica provides no recognition to same-sex unions, whether in the form of marriage or civil unions, and no law prohibits discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation or gender identity.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Papua New Guinea face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Male same-sex sexual activity is illegal, punishable by up to 14 years' imprisonment. The law is rarely enforced, but arrests still do happen, having occurred in 2015 and 2022. There are no legal restrictions against lesbian sex in the country.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Solomon Islands face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Male and female same-sex sexual activity is illegal, punishable by up to 14 years imprisonment, but the law is not enforced.

Oceania is, like other regions, quite diverse in its laws regarding LGBTQ rights. This ranges from significant rights, including same-sex marriage – granted to the LGBTQ community in New Zealand, Australia, Guam, Hawaiʻi, Easter Island, Northern Mariana Islands, Wallis and Futuna, New Caledonia, French Polynesia and the Pitcairn Islands – to remaining criminal penalties for homosexual activity in six countries and one territory. Although acceptance is growing across the Pacific, violence and social stigma remain issues for LGBTQ communities. This also leads to problems with healthcare, including access to HIV treatment in countries such as Papua New Guinea and the Solomon Islands where homosexuality is criminalised.
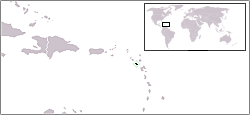
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in Montserrat face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal in Montserrat since 2001.
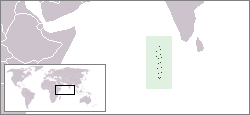
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) people are generally discriminated in the Maldives.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in TRNC (Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus) face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal in Northern Cyprus since 7 February 2014. Previous laws allowed three years prison sentences, according to Articles 171 and 173 of its criminal code. Female homosexuality was not criminalised. Arrests for homosexuality have occurred as recently as 2011.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) rights in Mauritius have expanded in the 21st century, although LGBTQ Mauritians may still face legal difficulties not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Prior to 2023, sodomy was criminalized by Section 250 of the Criminal Code. However, the Supreme Court of Mauritius fully decriminalized homosexuality in October 2023. Although same-sex marriage is not recognized in Mauritius, LGBTQ people are broadly protected from discrimination in areas such as employment and the provision of goods and services, making it one of the few African countries to have such protections for LGBTQ people. The Constitution of Mauritius guarantees the right of individuals to a private life.
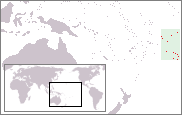
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in the Cook Islands face some legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents, but these challenges have gradually lessened in recent years. As of 1 June 2023, homosexual acts between men became legal in the Cook Islands after a vote by the Parliament of the Cook Islands. Female homosexual acts have never been illegal. Same-sex marriage is outlawed. Nevertheless, LGBT people do enjoy some limited legal protections, as employment discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation has been banned since 2013.
Nauruan law, since Nauru's independence from Australia in 1968, is derived primarily from English and Australian common law, though it also integrates indigenous customary law to a limited extent. Nauruan common law is founded mainly on statute law enacted by the Parliament of Nauru, and on precedents set by judicial interpretations of statutes, customs and prior precedents.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Samoa face legal challenges not faced by non-LGBT residents. Sexual contact between men is illegal, punishable by up to seven years’ imprisonment, but the law is not enforced.
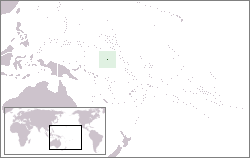
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people living in Nauru may face legal and social challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal since May 2016, but there are no legal recognition of same-sex unions, or protections against discrimination in the workplace or the provision of goods and services.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Palau do not possess the same legal protections as non-LGBT residents, and may face social challenges that are not experienced by others. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal in Palau since 23 July 2014, when the current Penal Code took effect, but households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex married couples. Same-sex marriage is constitutionally banned, and there are no anti-discrimination laws concerning sexual orientation and gender identity.

The majority of the countries of the Commonwealth of Nations, formerly known as the British Commonwealth, still criminalise sexual acts between consenting adults of the same sex and other forms of sexual orientation, gender identity and expression. Homosexual activity remains a criminal offence in 29 of the 56 sovereign states of the Commonwealth; and legal in only 27.
References
- ↑ "Where is it illegal to be gay?". BBC News. 10 February 2014. Retrieved 23 February 2014.
- ↑ "Gay Nauru News & Reports", GlobalGayz.com, 1 January 2009
- ↑ NAURU (Law) Archived 7 July 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ [rtsp://webcast.un.org/ondemand/conferences/unhrc/upr/10th/hrc110124am1-eng.rm?start=00:04:37&end=00:23:22 Address by Mathew Batsiua][ permanent dead link ] to the United Nations Human Rights Council, January 24, 2010
- ↑ National Report of Nauru Archived 8 December 2015 at the Wayback Machine to the Human Rights Council, November 2010
- ↑ "Freedom in the World 2015: Nauru". Freedom House . Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- ↑ The Age, 27 May 2016: Marital rape no longer allowed and suicide, homosexuality decriminalised at Nauru
