
Lactobacillus is a genus of Gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus Lactobacillus comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species; a taxonomic revision of the genus assigned lactobacilli to 25 genera.

Probiotics are live microorganisms promoted with claims that they provide health benefits when consumed, generally by improving or restoring the gut microbiota. Probiotics are considered generally safe to consume, but may cause bacteria-host interactions and unwanted side effects in rare cases. There is some evidence that probiotics are beneficial for some conditions, but there is little evidence for many of the health benefits claimed for them.

Lactobacillus acidophilus is a rod-shaped, Gram-positive, homofermentative, anaerobic microbe first isolated from infant feces in the year 1900. The species is most commonly found in humans, specifically the gastrointestinal tract, oral cavity, and vagina, as well as various fermented foods such as fermented milk or yogurt. The species most readily grows at low pH levels, and has an optimum growth temperature of 37 °C. Certain strains of L. acidophilus show strong probiotic effects, and are commercially used in dairy production. The genome of L. acidophilus has been sequenced.
Lactiplantibacillus plantarum is a widespread member of the genus Lactiplantibacillus and commonly found in many fermented food products as well as anaerobic plant matter. L. plantarum was first isolated from saliva. Based on its ability to temporarily persist in plants, the insect intestine and in the intestinal tract of vertebrate animals, it was designated as a nomadic organism. L. plantarum is Gram positive, bacilli shaped bacterium. L. plantarum cells are rods with rounded ends, straight, generally 0.9–1.2 μm wide and 3–8 μm long, occurring singly, in pairs or in short chains. L. plantarum has one of the largest genomes known among the lactic acid bacteria and is a very flexible and versatile species. It is estimated to grow between pH 3.4 and 8.8. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum can grow in the temperature range 12 °C to 40 °C. The viable counts of the "L. plantarum" stored at refrigerated condition (4 °C) remained high, while a considerable reduction in the counts was observed stored at room temperature.

Bacillus coagulans is a lactic acid–forming bacterial species first isolated and described in 1915 by B.W. Hammer at the Iowa Agricultural Experiment Station as a cause of an outbreak of coagulation in evaporated milk packed by an Iowa condensary. Separately isolated in 1935 and described as Lactobacillus sporogenes in the fifth edition of Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, it exhibits characteristics typical of both genera Lactobacillus and Bacillus; its taxonomic position between the families Lactobacillaceae and Bacillaceae was often debated. However, in the seventh edition of Bergey's, it was finally transferred to the genus Bacillus. DNA-based technology was used in distinguishing between the two genera of bacteria, which are morphologically similar and possess similar physiological and biochemical characteristics.
Histomonas meleagridis is a species of parasitic protozoan that infects a wide range of birds including chickens, turkeys, peafowl, quail and pheasants, causing infectious enterohepatitis, or histomoniasis. H. meleagridis can infect many birds, but it is most deadly in turkeys. It inhabits the lumen of cecum and parenchyma of liver, where it causes extensive necrosis. It is transmitted by another cecal parasite, the nematode Heterakis gallinarum.

Lacticaseibacillus caseiis an organism that belongs to the largest genus in the family Lactobacillaceae, a lactic acid bacteria (LAB), that was previously classified as Lactobacillus casei-01. This bacteria has been identified as facultatively anaerobic or microaerophilic, acid-tolerant, non-spore-forming bacteria. The taxonomy of this group has been debated for several years because researchers struggled to differentiate between the strains of L. casei and L. paracasei. It has recently been accepted as a single species with five subspecies: L. casei subsp. rhamnosus, L. casei subsp. alactosus, L. casei subsp. casei, L. casei subsp. tolerans, and L. casei subsp. pseudoplantarum. The taxonomy of this genus was determined according to the phenotypic, physiological, and biochemical similarities.

Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus is a bacterium that originally was considered to be a subspecies of L. casei, but genetic research found it to be a separate species in the L. casei clade, which also includes L. paracasei and L. zeae. It is a short Gram-positive homofermentative facultative anaerobic non-spore-forming rod that often appears in chains. Some strains of L. rhamnosus bacteria are being used as probiotics, and are particularly useful in treating infections of the female urogenital tract, most particularly very difficult to treat cases of bacterial vaginosis. The species Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus and Limosilactobacillus reuteri are commonly found in the healthy female genito-urinary tract and are helpful to regain control of dysbiotic bacterial overgrowth during an active infection. L. rhamnosus sometimes is used in dairy products such as fermented milk and as non-starter-lactic acid bacterium (NSLAB) in long-ripened cheese. While frequently considered a beneficial organism, L. rhamnosus may not be as beneficial to certain subsets of the population; in rare circumstances, especially those primarily involving weakened immune system or infants, it may cause endocarditis. Despite the rare infections caused by L. rhamnosus, the species is included in the list of bacterial species with qualified presumed safety (QPS) status of the European Food Safety Agency.
Limosilactobacillus reuteri is a lactic acid bacterium found in a variety of natural environments, including the gastrointestinal tract of humans and other animals. It does not appear to be pathogenic and may have health effects.
Limosilactobacillus fermentum is a Gram-positive species in the heterofermentative genus Limosilactobacillus. It is associated with active dental caries lesions. It is also commonly found in fermenting animal and plant material including sourdough and cocoa fermentation. A few strains are considered probiotic or "friendly" bacteria in animals and at least one strain has been applied to treat urogenital infections in women. Some strains of lactobacilli formerly mistakenly classified as L. fermentum have since been reclassified as Limosilactobacillus reuteri. Commercialized strains of L. fermentum used as probiotics include PCC, ME-3 and CECT5716

Histomoniasis is a commercially significant disease of poultry, particularly of chickens and turkeys, due to parasitic infection of a protozoan, Histomonas meleagridis. The protozoan is transmitted to the bird by the nematode parasite Heterakis gallinarum. H. meleagridis resides within the eggs of H. gallinarum, so birds ingest the parasites along with contaminated soil or food. Earthworms can also act as a paratenic host.

Pediococcus acidilactici is a species of Gram-positive cocci that is often found in pairs or tetrads. P. acidilactici is a homofermentative bacterium that can grow in a wide range of pH, temperature, and osmotic pressure, therefore being able to colonize the digestive tract. It has emerged as a potential probiotic that has shown promising results in animal and human experiments, though some of the results are limited. They are commonly found in fermented vegetables, fermented dairy products, and meat.
Lactobacillus gasseri is a species in the genus Lactobacillus identified in 1980 by François Gasser and his associates. It is part of the vaginal flora. Its genome has been sequenced. L. gasseri is a normal inhabitant of the lower reproductive tract in healthy women. It also produces Lactocillin.
Limosilactobacillus mucosae is a rod shaped species of lactic acid bacteria first isolated from pig intestines. It has mucus-binding activity. The species is an obligate anaerobe, catalase-negative, doesn't form spores and is non-motile. Its type strain is S32T, and has been found to be most closely related to Limosilactobacillus reuteri.

Lactobacillus johnsonii is a species in the genus Lactobacillus identified in 1980 by John L. Johnson, an American microbiologist and his associates. Its type strain is ATCC 33200. It is part of the healthy vaginal microbiota and has been identified as having probiotic properties. The L. johnsonii strain La1 was one of the first cultures to be proposed as a probiotic dairy supplement in 1995 at the Nestlé Research Center, Lausanne. Although yeast and bacteria have been used in dairy products for fermenting purposes for centuries, the investigation and choice of a microorganism as a fermenting agent based on its health benefits was novel at the time. Today the probiotic culture is used in the LC1 yogurt products by Nestlé.
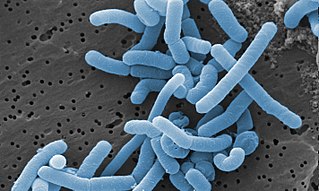
Lacticaseibacillus paracasei is a gram-positive, homofermentative species of lactic acid bacteria that are commonly used in dairy product fermentation and as probiotic cultures. Lc. paracasei is a bacterium that operates by commensalism. It is commonly found in many human habitats such as human intestinal tracts and mouths as well as sewages, silages, and previously mentioned dairy products. The name includes morphology, a rod-shaped bacterium with a width of 2.0 to 4.0μm and length of 0.8 to 1.0μm.
Lactobacillus crispatus is a common, rod-shaped species of genus Lactobacillus and is a hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) producing beneficial microbiota species located in both the vagina, through vaginal discharge, and the vertebrate gastrointestinal tract. The strain CTV-05 is used as a probiotic that can be used by premenopausal and postmenopausal women that experience recurrent urinary tract infections. It is being evaluated specifically for the prevention and treatment of bacterial vaginosis, which is characterized by the absence of Lactobacillus flora necessary to protect the host from infection.

Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus is a bacterial subspecies traditionally isolated from European yogurts. Lactobacillus bulgaricusGLB44 differs from the rest of the L. bulgaricus strains as it was isolated from the leaves of Galanthus nivalis in Bulgaria, becoming the only known strain of this subspecies that has vegan origin available as a commercial probiotic. Probiotics are health promoting bacteria which, when consumed in adequate amounts, confer a benefit on the host, normally associated with positive effects on the digestive and immune systems, and are usually prescribed during or after antibiotic treatment to alleviate the symptoms of antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Probiotics are also associated with decreasing of the risk of traveler's diarrhea.

Bifidobacterium bifidum is a bacterial species of the genus Bifidobacterium. B. bifidum is one of the most common probiotic bacteria that can be found in the body of mammals, including humans.
Proteobiotics are natural metabolites which are produced by fermentation process of specific probiotic strains. These small oligopeptides were originally discovered in and isolated from culture media used to grow probiotic bacteria and may account for some of the health benefits of probiotics.











