
Tulbaghia is a genus of monocotyledonous herbaceous perennial bulbs native to Africa, belonging to the Amaryllis family. It is one of only two known genera in the society garlic tribe within the onion subfamily. The genus was named for Ryk Tulbagh (1699–1771), one time governor of The Cape of Good Hope.

Rhamnaceae is a large family of flowering plants, mostly trees, shrubs, and some vines, commonly called the buckthorn family. Rhamnaceae is included in the order Rosales.

Olea is a genus of about 40 species in the family Oleaceae, native to warm temperate and tropical regions of the Middle East, southern Europe, Africa, southern Asia, and Australasia. They are evergreen trees and shrubs, with small, opposite, entire leaves. The fruit is a drupe. Leaves of Olea contain trichosclereids.

Zanthoxylum is a genus of about 250 species of deciduous and evergreen trees, shrubs and climbers in the family Rutaceae that are native to warm temperate and subtropical areas worldwide. It is the type genus of the tribe Zanthoxyleae in the subfamily Rutoideae. Several of the species have yellow heartwood, to which their generic name alludes.
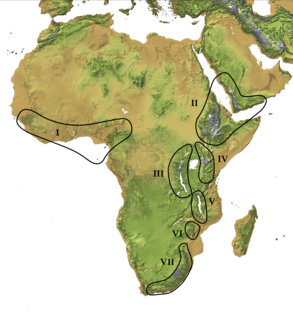
The Afromontane regions are subregions of the Afrotropical realm, one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms, covering the plant and animal species found in the mountains of Africa and the southern Arabian Peninsula. The Afromontane regions of Africa are discontinuous, separated from each other by lower-lying areas, and are sometimes referred to as the Afromontane archipelago, as their distribution is analogous to a series of sky islands.

The crested servaline genet, also known as the crested genet, is a genet species endemic to Nigeria and Cameroon. As the population has declined due to loss of habitat, it is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List. It was first recorded in the Mamfe Division in Cameroon and initially considered a subspecies of the servaline genet. But now it is regarded as a distinct species.

The genus of the myrrhs, Commiphora, is the most species-rich genus of flowering plants in the frankincense and myrrh family, Burseraceae. The genus contains approximately 190 species of shrubs and trees, which are distributed throughout the (sub-) tropical regions of Africa, the western Indian Ocean islands, the Arabian Peninsula, India, and Vietnam. The genus is drought-tolerant and common throughout the xerophytic scrub, seasonally dry tropical forests, and woodlands of these regions.

Colubrina is a genus of about 30 species of flowering plants in the family Rhamnaceae, native to warm temperate to tropical regions of Africa, the Americas, southern Asia, northern Australia, and the Indian Ocean islands. Common names include nakedwood, snakewood, greenheart and hogplum. The generic name is derived from the Latin word coluber, meaning "snake", and refers to the snake-like stems or stamens.

Lasiodiscus mildbraedii is small tree in the family Rhamnaceae. It occurs locally along the African east coast from South Africa northwards and in the African tropics. It is sometimes a dominant component of tropical forest understorey. Groups of small pale flowers are carried on long stalks in spring. The fruits reach maturity at the end of summer. The leaves have an opposite arrangement as in all members of Lasiodiscus. The leaf texture is somewhat rough and leathery. Leaf undersides are somewhat rufous toned.

The African pipit is a fairly small passerine bird belonging to the pipit genus Anthus in the family Motacillidae. It is also known as the grassveld pipit or grassland pipit. It was formerly lumped together with the Richard's, Australasian, mountain and paddyfield pipits in a single species, Richard's pipit, but is now often treated as a species in its own right.

Zenker's fruit bat is a species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae. It is found in Cameroon, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea, Liberia, and Nigeria. Its natural habitats are tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests and subtropical or tropical swamps. It is threatened by habitat destruction.

Grandidier's trident bat is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae endemic to Madagascar. It was formerly assigned to the genus Triaenops, but is now placed in the separate genus Paratriaenops.

Beilschmiedia is a genus of trees and shrubs in family Lauraceae. Most of its species grow in tropical climates, but a few of them are native to temperate regions, and they are widespread in tropical Asia, Africa, Madagascar, Australia, New Zealand, North America, Central America, the Caribbean, and South America. The best-known species to gardeners in temperate areas are B. berteroana and B. miersii because of their frost tolerance. Seeds of B. bancroftii were used as a source of food by Australian Aborigines. Timbers of some species are very valuable.

Trevoa is a genus of actinorhizal plants; these dicotyledon flora are trees or small shrubs. The genus was first proposed by Miers in 1825, but was not fully described until 1830 by Sir William Jackson Hooker. Genus members are notable for their ability to fix nitrogen. Species of this genus are generally found in the near coastal forests and arid shrubland of South America. Some species are localized in the mountains of central Chile; for example, the species Trevoa trinervis occurs in the La Campana National Park and other proximate areas of central Chile.

Sphaerotheriida is an order of millipedes in the infraclass Pentazonia, sometimes known as giant pill millipedes. They inhabit Southern Africa, Madagascar, South and Southeast Asia, Australia and New Zealand. Like the Northern Hemisphere pill millipedes of the order Glomerida, these millipedes can roll into a ball when disturbed. When they are rolled-up, most sphaerotheriidans reach a maximum size of a cherry or golf ball, but some species from Madagascar can even reach the size of an orange. When rolled-up, predators are unable to unravel giant pill millipedes since the margins of their second and last dorsal plates fit perfectly into one another, creating a sealed ball. A few giant pill millipede species are able to produce sound, the only millipedes known to do this. This order of millipedes is also unique in that some African species are used for medicinal purposes.
Colubrina greggii is a species of flowering plant in the family Rhamnaceae, that is commonly known as the Sierra nakedwood or Gregg's colubrina. It is native to eastern Mexico, with a disjunct population in southern Texas in the United States. It is very similar to C. arborescens of Southern Florida and the Caribbean, and herbarium specimens of the two species are difficult to distinguish. The name honours American botanist Josiah Gregg, who collected the holotype near Monterrey, Nuevo León in 1848.

Metarungia pubinervia is an Afrotropical plant species in the acanthus family, which is native to forest understorey in the Afromontane archipelago. It is widespread in eastern Africa, with isolated populations in southern Africa and Nigeria. The species is named for the fine down that covers the main leaf veins (-nervia).

Landolphia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae first described as a genus in 1806. They take the form of vines that scramble over host trees. Landolphia is native to tropical Africa.
Lasiodiscus fasciculiflorus is a species of shrub or small tree in the family Rhamnaceae that is native to forests of the West African tropics. It occurs from Sierra Leone to Nigeria and the D.R.C.. The bark is used in medicine to treat various ailments.

















